
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780133840544
Author: George F. Limbrunner, Craig D'Allaird, Leonard Spiegel
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 4.35SP
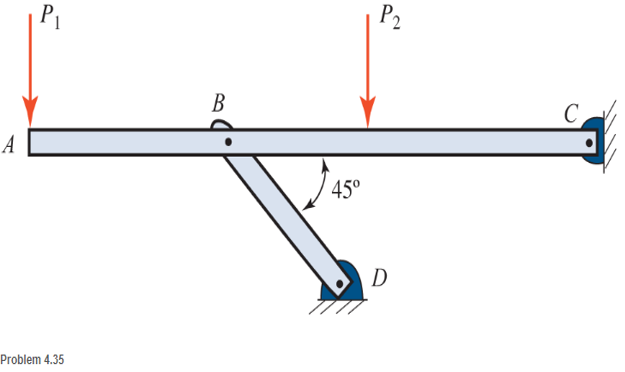
For the structure shown, draw free-body diagram for both the beam ABC and the link BD. The members are weightless.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule06:07
Students have asked these similar questions
The T-bar AEBF is connected to rod CD, with the joint at F being equivalent to a slider bearing. The supports at A and C are slider bearings, and thrust bearings are found at B and D. The two applied forces, which act at the midpoint of the arm EF, are parallel to the y- and z-axes, respectively. Neglecting the weights of the members, draw the FBDs for the entire structure, the T-bar, and rod CD. Determine the total number of unknowns.
Problem 2: For the frame shown, find the
horizontal and vertical components of the
reactions at A and C. The cable supports a mass
of 100kg. Assume the pulley is frictionless.
0.3 m
Partial Ans.
Cx = 654 N
1.5 m
2 m
0.5 m
Calculate the force in member GH of the truss and indicate whether it is in tension or compression, using either method of joints or method of sections.
Required: Draw the FBD(s) as needed for analysis-all equilibrium equations must correspond to a FBD that you have drawn. Make sure to clearly indicate which FBD
your equation(s) correspond to.
K
J
H
4 ft
C
- 3 ft 3 ft -- 3 ft- 3 ft-3 ft
1500 lb 1500 lb 1500 lb 1500 lb 1500 lb
Chapter 4 Solutions
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Ch. 4 - and 4.2 Sketch free-body diagram for the members...Ch. 4 - Sketch free-body diagram for the members shown.Ch. 4 - A steel cylinder having a mass of 120 kgis...Ch. 4 - A 50-lb block is supported by a pin support and a...Ch. 4 - A cylinder weighing 200 lb is supported on an...Ch. 4 - A weight W is supported by a flexible cable and an...Ch. 4 - The ladder shown is supported by a smooth...Ch. 4 - What horizontal force F applied at the center of...Ch. 4 - Calculate the force in cable AB and the angle (...Ch. 4 - Calculate the horizontal force F that should be...
Ch. 4 - Calculate the reactions of the two smooth inclined...Ch. 4 - Calculate the force in each cable for the...Ch. 4 - Three members of a truss intersect at joint B as...Ch. 4 - Four concurrent forces in equilibrium act at point...Ch. 4 - The beam shown carries vertical concentrated...Ch. 4 - Find the reactions at A and B for the beam shown....Ch. 4 - A simply supported beam spans 10 m. The beam...Ch. 4 - The beam shown carries vertical loads. Calculate...Ch. 4 - Calculate the reaction at each support for the...Ch. 4 - Calculate the reactions at A and B for the beam...Ch. 4 - Calculate the reactions at A and B for the beam...Ch. 4 - A 12-ft simple beam is supported at each end. It...Ch. 4 - The beam shown carries vertical loads as...Ch. 4 - Determine the reactions for the beam shown. The...Ch. 4 - Calculate the reaction at each support for the...Ch. 4 - Calculate the wall reactions for the cantilever...Ch. 4 - Determine the reactions at supports A and B of the...Ch. 4 - A mass M of 300 kg is supported by a boom, as...Ch. 4 - Rework Problem 4.28 assuming that point D has been...Ch. 4 - Calculate the force in the tie rod BC and the...Ch. 4 - The davit shown is used in pairs for...Ch. 4 - For the following computer problems, any...Ch. 4 - For the following computer problems, any...Ch. 4 - For the following computer problems, any...Ch. 4 - For the structure shown, draw free-body diagram...Ch. 4 - A 1200-lb load is supported by a cable that runs...Ch. 4 - For the pin-connected frame shown, sketch a...Ch. 4 - For the concurrent force system shown, calculate...Ch. 4 - A strut having a mass of 40 kg/m is supported by a...Ch. 4 - Calculate the reaction at each support for the...Ch. 4 - Calculate the reaction at each support for the...Ch. 4 - A beam supports a nonuniformly distributed load as...Ch. 4 - Calculate the reactions at each support for the...Ch. 4 - Compute reactions at each support for the beam...Ch. 4 - A rod of uniform cross section weighs 4 lb/ft and...Ch. 4 - A 12-ft-long weightiness member supports two...Ch. 4 - A uniform rod AB, having a weight of 5.00 lb and a...Ch. 4 - The plastic barrel tent anchor of Problem 2.11...Ch. 4 - Compute the reactions at A and B for the bracket...Ch. 4 - The truss shown is supported by a pin at A and a...Ch. 4 - Find the reactions at supports A and B for the...Ch. 4 - Find the reactions at supports A and B for the...Ch. 4 - Determine the reactions at A and B for the truss...Ch. 4 - A 40-ft ladder weighing 130 lb is pin-connected to...Ch. 4 - The frame shown is pin-connected at point A and...