
An Introduction to Physical Science
14th Edition
ISBN: 9781305079120
Author: James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher: Brooks Cole
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 15SA
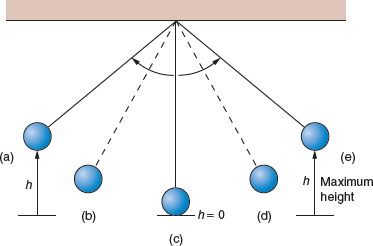
A simple pendulum as shown in ● Fig. 4.24 oscillates back and forth. Use the letter designations in the figure to identify the pendulum’s position(s) for the following conditions. (There may be more than one answer. Consider the pendulum to be ideal with no energy losses.)
- (a) Position(s) of instantaneous rest ___
- (b) Position(s) of maximum velocity ___
- (c) Position(s) of maximum Ek ___
- (d) Position(s) of maximum Ep ___
- (e) Position(s) of minimum Ek ___
- (f) Position(s) of minimum Ep ___
- (g) Position(s) after which Ek increases ___
- (h) Position(s) after which Ep increases ___
- (i) Position(s) after which Ek decreases ___
- (j) Position(s) after which Ep decreases ___
Figure 4.24 The Simple Pendulum and Energy
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
A beam of alpha-particles of energy 7.3MeV is used.The protons emitted at an angle of zero degree are found to have energy of 9.34MeV.Find the Q-value of this reaction .
An aluminum rod and a copper rod have the same length of 100cm at 5C. At what temperatures would one of the rods be 0.5 mm longer than the other? Which rod is longer at such temperature?
Chapter 4 Solutions
An Introduction to Physical Science
Ch. 4.1 - Is work a vector quantity? In other words, does it...Ch. 4.1 - What are the units of work?Ch. 4.2 - By what process is energy transferred from one...Ch. 4.2 - To find the difference in gravitational potential...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 4.1CECh. 4.3 - Overall, can energy be created or destroyed?Ch. 4.3 - What is the difference between total energy and...Ch. 4.3 - Find the kinetic energy of the stone in the...Ch. 4.4 - What is the difference in the operations of a 2-hp...Ch. 4.4 - Electric bills from power companies charge for so...
Ch. 4.4 - A student expends 7.5 W of power in lifting a...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 4.4CECh. 4.5 - Prob. 1PQCh. 4.5 - Prob. 2PQCh. 4.6 - What is the difference between alternative and...Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 2PQCh. 4 - KEY TERMS 1. work (4.1) 2. joule 3. foot-pound 4....Ch. 4 - Prob. BMCh. 4 - Prob. CMCh. 4 - Prob. DMCh. 4 - Prob. EMCh. 4 - Prob. FMCh. 4 - Prob. GMCh. 4 - Prob. HMCh. 4 - Prob. IMCh. 4 - Prob. JMCh. 4 - Prob. KMCh. 4 - Prob. LMCh. 4 - Prob. MMCh. 4 - KEY TERMS 1. work (4.1) 2. joule 3. foot-pound 4....Ch. 4 - KEY TERMS 1. work (4.1) 2. joule 3. foot-pound 4....Ch. 4 - Work is done on an object when it is ___. (4.1)...Ch. 4 - Which of the following is a unit of work? (4.1)...Ch. 4 - Prob. 3MCCh. 4 - Which of the following objects has the greatest...Ch. 4 - A pitcher throws a fastball. When the catcher...Ch. 4 - The reference point for gravitational potential...Ch. 4 - When the height of an object is changed, the...Ch. 4 - Mechanical energy is ___. (4.2) (a) the sum of...Ch. 4 - On which of the following does the speed of a...Ch. 4 - Power is expressed by which of the following...Ch. 4 - If motor A has twice as much horsepower as motor...Ch. 4 - Prob. 12MCCh. 4 - Which one of the following would not be classified...Ch. 4 - Prob. 14MCCh. 4 - Work is equal to the force times the ___ distance...Ch. 4 - Prob. 2FIBCh. 4 - The unit N m is given the special name of ___ ....Ch. 4 - Prob. 4FIBCh. 4 - Prob. 5FIBCh. 4 - The stopping distance of an automobile on a level...Ch. 4 - Kinetic energy is commonly referred to as the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 8FIBCh. 4 - Prob. 9FIBCh. 4 - Prob. 10FIBCh. 4 - Prob. 11FIBCh. 4 - Prob. 12FIBCh. 4 - Renewable energy sources cannot be ___ . (4.6)Ch. 4 - Gasohol is gasoline mixed with ___ . (4.6)Ch. 4 - Prob. 1SACh. 4 - Do all forces do work? Explain.Ch. 4 - What does work on a shuffleboard puck as it slides...Ch. 4 - A weight lifter holds 900 N (about 200 lb) over...Ch. 4 - For the situation in Fig. 4.4a, if the applied...Ch. 4 - Car B is traveling twice as fast as car A, but car...Ch. 4 - Prob. 7SACh. 4 - If the speed of a moving object is doubled, how...Ch. 4 - A book sits on a library shelf 1.5 m above the...Ch. 4 - (a) A car traveling at a constant speed on a level...Ch. 4 - An object is said to have a negative potential...Ch. 4 - Prob. 12SACh. 4 - A ball is dropped from a height at which it has 50...Ch. 4 - Prob. 14SACh. 4 - A simple pendulum as shown in Fig. 4.24...Ch. 4 - Two students throw identical snowballs from the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 17SACh. 4 - When you throw an object into the air, is its...Ch. 4 - Prob. 19SACh. 4 - Persons A and B do the same job, but person B...Ch. 4 - What does a greater power rating mean in terms of...Ch. 4 - What do we pay the electric company for, power or...Ch. 4 - Prob. 23SACh. 4 - Prob. 24SACh. 4 - Prob. 25SACh. 4 - On average, how much energy do you radiate each...Ch. 4 - Prob. 27SACh. 4 - Prob. 28SACh. 4 - Prob. 29SACh. 4 - Prob. 30SACh. 4 - Prob. 1VCCh. 4 - A fellow student tells you that she has both zero...Ch. 4 - Two identical stones are thrown from the top of a...Ch. 4 - A person on a trampoline can go higher with each...Ch. 4 - With which of our five senses can we detect...Ch. 4 - What are three common ways to save electricity to...Ch. 4 - A worker pushes horizontally on a large crate with...Ch. 4 - While rearranging a dorm room, a student does 400...Ch. 4 - A 5.0-kilo bag of sugar is on a counter. How much...Ch. 4 - How much work is required to lift a 6.0-kg...Ch. 4 - A man pushes a lawn mower on a level lawn with a...Ch. 4 - If the man in Exercise 5 pushes the mower with 40%...Ch. 4 - How much work does gravity do on a 0.150-kg ball...Ch. 4 - A student throws the same ball straight upward to...Ch. 4 - (a) What is the kinetic energy in joules of a...Ch. 4 - A 60-kg student traveling in a car with a constant...Ch. 4 - What is the kinetic energy of a 20-kg dog that is...Ch. 4 - Which has more kinetic energy, a 0.0020-kg bullet...Ch. 4 - Prob. 13ECh. 4 - How much farther would the force in Exercise 13...Ch. 4 - What is the potential energy of a 3.00-kg object...Ch. 4 - How much work is required to lift a 3.00-kg object...Ch. 4 - An object is dropped from a height of 12 m. At...Ch. 4 - A 1.0-kg rock is dropped from a height of 6.0 m....Ch. 4 - A sled and rider with a combined weight of 60 kg...Ch. 4 - A 30.0-kg child starting from rest slides down a...Ch. 4 - If the man in Exercise 5 pushes the lawn mower 6.0...Ch. 4 - If the man in Exercise 5 expended 60 W of power in...Ch. 4 - A student who weighs 556 N climbs a stairway...Ch. 4 - A 125-lb student races up stairs with a vertical...Ch. 4 - On a particular day, the following appliances are...Ch. 4 - Prob. 26E
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS Question 01 A solid circular cylinder and a solid spherical ball of the same mass and radius are rolling together down the same inclined. Calculate the ratio of their kinetic energy. Assume pure rolling motion Question 02 A sphere and cylinder of the same mass and radius start from ret at the same point and more down the same plane inclined at 30° to the horizontal Which body gets the bottom first and what is its acceleration b) What angle of inclination of the plane is needed to give the slower body the same acceleration Question 03 i) Define the angular velocity of a rotating body and give its SI unit A car wheel has its angular velocity changing from 2rads to 30 rads seconds. If the radius of the wheel is 400mm. calculate ii) The angular acceleration iii) The tangential linear acceleration of a point on the rim of the wheel Question 04 in 20arrow_forwardQuestion B3 Consider the following FLRW spacetime: t2 ds² = -dt² + (dx² + dy²+ dz²), t2 where t is a constant. a) State whether this universe is spatially open, closed or flat. [2 marks] b) Determine the Hubble factor H(t), and represent it in a (roughly drawn) plot as a function of time t, starting at t = 0. [3 marks] c) Taking galaxy A to be located at (x, y, z) = (0,0,0), determine the proper distance to galaxy B located at (x, y, z) = (L, 0, 0). Determine the recessional velocity of galaxy B with respect to galaxy A. d) The Friedmann equations are 2 k 8πG а 4πG + a² (p+3p). 3 a 3 [5 marks] Use these equations to determine the energy density p(t) and the pressure p(t) for the FLRW spacetime specified at the top of the page. [5 marks] e) Given the result of question B3.d, state whether the FLRW universe in question is (i) radiation-dominated, (ii) matter-dominated, (iii) cosmological-constant-dominated, or (iv) none of the previous. Justify your answer. f) [5 marks] A conformally…arrow_forwardSECTION B Answer ONLY TWO questions in Section B [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-B sub question.] Question B1 Consider the line element where w is a constant. ds²=-dt²+e2wt dx², a) Determine the components of the metric and of the inverse metric. [2 marks] b) Determine the Christoffel symbols. [See the Appendix of this document.] [10 marks] c) Write down the geodesic equations. [5 marks] d) Show that e2wt it is a constant of geodesic motion. [4 marks] e) Solve the geodesic equations for null geodesics. [4 marks]arrow_forward
- Page 2 SECTION A Answer ALL questions in Section A [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-A sub question.] Question A1 SPA6308 (2024) Consider Minkowski spacetime in Cartesian coordinates th = (t, x, y, z), such that ds² = dt² + dx² + dy² + dz². (a) Consider the vector with components V" = (1,-1,0,0). Determine V and V. V. (b) Consider now the coordinate system x' (u, v, y, z) such that u =t-x, v=t+x. [2 marks] Write down the line element, the metric, the Christoffel symbols and the Riemann curvature tensor in the new coordinates. [See the Appendix of this document.] [5 marks] (c) Determine V", that is, write the object in question A1.a in the coordinate system x'. Verify explicitly that V. V is invariant under the coordinate transformation. Question A2 [5 marks] Suppose that A, is a covector field, and consider the object Fv=AAμ. (a) Show explicitly that F is a tensor, that is, show that it transforms appropriately under a coordinate transformation. [5 marks] (b)…arrow_forwardHow does boiling point of water decreases as the altitude increases?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 14 Z In figure, a closed surface with q=b= 0.4m/ C = 0.6m if the left edge of the closed surface at position X=a, if E is non-uniform and is given by € = (3 + 2x²) ŷ N/C, calculate the (3+2x²) net electric flux leaving the closed surface.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardsuggest a reason ultrasound cleaning is better than cleaning by hand?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University
Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g7u6pIfUVy4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY