
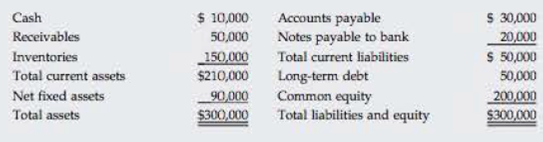
The new owner thinks that inventories are excessive and can be lowered to the point where the current ratio is equal to the industry average, 25×, without affecting sales or net income. If inventories are sold and not replaced (thus reducing the current ratio to 25×); if the funds generated are used to reduce common equity (stock can be repurchased at book value); and if no other changes occur, by how much will the ROE change? What will be the firm’s new quick ratio?
To identify: The change in return on equity and new quick ratio.
Quick Ratio: A part of liquidity ratios, quick ratio reflects the ability to oblige the short term debts of a company. It is calculated based on the liquid assets and current liabilities; a company has in an accounting period.
Return on Equity: Return on equity represents the amount earned as return by equity share holders; it can be calculated by dividing earnings available for equity share holders to total equity capital.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of return on equity
Items required for the calculation of return on equity are net income and common equity.
Given,
Net income is $15,000.
Common equity is $200,000.
Formula to calculate return on equity ratio,
Where,
- ROE is return on equity.
Substitute $15,000 for net income and $200,000 for common equity in the above formula,
Hence, the return on equity is 0.075 or 7.5%.
Compute the quick ratio
Given,
The current assets are $210,000.
The inventories are $150,000.
The current liabilities are $50,000.
Formula to compute quick ratio,
Substitute $210,000 for current assets, $150,000 for inventories and $50,000 for current liabilities in the above formula,
The quick ratio is 1.2 times.
In order to compute new quick ratio, old current ratio, new current assets and new return on equity need to calculate.
Computation of old current ratio
The items required for the calculation of current ratio are current liabilities and current assets.
Given,
Current assets are $210,000.
Current liabilities are $50,000.
Formula to calculate current ratio,
Substitute $210,000 for current assets and $50,000 for current liabilities in the above formula,
Hence, old current ratio is 4.2 times.
The new current ratio which is required to take is 2.5 times.
Compute the change in assets due to the current ratio as 2.5 times.
The current liabilities are $50,000. (Given)
The current ratio is 2.5 times.
Formula to calculate new current assets derives from the formula of current ratio,
Substitute $50,000 for current liabilities and 2.5 for current ratio in the above formula,
The new current assets are $125,000.
The difference between the currents assets refers the value of sold inventory.
Compute the sold inventory due to change in current assets
The current assets are $210,000. (Given)
The new current assets are $125,000. (Calculated)
Formula to calculate the sold inventory,
Substitute $210,000 for old current assets and $125,000 for new current assets in the above formula,
The value of inventor is curtailed by the $85,000.
Compute the balance inventory
The total inventory is $150,000. (Given)
The sold inventory is $85,000. (Calculated)
Formula to calculate the balance inventory,
Substitute $150,000 for inventory and $85,000 for sold inventory in the above formula,
The balanced inventory is $65,000.
Due to the sale the cash balance would also decrease by 65,000.
Computation of cash balance after the sale of inventory
Cash balance is $10,000.
The sale of inventory is $65,000.
Formula to calculate the new cash balance,
Substitute $10,000 for old balance and $65,000 for sold inventory in the above formula,
The cash balance after the sale of inventory is $55,000.
From the cash balance after sale of inventory, equity can be bought back. So the level of cash balance will reduce and equity will reduce by $65,000.
Compute the reduced equity:
The equity balance is $200,000. (Given)
The buyback equity share is $65,000. (Calculated)
Formula to calculate the reduced capital,
Substitute $200,000 for total equity shares and $65,000 for buyback shares in the above formula,
The reduced equity shares are $135,000.
Compute the new return on equity
The net income is $15,000. (Given)
The equity value is $135,000. (Calculated)
Formula to calculate the return on equity,
Where,
- ROE is return on equity.
Substitute $15,000 for net income and $135,000 for common equity in the above formula,
Hence, the return on equity is 0.1111 or 11.11%.
Compute the new quick ratio
The new current assets are $125,000.
The new inventories are $65,000.
The current liabilities are $50,000.
Formula to calculate quick ratio,
Substitute $125,000 for current assets, $65,000 for inventories and $50,000 for current liabilities in the above formula,
The new quick ratio is 1.2 times.
Quick ratio has remained same as there is no other current asset has changed except inventory and inventory is not the part of the terms used for the calculation of quick ratio.
Hence, the change in return on equity is 11.11% and there is no change in quick ratio and it is 1.2 times.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Course List)
- (d) Estimate the value of a share of Cisco common stock using the discounted cash flow (DCF) model as of July 27, 2019 using the following assumptions Assumptions Discount rate (WACC) Common shares outstanding 7.60% 5,029.00 million Net nonoperating obligations (NNO) $(8,747) million NNO is negative, which means that Cisco has net nonoperating investments CSCO ($ millions) DCF Model Reported 2019 Forecast Horizon 2020 Est. 2021 Est. 2022 Est. 2023 Est. Terminal Period Increase in NOA FCFF (NOPAT - Increase in NOA) $ 1241 1303 1368 10673 11207 11767 1437 $ 12354 302 ✓ Present value of horizon FCFF 9918 9679 9445 ✔ 0 × Cum. present value of horizon FCFF $ 0 × Present value of terminal FCFF 0 ☑ Total firm value 0 ☑ NNO -8747 ✓ Firm equity value $ 0 ☑ Shares outstanding (millions) 5029 Stock price per share $ 40.05arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Don't used Ai solution and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardQ1: Blossom is 30 years old. She plans on retiring in 25 years, at the age of 55. She believes she will live until she is 105. In order to live comfortably, she needs a substantial retirement income. She wants to receive a weekly income of $5,000 during retirement. The payments will be made at the beginning of each week during her retirement. Also, Blossom has pledged to make an annual donation to her favorite charity during her retirement. The payments will be made at the end of each year. There will be a total of 50 annual payments to the charity. The first annual payment will be for $20,000. Blossom wants the annual payments to increase by 3% per year. The payments will end when she dies. In addition, she would like to establish a scholarship at Toronto Metropolitan University. The first payment would be $80,000 and would be made 3 years after she retires. Thereafter, the scholarship payments will be made every year. She wants the payments to continue after her death,…arrow_forwardCould you please help explain what is the research assumptions, research limitations, research delimitations and their intent? How the research assumptions, research limitations can shape the study design and scope? How the research delimitations could help focus the study and ensure its feasibility? What are the relationship between biblical principles and research concepts such as reliability and validity?arrow_forward
- What is the concept of the working poor ? Introduction form. Explain.arrow_forwardWhat is the most misunderstanding of the working poor? Explain.arrow_forwardProblem Three (15 marks) You are an analyst in charge of valuing common stocks. You have been asked to value two stocks. The first stock NEWER Inc. just paid a dividend of $6.00. The dividend is expected to increase by 60%, 45%, 30% and 15% per year, respectively, in the next four years. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 4% per year in perpetuity. Calculate NEWER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. The required rate of return for NEWER stock is 14% compounded annually. What is NEWER’s stock price? The second stock is OLDER Inc. OLDER Inc. will pay its first dividend of $10.00 three (3) years from today. The dividend will increase by 30% per year for the following four (4) years after its first dividend payment. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 3% per year in perpetuity. Calculate OLDER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8. The required rate of return for OLDER stock is 16% compounded annually. What is OLDER’s stock price? Now assume that…arrow_forward
- Problem Three (15 marks) You are an analyst in charge of valuing common stocks. You have been asked to value two stocks. The first stock NEWER Inc. just paid a dividend of $6.00. The dividend is expected to increase by 60%, 45%, 30% and 15% per year, respectively, in the next four years. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 4% per year in perpetuity. Calculate NEWER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. The required rate of return for NEWER stock is 14% compounded annually. What is NEWER’s stock price? The second stock is OLDER Inc. OLDER Inc. will pay its first dividend of $10.00 three (3) years from today. The dividend will increase by 30% per year for the following four (4) years after its first dividend payment. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 3% per year in perpetuity. Calculate OLDER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8. The required rate of return for OLDER stock is 16% compounded annually. What is OLDER’s stock price? Now assume that…arrow_forwardYour father is 50 years old and will retire in 10 years. He expects to live for 25 years after he retires, until he is 85. He wants a fixed retirement income that has the same purchasing power at the time he retires as $45,000 has today. (The real value of his retirement income will decline annually after he retires.) His retirement income will begin the day he retires, 10 years from today, at which time he will receive 24 additional annual payments. Annual inflation is expected to be 4%. He currently has $240,000 saved, and he expects to earn 8% annually on his savings. Required annuity payments Retirement income today $45,000 Years to retirement 10 Years of retirement 25 Inflation rate 4.00% Savings $240,000 Rate of return 8.00% Calculate value of…arrow_forwardProblem Three (15 marks) You are an analyst in charge of valuing common stocks. You have been asked to value two stocks. The first stock NEWER Inc. just paid a dividend of $6.00. The dividend is expected to increase by 60%, 45%, 30% and 15% per year, respectively, in the next four years. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 4% per year in perpetuity. Calculate NEWER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. The required rate of return for NEWER stock is 14% compounded annually. What is NEWER’s stock price? The second stock is OLDER Inc. OLDER Inc. will pay its first dividend of $10.00 three (3) years from today. The dividend will increase by 30% per year for the following four (4) years after its first dividend payment. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 3% per year in perpetuity. Calculate OLDER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8. The required rate of return for OLDER stock is 16% compounded annually. What is OLDER’s stock price? Now assume that…arrow_forward
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning