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.56SPCh. 4 - A horizontal beam is pin-connected to a wall at...Ch. 4 - Calculate the force in the cable for the structure...Ch. 4 - The Thenard shutter dam shown was originally...Ch. 4 - An inclined railway can be used to lift heavy...Ch. 4 - Two cylinders are supported in a box, as shown....
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The 60 mm-diameter steel shaft is subjected to the torques shown. Determine the angle of twist of end A with re...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Determine the components of the force acting parallel and perpendicular to the axis of the pole. Prob. F2-30
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
1.1 What is the difference between an atom and a molecule? A molecule and a crystal?
Manufacturing Engineering & Technology
The quantity ms into s.
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
What parts are included in the vehicle chassis?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, and Service (5th Edition)
What parts are included in the vehicle chassis?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3. In the given truss below calculate the forces in members CG and CF. Indicate if tension of compression. 2 kN 2 m B 2 m 2 m A 4 kN G 3 marrow_forwardCalculate the forces in members AC, AD, and DE for the loaded truss. Restraining link BC is horizontal. Forces are positive if in tension, negative if in compression. B 4' 4' 670 lb Answer: AC = i Ib AD = Ib DE = i Ibarrow_forwardProblem 3: Consider the truss shown. a. Find the support reactions at A and D. Indicate the direction of the forces acting on the truss b. Find the forces in members DH, DE and HI using the method of joints. State whether they are in tension (T) or compression (C). 50 N 2m 2m 2m H 1.5 m 40 N- 1.5 m F E B 1.5 marrow_forward
- Find the force acting in each of the members of the truss shown below. Remember to specify if each member is in tension or compression. 6 ft - 6 ft 6 ft 500 lbs 6 ftarrow_forwardFor the truss loaded below, find the force in member KJ, KD, and CD using method of sections. State whether the members are in tension or compression. 4. K Summary: 3 m Force (kN) Member KJ B C E F KD CD -2 m--2 m--2 m--2 m--2 m-2 m- 20 kN 30 kN 40 kNarrow_forwardCalculate the forces in members BE and BD of the loaded truss. The forces are positive if in tension, negative if in compression. Assume F = 6.2 kN, a = 3.4 m, b = 3 m, c = 2 m, and d = 2 m. b b A F Answers: BE = BD = a i IN E a D KN kNarrow_forward
- For the truss shown, Calculate the reactions at the supports Calculate all member forces using the method of joints. Hint: Start at joint Darrow_forward3. For the truss shown, draw the free body diagram for joints A, B, C, and D. Also, using equilibrium equations for ijust node B, find the force in member AB. 250 Ib A 30° 8 ft В 6 ft 6 ftarrow_forwardCompute the magnitude of the pin reaction at B. Neglect the weights of the structural members.arrow_forward
- Find the forces in members CD, DH, and HI.arrow_forwardThe cable carrying three 400-lb loads has a sag at C of hC=14ft. Calculate the force in each segment of the cable.arrow_forwardFind the smallest value of P for which the crate in the Prob. 4.34 will be in equilibrium in the position shown. (Hint: A rope can only support a tensile force.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Types Of loads - Engineering Mechanics | Abhishek Explained; Author: Prime Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4JVoL9wb5yM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY