
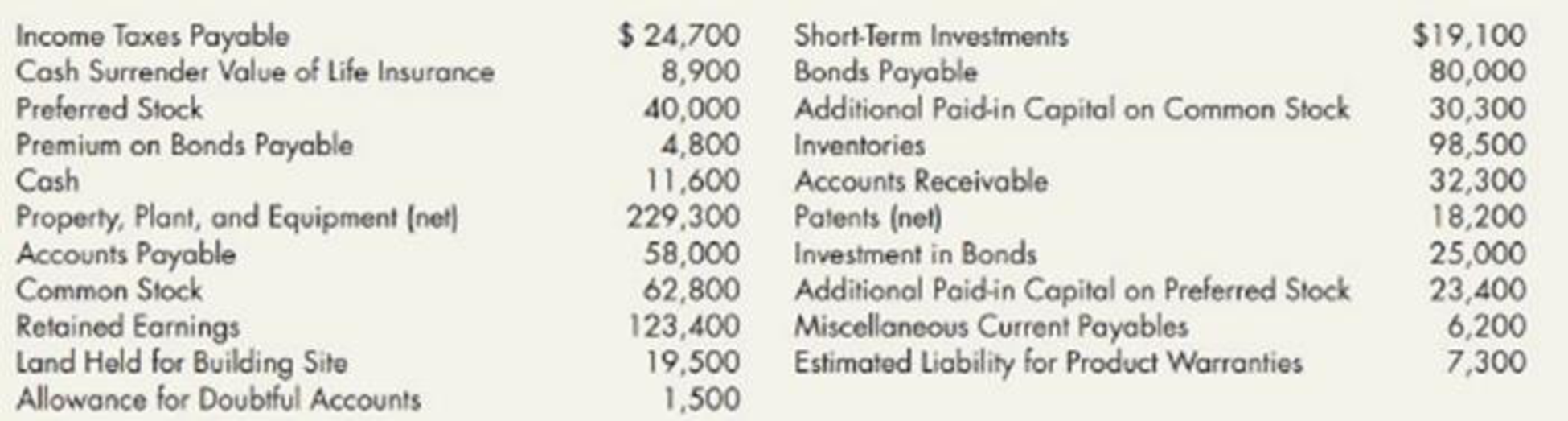
Additional information:
- 1. The company reports on the balance sheet the total amount for inventories and the net book value of property, plant, and equipment, with the related details for each account disclosed in notes.
- 2. The
straight line method is used todepreciate buildings, machinery, and equipment, based upon their cost and estimated residual value’s and lives. A breakdown of property, plant, and equipment shows the following: land at a cost of $32,000, buildings at a cost of $182,400 and a net book value of $120,200, machinery at a cost of $63,900, and relatedaccumulated depreciation of $18,600, and equipment (40% depreciated) at a cost of $53,000. - 3. Patents are amortized on a straight line basis directly to the Patent account.
- 4. Inventories are listed at the lower of cost or market value using an average cost. The inventories include raw-materials, $22,200; work in process, $34,700; and finished goods, $41,600.
- 5. Common stock has a $10 par value per share, 12,000 shares are authorized, and 6,280 shares have been issued.
- 6.
Preferred stock has a $100 par value per share, 1,000 shares are authorized, and 400 shares have been issued. - 7. The investment in bonds is carried at the original cost, which is the face value, and is being held to maturity.
- 8. Short-term investments in marketable securities were purchased at year-end.
- 9. The bonds payable mature on December 31, 2024.
- 10. The company attaches a 1-year warranty on all the products it sells.
Required:
- 1. Prepare Wicks Construction’s December 31, 2019, balance sheet (including appropriate parenthetical notations).
- 2. Prepare notes to accompany the balance sheet that itemize company accounting policies; inventories; and property, plant, and equipment.
- 3. Next Level Compute the
current ratio and the quick ratio. How do these two ratios provide different information about the company’s liquidity? Why are these ratios useful?
1.
Prepare the balance sheet of Company W for December 31, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet: This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and stockholders (stockholders’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by stockholders and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity.
The balance sheet of company W is prepared as follows:
| Company W | |||
| Balance Sheet | |||
| December 31,2019 | |||
| Current Assets: | Amount ($) | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash | $11,600 | ||
| Short-term investments in marketable securities [Refer to subpart 2 (note 1)] | $19,100 | ||
| Accounts receivable | $32,300 | ||
| Less: Allowance for doubtful accounts | ($1,500) | $30,800 | |
| Inventories [Refer to subpart 2 (Notes 1 and 2) ] | $98,500 | ||
| Total current assets | $160,000 | ||
| Long-Term Investments: | |||
| Investment in bonds [Refer to subpart 2 (note 1)] | $25,000 | ||
| Land held for building site | $19,500 | ||
| Cash surrender value of life insurance | $8,900 | ||
| Total long-term investments | $53,400 | ||
| Property, plant, and equipment [Refer to subpart 2 (Notes 1 and 3) ] | $229,300 | ||
| Intangible Assets: | |||
| Patents (net) [Refer to subpart 2 (Notes 1 and 2) ] | $18,200 | ||
| Total Assets | $460,900 | ||
| Liabilities | |||
| Current Liabilities: | |||
| Accounts payable | $58,000 | ||
| Income taxes payable | $24,700 | ||
| Miscellaneous current payables | $6,200 | ||
| Estimated liability for product warranties | $7,300 | ||
| Total current liabilities | $96,200 | ||
| Long-Term Liabilities: | |||
| Bonds payable (mature on 12/31/2024) | $80,000 | ||
| Premium on bonds payable | $4,800 | ||
| Total long-term liabilities | $84,800 | ||
| Total Liabilities | $181,000 | ||
| Shareholders’ Equity | |||
| Contributed Capital: | |||
| Preferred stock, $100 par, 1,000 shares authorized, 400 shares issued | $40,000 | ||
| Common stock, $10 par, 12,000 shares authorized, 6,280 shares issued | $62,800 | ||
| Additional paid-in capital on: | |||
| Preferred stock | $23,400 | ||
| Common stock | $30,300 | ||
| Total contributed capital | $156,500 | ||
| Retained earnings | $123,400 | ||
| Total Shareholders’ Equity | $279,900 | ||
| Total Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity | $460,900 | ||
Table (1)
Therefore, the amount of total assets and total liabilities and stockholders’ equity equals $460,900.
