
Special Order
Fairmount Travel Gear produces backpacks and sells them to vendors who sell them under their own label. The cost of one of its backpacks follows:
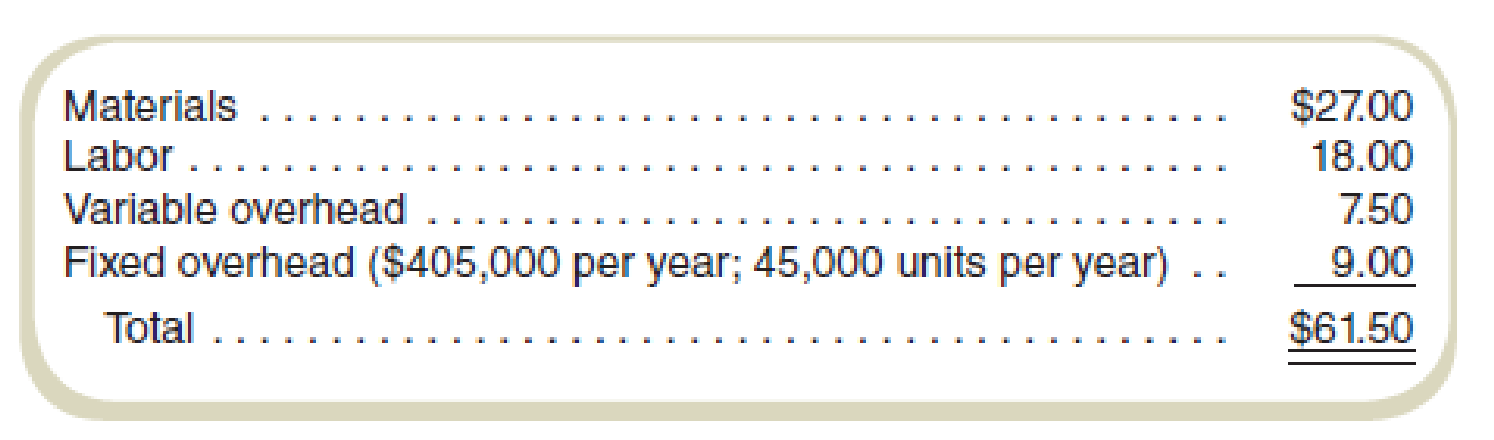
Riverside Discount Mart, a chain of low-price stores, has asked Fairmount to supply it with 3,000 backpacks for a special promotion Riverside is planning. Riverside has offered to pay Fairmount a unit price of $63 per pack. The regular selling price is $90. The special order would require some modification to the basic model. These modifications would add $6.00 per unit in material cost, $2.50 per unit in labor cost, and $0.70 in variable
Required
- a. Prepare a schedule to show the impact of filling the Riverside order on Fairmont’s profits for the year.
- b. Would you recommend that Fairmont accept the order?
- c. Considering only profit, determine the minimum quantity of backpacks in the special order that would make it profitable.
a.
Calculate the impact on operating profit because of the special order.
Answer to Problem 41E
The operating profit decreases by $3,600 because of the special order of 3,000 backpacks.
Explanation of Solution
Operating profit: The operating profit is the excess of total revenues over total expenses after adjusting for depreciation and taxes.
- • A special order has a price of $63 and 3,000 units (backpacks).
- • Fixed cost for special order will increase by $7,500 because of rental equipment.
- • Special order will require the additional material cost of $6, the labor cost of $2.5 and variable cost of$0.70.
Compute the impact on operating profit because of the special order:
| Particulars | Status Quo: 45,000 units | Alternative: 48,000 units | Difference |
| Sales revenue | $4,050,000 | $4,239,000(1) | $189,000 higher |
| Less: material | $1,215,000 | $1,314,000(2) | $99,000 higher |
| Labor | $810,000 | $871,500(3) | $61,500 higher |
| Variable cost | $337,500 | $362,100(4) | $24,600 higher |
| Total variable overhead | $2,362,500 | $2,547,600 | $185,100 higher |
| Contribution margin | $1,687,500 | $1,691,400 | $3,900 higher |
| Less: fixed overhead | $405,000 | $412,500(5) | $7,500 higher |
| Operating profit | $1,282,500 | $1,278,900 | $3,600 lower |
Table: (2)
Thus, the operating profit decreases by $3,600 because of the special order of 3,000 backpacks.
