
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The labeled bonds in the given compound are to be arranged in the order of increasing bond lengths.
Concept introduction:
In hybridization, one
Answer to Problem 4.1P
The increasing order of bond-lengths in the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
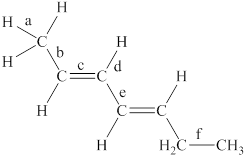
Figure 1
The bond with higher percentage of s-character has electron density closer to the nucleus and thus, has shorter bond length. The order of percentage
• Bond ‘a’ is present between the
• Bond ‘c’ is present between the two
• Due to the conjugation between two pi bonds, the bond length of ‘e’ is in between the carbon-carbon single bond and carbon-carbon double bond.
• Bond ‘b’ is present between one
• The
From the above points, it is concluded that the order of bond-lengths in the given compound is
The increasing order of bond-lengths in the given compound is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY STUDY GUIDE AND S
- Please help me solve this reaction.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