2.
Prepare notes to accompany the balance sheet that itemize company accounting policies, inventories, and property, plant and equipment.
Explanation of Solution
Accompanying Notes to the balance sheet:
Note (1):
Summary of important accounting policies:
- Inventories are valued at the lower of average cost or market.”.
- Property, plant, and equipment are recorded at cost less accumulated depreciation. The straight-line method is used to depreciate all property, plant, and equipment, except land”.
- Patents are amortized on a straight-line basis directly to the Patent account”.
- Temporary investments in marketable securities are stated at their market value”.
- Investment in bonds is carried at original cost (face value) and is being held to maturity”.
Note (2):
Composition of inventories:
The inventories of the company as of December 31, 2019, are composed of the following components:
| Particulars | Amount |
| Raw materials | $22,200 |
| Work in process | $34,700 |
| Finished goods | $41,600 |
| Total | $98,500 |
Table (2)
Note (3)
Composition of property, plant, and equipment:
The property, plant, and equipment of the company as of December 31, 2019, comprise the following:
| Item | Cost | Accumulated Depreciation | Book value |
| Land | $32,000 | $32,000 | |
| Buildings | $182,400 | $62,200 | $120,000 |
| Machinery | $63,900 | $18,600 | $45,300 |
| Equipment | $53,000 | $21,200 | $31,800 |
| Total | $331,300 | $102,000 | $229,300 |
Table (3)
3.
Compute the current ratio and the quick ratio, state the way in which the two ratios provide different information about the liquidity of the company and explain the way in which these ratios are useful.
Explanation of Solution
Current ratio: The financial ratio which evaluates the ability of a company to pay off the debt obligations which mature within one year or within completion of operating cycle is referred to as current ratio. This ratio assesses the liquidity of a company.
Quick ratio: The financial ratio which evaluates the ability of a company to pay off the instant debt obligations is referred to as quick ratio. Quick assets are cash, marketable securities, and accounts receivables. This ratio assesses the short-term liquidity of a company from its most liquid (quick) assets.
Calculate the current ratio:
Therefore, the current ratio is 1.66:4.
Compute quick ratio:
Therefore, the quick ratio is 0.64:1.
- Current ratio evaluates the liquidity
- Quick ratio analyzes a company’s potential working capital.
- Comparison of these two ratios states the amount of liquidity that comes from the inventory, which is not as liquid as the quick assets.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting and Analysis (Looseleaf)
- What was the total amount of the merchandise purchase?arrow_forwardColton Inc. is a merchandising company. Last month, the company's cost of goods sold was $85,600. The company's beginning merchandise inventory was $18,200, and its ending merchandise inventory was $30,500. What was the total amount of the company's merchandise purchases for the month? correct answerarrow_forwardColton Inc. is a merchandising company. Last month, the company's cost of goods sold was $85,600. The company's beginning merchandise inventory was $18,200, and its ending merchandise inventory was $30,500. What was the total amount of the company's merchandise purchases for the month?arrow_forward
- Please provide accurate answerarrow_forwardAtlas Corporation has forecasted sales of $4,000 in January, $5,500 in February, and $7,000 in March. All sales are on credit. The company collects 40% of sales in the month of the sale and the remaining 60% in the following month. What will be the balance in accounts receivable at the beginning of April?arrow_forwardAtlas Corporation has forecasted sales of $4,000 in January, $5,500 in February, and $7,000 in March. All sales are on credit. The company collects 40% of sales in the month of the sale and the remaining 60% in the following month. What will be the balance in accounts receivable at the beginning of April?Solve thisarrow_forward
- Solve this Accounting problemarrow_forwardNeed answerarrow_forwardA business has $210,000 total liabilities. At start-up, the owners invested $500,000 in the business. Unfortunately, the business has suffered a cumulative loss of $200,000 up to the present time. What is the amount of its total assets at the present time? No WRONG ANSWERarrow_forward
- Bal Engineering has $60,000 in assets. They also have $25,000 in liabilities and $5,000 in expenses, and they paid out $7,500 in dividends this year. The extended accounting equation is assets = liabilities + (revenue - (expenses + dividends)). What would their revenue need to be for their accounts to be in balance?arrow_forwardAccurate answerarrow_forwardCompute production cost per unit under variable costing.arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning

