
EBK PHYSICS OF EVERYDAY PHENOMENA
8th Edition
ISBN: 8220106637050
Author: Griffith
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 11CQ
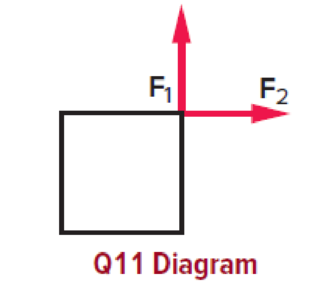
Two equal forces act on an object in the directions pictured in the diagram. If these are the only forces involved, will the object be accelerated? Explain, using a diagram.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
4. Does the period of simple harmonic motion depend on amplitude?
Show that x(t) = A cos (wt) + B sin (wt) is a solution to the differential equation of the mass/spring system
2. List three places besides in springs where Hooke's law applies.
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS OF EVERYDAY PHENOMENA
Ch. 4 - Did Galileos work on motion precede in time that...Ch. 4 - Why did Aristotle believe that heavier objects...Ch. 4 - Aristotle believed that a force was necessary to...Ch. 4 - How did Aristotle explain the continued motion of...Ch. 4 - Did Galileo develop a more complete theory of...Ch. 4 - Two equal forces act on two different objects, one...Ch. 4 - A 3-kg block is observed to accelerate at a rate...Ch. 4 - Two equal-magnitude horizontal forces act on a box...Ch. 4 - Is it possible for the final temperature of the...Ch. 4 - Suppose that a bullet is fired from a rifle in...
Ch. 4 - Two equal forces act on an object in the...Ch. 4 - An object moving horizontally across a table is...Ch. 4 - A car goes around a curve traveling at constant...Ch. 4 - Is Newtons first law of motion explained by the...Ch. 4 - Is the mass of an object the same thing as its...Ch. 4 - The gravitational force acting on a lead ball is...Ch. 4 - The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is...Ch. 4 - Is mass a force? Explain.Ch. 4 - Two identical cans, one filled with lead shot and...Ch. 4 - A boy sits at rest on the floor. What two vertical...Ch. 4 - The engine of a car is part of the car and cannot...Ch. 4 - It is difficult to stop a car on an icy road...Ch. 4 - A ball hangs from a string attached to the...Ch. 4 - Would the tablecloth trick (see everyday...Ch. 4 - When a magician performs the tablecloth trick (see...Ch. 4 - A sprinter accelerates at the beginning of a...Ch. 4 - A mule is attempting to move a cart loaded with...Ch. 4 - The upward normal force exerted by the floor on a...Ch. 4 - A toy battery-powered tractor pushes a book across...Ch. 4 - If you get into an elevator on the top floor of a...Ch. 4 - If the elevator cable breaks and you find yourself...Ch. 4 - Two masses, m1 and m2, connected by a string, are...Ch. 4 - Two blocks with the same mass are connected by a...Ch. 4 - Suppose that a skydiver wears a specially...Ch. 4 - Prob. 35CQCh. 4 - Prob. 36CQCh. 4 - Prob. 1ECh. 4 - Prob. 2ECh. 4 - Prob. 3ECh. 4 - Prob. 4ECh. 4 - Prob. 5ECh. 4 - Prob. 6ECh. 4 - Prob. 7ECh. 4 - Prob. 8ECh. 4 - Prob. 9ECh. 4 - Prob. 10ECh. 4 - Prob. 11ECh. 4 - Prob. 12ECh. 4 - One of the authors of this text has a weight of...Ch. 4 - Prob. 14ECh. 4 - Prob. 15ECh. 4 - Prob. 16ECh. 4 - Prob. 17ECh. 4 - Prob. 18ECh. 4 - Prob. 19ECh. 4 - Prob. 1SPCh. 4 - Prob. 2SPCh. 4 - Prob. 3SPCh. 4 - Prob. 4SPCh. 4 - Prob. 5SPCh. 4 - Prob. 6SPCh. 4 - Prob. 7SP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. What is the spring constant of a spring that starts 10.0 cm long and extends to 11.4 cm with a 300 g mass hanging from it?arrow_forwardplease help me solve all parts of this question from physics. thanks so much in advance! :)))arrow_forwardA fluid with density 263 kg/m3 flows through a pipe of varying diameter and height. At location 1 the flow speed is 13.5 m/s and the diameter of the pipe is 7.4 cm down to location 2 the pipe diameter is 16.9 cm. Location 1 is 6.3 meters higher than location 2. What is the difference in pressure P2 - P1? Using units in Pascals and use g = 9.81 m/s2.arrow_forward
- The kitchen had a temperature 46 degrees Fahrenheit and was converted it to Kelvin. What is the correct number for this temperature (46 F) on the Kelvin scale?arrow_forwardWater is traveling at a speed of 0.65 m/s through a pipe with a cross-section radius of 0.23 meters. The water enters a section of pipe that has a smaller radius, only 0.11 meters. What is the speed of the water traveling in this narrower section of pipe?arrow_forwardA particular water pipe has a radius of 0.28 meters. If the pipe is completely filled with water, moving with average velocity 0.45 m/s, what is the flow rate of water through the pipe with units of cubic meters of water per second?arrow_forward
- Water is flowing through a horizontal pipe with two segments. In one segment, the water flows at a speed v1 = 4.52 m/s. In the second segment the speed of the water is v2 = 2.38 m/s. Based on Bernoulli's Principle, what is the difference in pressure (P2 - P1) between the two segments? Assume that the density of the water is 997 kg/m3 and give your answer as the number of Pascals (i.e. N/m2).arrow_forwardWater from the faucet is supplied to the hose at a rate of 0.00057 m3/s. At what speed (number of meters per second) does the water exit the nozzle if the cross sectional area of the narrow nozzle is 2.1 x 10-6 m2?arrow_forwardJason Fruits/Indiana University Research Communications Silver/ silver oxide Zinc zinc/oxidearrow_forward
- Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0 along a straight road. Car Q starts from rest at instant 1, and moves to the west with increasing speed. At instant 5, car Q has speed w0 relative to the road (w0 < v0). Instants 1-5 are separated by equal time intervals. At instant 3, cars P and Q are adjacent to one another (i.e., they have the same position). In the reference frame o f the road, at instant 3 i s the speed o f car Q greater than, less than, or equal to the speed of car P? Explain.arrow_forwardCar P moves to the west with constant speed v0 along a straight road. Car Q starts from rest at instant 1, and moves to the west with increasing speed. At instant 5, car Q has speed w0 relative to the road (w0 < v0). Instants 1-5 are separated by equal time intervals.arrow_forwardCar P moves to the west with constant speed v0 along a straight road. Car Q starts from rest at instant 1, and moves to the west with increasing speed. At instant 5, car Q has speed w0 relative to the road (w0 < v0). Instants 1-5 are separated by equal time intervals. Sketch and label a vector diagram illustrating the Galilean transformation of velocities that relates velocity of car P relative to the road, velocity of car Q relative to road, and velocity of car Q relative to car P at instant 3. In the frame of car P, at instant 3 is car Q moving to the west, moving to the east, or at rest? Explain.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's First Law of Motion: Mass and Inertia; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1XSyyjcEHo0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY