
Concept explainers
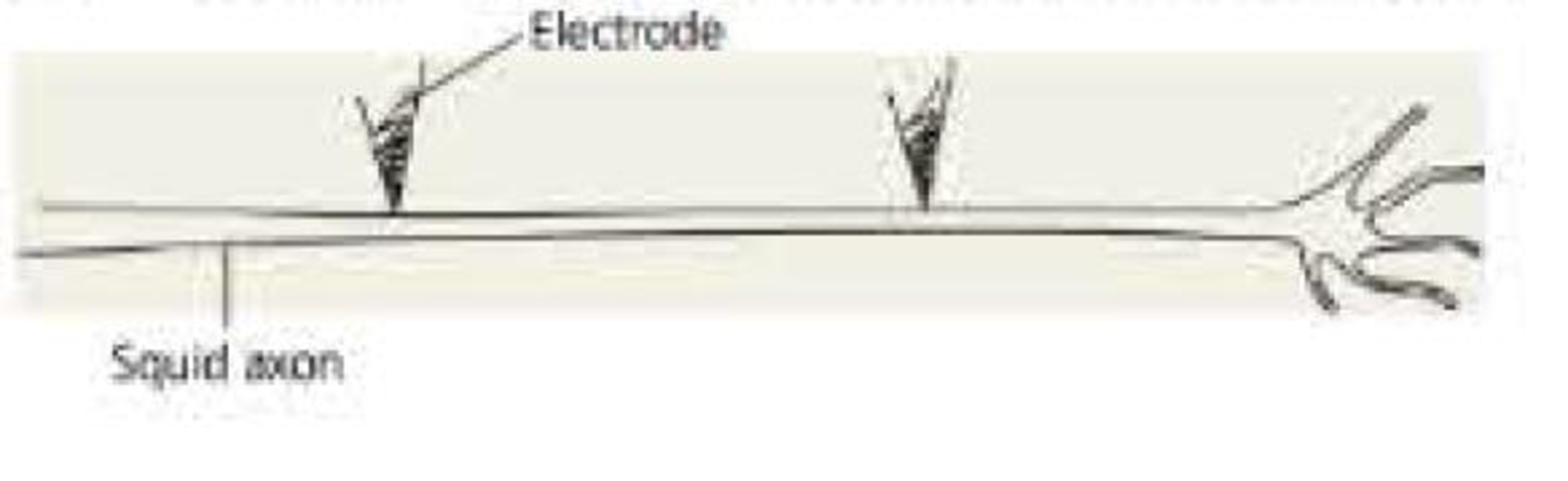
DRAW IT Suppose a researcher inserts a pair of electrodes at two different positions along the middle of an axon dissected out of a squid. By applying a depolarizing stimulus, the researcher brings the plasma membrane at both positions to threshold. Using the drawing below as a model, create one or more drawings that illustrate where each action potential would terminate.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 37 Solutions
Campbell Biology in Focus, Books a la Carte Edition; Modified Mastering Biology with Pearson eText - ValuePack Access Card - for Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
EBK INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
SEELEY'S ANATOMY+PHYSIOLOGY
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
- AaBbCc X AaBbCc individuals are crossed. What is the probability of their offspring having a genotype AABBCC?arrow_forwardcircle a nucleotide in the imagearrow_forward"One of the symmetry breaking events in mouse gastrulation requires the amplification of Nodal on the side of the embryo opposite to the Anterior Visceral Endoderm (AVE). Describe one way by which Nodal gets amplified in this region." My understanding of this is that there are a few ways nodal is amplified though I'm not sure if this is specifically occurs on the opposite side of the AVE. 1. pronodal cleaved by protease -> active nodal 2. Nodal -> BMP4 -> Wnt-> nodal 3. Nodal-> Nodal, Fox1 binding site 4. BMP4 on outside-> nodal Are all of these occuring opposite to AVE?arrow_forward
- If four babies are born on a given day What is the chance all four will be girls? Use genetics lawsarrow_forwardExplain each punnet square results (genotypes and probabilities)arrow_forwardGive the terminal regression line equation and R or R2 value: Give the x axis (name and units, if any) of the terminal line: Give the y axis (name and units, if any) of the terminal line: Give the first residual regression line equation and R or R2 value: Give the x axis (name and units, if any) of the first residual line : Give the y axis (name and units, if any) of the first residual line: Give the second residual regression line equation and R or R2 value: Give the x axis (name and units, if any) of the second residual line: Give the y axis (name and units, if any) of the second residual line: a) B1 Solution b) B2 c)hybrid rate constant (λ1) d)hybrid rate constant (λ2) e) ka f) t1/2,absorb g) t1/2, dist h) t1/2, elim i)apparent central compartment volume (V1,app) j) total AUC (short cut method) k) apparent volume of distribution based on AUC (VAUC,app) l)apparent clearance (CLapp) m) absolute bioavailability of oral route (need AUCiv…arrow_forward
- You inject morpholino oligonucleotides that inhibit the translation of follistatin, chordin, and noggin (FCN) at the 1 cell stage of a frog embryo. What is the effect on neurulation in the resulting embryo? Propose an experiment that would rescue an embryo injected with FCN morpholinos.arrow_forwardParticipants will be asked to create a meme regarding a topic relevant to the department of Geography, Geomatics, and Environmental Studies. Prompt: Using an online art style of your choice, please make a meme related to the study of Geography, Environment, or Geomatics.arrow_forwardPlekhg5 functions in bottle cell formation, and Shroom3 functions in neural plate closure, yet the phenotype of injecting mRNA of each into the animal pole of a fertilized egg is very similar. What is the phenotype, and why is the phenotype so similar? Is the phenotype going to be that there is a disruption of the formation of the neural tube for both of these because bottle cell formation is necessary for the neural plate to fold in forming the neural tube and Shroom3 is further needed to close the neural plate? So since both Plekhg5 and Shroom3 are used in forming the neural tube, injecting the mRNA will just lead to neural tube deformity?arrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