Working note 1:
Compute the sales revenue for an alternative:
Working note 2:
Compute the material cost for the alternative:
Working note 3:
Compute the labor cost for the alternative:
Working note 4:
Compute the variable cost for the alternative:
Working note 5:
Compute the fixed cost for the alternative:
Working note 6:
Compute the revised costs:
| Particulars | Amount | Additional cost | Total |
| Material cost | $27 | $6.0 | $33 |
| Labor | $18 | $2.5 | $20.5 |
| Variable overhead | $7.5 | $0.7 | $8.2 |
Table: (6)
b.
Recommend whether Company F should accept the offer or not.
Explanation of Solution
Company F should not accept the offer. The operating profit decreases by $3,600 because of the special order of 3,000 backpacks. Accepting the offer will decrease the operating profit by $3,600.
Thus, Company F should not accept the offer as per the loss of the operating profit.
c.
Considering only the profit, determine the minimum quantity of backpacks in the special order that would make it profitable, assuming capacity is available.
Answer to Problem 41E
Company F should sell 5,769 units in order to make the business profitable.
Explanation of Solution
Breakeven point (BEP): The breakeven point or BEP is that level of output at which the total revenue is equal to the total cost. The BEP means there are no operating income and no operating losses. The management keeps an eye on the breakeven point in order to avoid the operating losses in order to avoid losses.
Contribution margin: The excess of sales price over the variable expenses is referred to as the contribution margin. It is computed by deducting the variable expenses from the sales revenue.
Company F should use the break-even analysis to find out the minimum quantity of backpacks in the special order that would make it profitable. Total variable cost is $61.7
Compute the break-even point:
Thus, Company F should sell 5,769 units in order to make the business profitable.
Working note 4:
Compute the contribution margin:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Fundamentals of Cost Accounting
- L.L. Bean operates two factories that produce its popular Bean boots (also known as "duck boots") in its home state of Maine. Since L.L. Bean prides itself on manufacturing its boots in Maine and not outsourcing, backorders for its boots can be high. In 2014, L.L. Bean sold about 450,000 pairs of the boots. At one point during 2014, it had a backorder level of about 100,000 pairs of boots. L.L. Bean can manufacture about 2,200 pairs of its duck boots each day with its factories running 24/7. In 2015, L.L. Bean expects to sell more than 500,000 pairs of its duck boots. As of late November 2015, the backorder quantity for Bean Boots was estimated to be about 50,000 pairs. Question: Now assume that 5% of the L.L. Bean boots are returned by customers for various reasons. L. Bean has a 100% refund policy for returns, no matter what the reason. What would the journal entry be to accrue L.L. Bean's sales returns for this one pair of boots?arrow_forwardThe following data were taken from the records of Splish Brothers Company for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2025. Raw Materials Inventory 7/1/24 $58,100 Accounts Receivable $28,000 Raw Materials Inventory 6/30/25 46,600 Factory Insurance 4,800 Finished Goods Inventory 7/1/24 Finished Goods Inventory 6/30/25 99,700 Factory Machinery Depreciation 17,100 21,900 Factory Utilities 29,400 Work in Process Inventory 7/1/24 21,200 Office Utilities Expense 9,350 Work in Process Inventory 6/30/25 29,400 Sales Revenue 560,500 Direct Labor 147,550 Sales Discounts 4,700 Indirect Labor 25,360 Factory Manager's Salary 63,400 Factory Property Taxes 9,910 Factory Repairs 2,500 Raw Materials Purchases 97,300 Cash 39,200 SPLISH BROTHERS COMPANY Income Statement (Partial) $arrow_forwardNo AIarrow_forward
- L.L. Bean operates two factories that produce its popular Bean boots (also known as "duck boots") in its home state of Maine. Since L.L. Bean prides itself on manufacturing its boots in Maine and not outsourcing, backorders for its boots can be high. In 2014, L.L. Bean sold about 450,000 pairs of the boots. At one point during 2014, it had a backorder level of about 100,000 pairs of boots. L.L. Bean can manufacture about 2,200 pairs of its duck boots each day with its factories running 24/7.In 2015, L.L. Bean expects to sell more than 500,000 pairs of its duck boots. As of late November 2015, the backorder quantity for Bean Boots was estimated to be about 50,000 pairs. Question: Assume that a pair of 8" Bean Boots are ordered on December 3, 2015. The order price is $109. The sales tax rate in the state in which the boots are order is 7%. L.L. Bean ships the boots on January 29, 2016. Assume same-day shipping for the sake of simplicity. On what day would L.L. Bean recognize the…arrow_forwardFinancial accounting questionarrow_forward2 Questionarrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
