
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
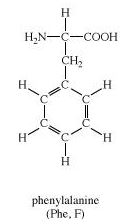
Phenylalanine is an α-amino acid with the formula Phenylalanine is an α-amino acid with the formula C9H11NO2.
Here, the benzyl group is substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of terminal hydrogen of alanine.
Lidocaine, also known as xylocaine and lignocaine, is a medication used to numb tissue in a specific area.
Formula: C14H22N2O
Answer to Problem 19VC
Here, Primary
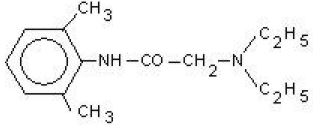
Here, amide group is present as functional group in this molecule.
Explanation of Solution
From the structure of phenylalanine, it is quite evident that the terminal hydrogen of alanine is replaced by a benzyl or phenyl group.
In this way, carbon forms a covalent bond with another carbon atom or other atoms.
-NH2 group and –COOH groups are present in Phenylalanine.
-NH and C=O (Amide) groups are present as functional groups in Lidocaine.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Please help with identifying these.arrow_forwardFor the reaction: CO2(g) + H2(g) --> CO (g) + H2O (g) Kc= 0.64 at 900 degrees celcius. if initially you start with 1.00 atmoshpere of carbon dioxide and 1 atmoshpere of hydrogen gas, what are the equilibrium partial pressuses of all species.arrow_forwardCan I please get this answered? With the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forward
- Draw the Hofmann product of the dehydroiodination of this alkyl iodide. ☐ : + Explanation Check esc F1 2 3 I 88 % 5 F5 I. X © tBuOK Click and drag to sta drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Te BI BB F6 W E R Y S H Karrow_forwardCan I please get help with this graph, if you could show exactly where it needs to pass through please.arrow_forwardDraw the condensed structure of 1,3-dihydroxy-2-pentanone. Explanation Check Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. Х C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of use +arrow_forward
- 0.500 moles of NOCl are placed into a 1.00 L vessesl at 700K and after the system comes to equilibrium, the consentration of NOCl is 0.440 M. Calculate the equilibrium constant Kc for the reaction: 2NOCL (g) --> 2NO (g) + Cl2 (g)arrow_forwardWhat is the hydronium ion concentration in a solution of water that has a hydroxide ion concentrationof 1.0 x 10-2 M?arrow_forwardIdentify conjugate acid-base pairs in the following reactions:HBr (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ H3O+ (aq) + Br- (aq) - OH (aq) + CH3COOH (aq) ⇌ H2O (l) + CH3COO- (aq)arrow_forward
- 4:45 PM Tue Apr 1 K 77% Problem 9 of 10 Submit Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting structure, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Then draw any missing organic intermediates or products for this reaction. Include all lone pairs in the structures. Ignore inorganic byproducts, counterions, and solvents. :0: H Select to Add Arrows HI CH3OH H+ ·HO CH3OH, H+ 0:0 H H Select to Add Arrows tion Versirate CH3OH, H* Select to Draw Productarrow_forwardCan I please get help with this graph? If you can show exactly where it needs to pass through.arrow_forwardG 1. PPh3, THF 2. 3. LiH, THF ' THF H Harrow_forward

 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


