
Determine the point groups for
a. Ethane (staggered conformation)
b. Ethane (eclipsed conformation)
c. Chloroethane (staggered conformation)
d. 1,2-Dichloroethane (staggered anti conformation)
(a)
Interpretation:
The point group for Ethane with staggered conformation is to be determined.
Concept Introduction :
A point group defines all the operations of symmetry that could be performed on a molecule, results in an indistinguishable conformation from the original.
Answer to Problem 4.1P
The point group of ethane with staggered conformation is D3d.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of ethane in staggered conformation can be drawn as
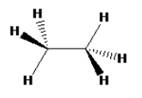
Ethane with staggered conformation has a C3 rotational axis that passes through C-C bond. There are 3 C2 rotational axes that will be perpendicular to the C3 rotational axis. It passes through the mid point of the C-C bond and doesnot have any
(b)
Interpretation: The point group for Ethane with eclipsed conformation is to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
A point group defines all the operations of symmetry that could be performed on a molecule, results in an indistinguishable conformation from the original.
Answer to Problem 4.1P
The point group of ethane with eclipsed conformation is D3h.
Explanation of Solution
The structure for ethane in eclipsed conformation is
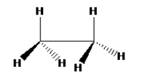
C3-rotational axis that passes through C-C bond is present in ethane in eclipsed conformation. This conformation has three C2 axes which are perpendicular to the principal C3 rotational axes and it passes through the mid-point of the C-C bond. The point group of the eclipsed ethane molecule is D3h as it has a plane of
(c)
Interpretation: The point group for chloroethane with staggered conformation is to be determined.
Concept Introduction : A point group defines all the operations of symmetry that could be performed on a molecule, results in an indistinguishable conformation from the original.
Answer to Problem 4.1P
The point group in chloroethane with staggered conformation is Cs.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of Chloroethane with staggered conformation can be drawn as
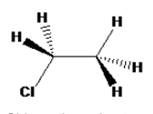
The staggered conformation of chloroethane do not have any rotational axis.
(d)
Interpretation:
The point group for 1,2-dichloroethane with staggered anti-conformation is to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
A point group defines all the operations of symmetry that could be performed on a molecule, results in an indistinguishable conformation from the original.
Answer to Problem 4.1P
The point group of 1,2-dichloroethane with staggered anti-conformation is C2h.
Explanation of Solution
The staggered anti-conformation of 1,2-dichloroethane has C2 rotational axis and it passes through the mid-point of C-C bond. This is perpendicular to the plane of Cl-C-C-Cl. The point group of the molecule is C2h as it has only one
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Inorganic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Chemistry (7th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
- Name an interesting derivative of barbituric acid, describing its structure.arrow_forwardBriefly describe the synthesis mechanism of barbituric acid from the condensation of urea with a β-diketone.arrow_forwardGiven the hydrazones indicated, draw the structures of the enamines that can be formed. Indicate the most stable enamine (explain). C6H5 C6H5 H C6H5 Harrow_forward
- 4. Propose a Synthesis for the molecule below. You may use any starting materials containing 6 carbons or less (reagents that aren't incorporated into the final molecule such as PhзP do not count towards this total, and the starting material can have whatever non-carbon functional groups you want), and any of the reactions you have learned so far in organic chemistry I, II, and III. Your final answer should show each step separately, with intermediates and conditions clearly drawn.arrow_forwardIndicate the importance of the indole ring. Find a representative example and list 5 structures.arrow_forwardΌΗ 1) V2 CO 3 or Nalt In منهarrow_forward
- 6. The equilibrium constant for the reaction 2 HBr (g) → H2(g) + Br2(g) Can be expressed by the empirical formula 11790 K In K-6.375 + 0.6415 In(T K-¹) - T Use this formula to determine A,H as a function of temperature. Calculate A,-H at 25 °C and at 100 °C.arrow_forward3. Nitrosyl chloride, NOCI, decomposes according to 2 NOCI (g) → 2 NO(g) + Cl2(g) Assuming that we start with no moles of NOCl (g) and no NO(g) or Cl2(g), derive an expression for Kp in terms of the equilibrium value of the extent of reaction, Seq, and the pressure, P. Given that K₂ = 2.00 × 10-4, calculate Seq/ of 29/no when P = 0.080 bar. What is the new value по ƒª/ at equilibrium when P = 0.160 bar? Is this result in accord with Le Châtelier's Principle?arrow_forwardConsider the following chemical equilibrium: 2SO2(g) + O2(g) = 2SO3(g) • Write the equilibrium constant expression for this reaction. Now compare it to the equilibrium constant expression for the related reaction: • . 1 SO2(g) + O2(g) = SO3(g) 2 How do these two equilibrium expressions differ? What important principle about the dependence of equilibrium constants on the stoichiometry of a reaction can you learn from this comparison?arrow_forward
- Given Kp for 2 reactions. Find the Kp for the following reaction: BrCl(g)+ 1/2 I2(g) ->IBr(g) + 1/2 Cl2(g)arrow_forwardFor a certain gas-phase reaction at constant pressure, the equilibrium constant Kp is observed to double when the temperature increases from 300 K to 400 K. Calculate the enthalpy change of the reaction, Ah, using this information.arrow_forwardHydrogen bonding in water plays a key role in its physical properties. Assume that the energy required to break a hydrogen bond is approximately 8 kJ/mol. Consider a simplified two-state model where a "formed" hydrogen bond is in the ground state and a "broken" bond is in the excited state. Using this model: • Calculate the fraction of broken hydrogen bonds at T = 300 K, and also at T = 273 K and T = 373 K. • At what temperature would approximately 50% of the hydrogen bonds be broken? • What does your result imply about the accuracy or limitations of the two-state model in describing hydrogen bonding in water? Finally, applying your understanding: • Would you expect it to be easier or harder to vaporize water at higher temperatures? Why? If you were to hang wet laundry outside, would it dry more quickly on a warm summer day or on a cold winter day, assuming humidity is constant?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

