
Laplace Transforms
In the last few chapters, we have looked at several ways to use
The Laplace transform is defined in terms of an integral as
7
e""
ft
Note that the input to a Laplace transform is a function of time, /(/), and the output is a function of frequency, F(j), Although many real-world examples require the use of
Let's stan with a simple example. Here we calculate the Laplace transform of /(f) = t. We have
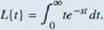
This is an improper integral, so we express it in terms of a limit, which gives
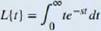
Now we use integration by pans to evaluate the integral. Note that we are integrating with respect to t, so we treat the variable s as a constant. We have
u—t dv — dt
du=dt v
— — ye_ir.
Then we obtain
= + +
= ~K + °1 -
= JinL[[-i,-]-±[e--lj]
- c + c
= 0-0 + -L
s“
_x
2* s
1. Calculate the Laplace transform of /(/) = 1.
3.Calculate the Laplace transform of /(/) = : (Note, you will have to integrate by parts twice.)
Laplace transforms are often used to solve differential equations. Differential equations are not covered in detail until later in this book; but, for now, let’s look at the relationship between the Laplace transform of a function and the Laplace transform of its derivative.
Let’s start with the definition of the Laplace transform. We have
WW! = r™ r'
= lim / e~st fifth.
4.Use integration by parts to evaluate Jjm^ e~sl fifth. (Let « = /{/) and dv — e '!dt.) After integrating by parts and evaluating the limit, you should see that
Then,
Thus, differentiation in the time domain simplifies to multiplication by s in the frequency domain.
The final thing we look at in this project is how the Laplace transforms of fit] and its antiderivative are
related. Let g(r) — f(u}dii. Then,
¦'o
lim /
:-* caj" 5.Use integration by parts to evaluate hrn^y e ’ g(t)dl. (Let u = gif) and dv = e dt. Note, by the way,
that we have defined gif, du — fifth.)
As you might expect, you should see that
L|^(r)| = |-L[/(/)i.
Integration in the time domain simplifies to division by s in ±e frequency domain.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Calculus Volume 2
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
- Question 1: Let X be a random variable with p.m.f (|x| +1)² x= -2, -1, 0, 1,2 f(x) = C 0, O.W 1. The value of c. 2. The c.d.f. 3. E(X). 4. E(2x+3). 5. E(X²). 6. E(3x²+4). 7. E(X(3X+4)). 8. Var(X). 9. Var (6-3X). 10. Find the m.g.f of the random variable Xarrow_forwardI need help explaining on this examplearrow_forwardProve that 1) | RxX (T) | << = (R₁ " + R$) 2) find Laplalse trans. of Normal dis: 3) Prove thy t /Rx (z) | < | Rx (0)\ 4) show that evary algebra is algebra or not.arrow_forward
- = 5 37 A 4 8 0.5 06 9arrow_forwardFor each of the time series, construct a line chart of the data and identify the characteristics of the time series (that is, random, stationary, trend, seasonal, or cyclical). Month Number (Thousands)Dec 1991 65.60Jan 1992 71.60Feb 1992 78.80Mar 1992 111.60Apr 1992 107.60May 1992 115.20Jun 1992 117.80Jul 1992 106.20Aug 1992 109.90Sep 1992 106.00Oct 1992 111.80Nov 1992 84.50Dec 1992 78.60Jan 1993 70.50Feb 1993 74.60Mar 1993 95.50Apr 1993 117.80May 1993 120.90Jun 1993 128.50Jul 1993 115.30Aug 1993 121.80Sep 1993 118.50Oct 1993 123.30Nov 1993 102.30Dec 1993 98.70Jan 1994 76.20Feb 1994 83.50Mar 1994 134.30Apr 1994 137.60May 1994 148.80Jun 1994 136.40Jul 1994 127.80Aug 1994 139.80Sep 1994 130.10Oct 1994 130.60Nov 1994 113.40Dec 1994 98.50Jan 1995 84.50Feb 1995 81.60Mar 1995 103.80Apr 1995 116.90May 1995 130.50Jun 1995 123.40Jul 1995 129.10Aug 1995…arrow_forwardFor each of the time series, construct a line chart of the data and identify the characteristics of the time series (that is, random, stationary, trend, seasonal, or cyclical). Year Month Units1 Nov 42,1611 Dec 44,1862 Jan 42,2272 Feb 45,4222 Mar 54,0752 Apr 50,9262 May 53,5722 Jun 54,9202 Jul 54,4492 Aug 56,0792 Sep 52,1772 Oct 50,0872 Nov 48,5132 Dec 49,2783 Jan 48,1343 Feb 54,8873 Mar 61,0643 Apr 53,3503 May 59,4673 Jun 59,3703 Jul 55,0883 Aug 59,3493 Sep 54,4723 Oct 53,164arrow_forward
- Consider the table of values below. x y 2 64 3 48 4 36 5 27 Fill in the right side of the equation y= with an expression that makes each ordered pari (x,y) in the table a solution to the equation.arrow_forwardsolving for xarrow_forwardConsider the table of values below. x y 2 63 3 70 4 77 5 84 Fill in the right side of the equation y= with an expression that makes each ordered pari (x,y) in the table a solution to the equation.arrow_forward
- find the value of each variablearrow_forwardConsider the following system of equations, Ax=b : x+2y+3z - w = 2 2x4z2w = 3 -x+6y+17z7w = 0 -9x-2y+13z7w = -14 a. Find the solution to the system. Write it as a parametric equation. You can use a computer to do the row reduction. b. What is a geometric description of the solution? Explain how you know. c. Write the solution in vector form? d. What is the solution to the homogeneous system, Ax=0?arrow_forward2. Find a matrix A with the following qualities a. A is 3 x 3. b. The matrix A is not lower triangular and is not upper triangular. c. At least one value in each row is not a 1, 2,-1, -2, or 0 d. A is invertible.arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
