
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
To show there is always unstable fixed point at
Concept Introduction:
To check the stability at any point, differentiate the equation and put the value in it.
For small value of x predation is very weak, thus the budworm population increases exponentially, when
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
Instability at
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given expression is dimensionless for budworm population growth
Where
To check the stability of the equation at
By substituting
Given condition is
This result is also verified by plotting graph for equation
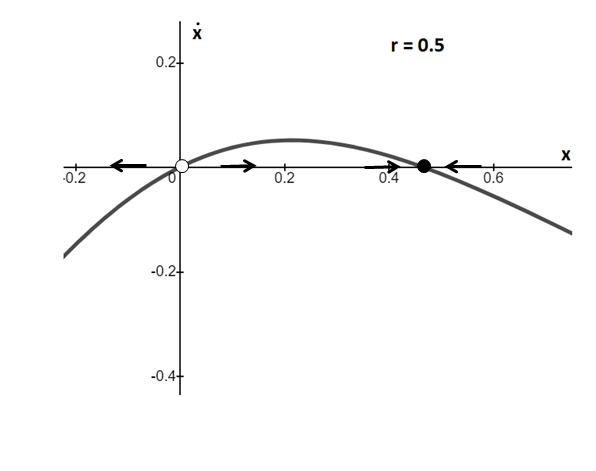
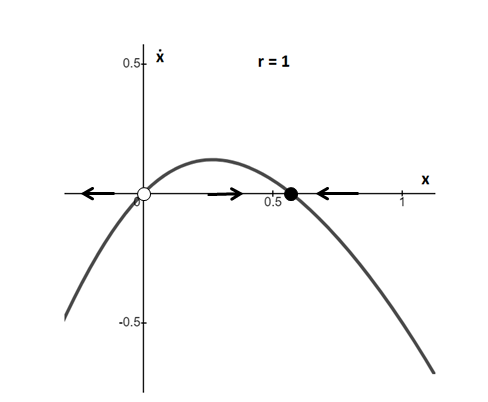
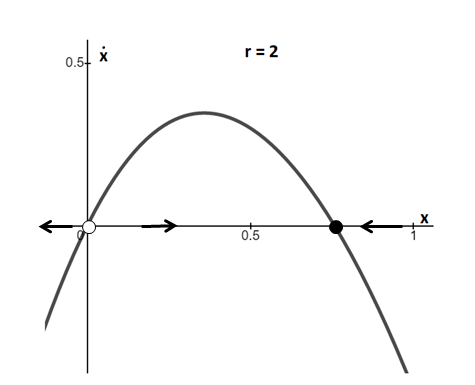
From the above graphs, it is clear that for
For the given type of system, there is always an unstable fixed point at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos
- 2) Prove that for all integers n > 1. dn 1 (2n)! 1 = dxn 1 - Ꮖ 4 n! (1-x)+/arrow_forwardDefinition: A topology on a set X is a collection T of subsets of X having the following properties. (1) Both the empty set and X itself are elements of T. (2) The union of an arbitrary collection of elements of T is an element of T. (3) The intersection of a finite number of elements of T is an element of T. A set X with a specified topology T is called a topological space. The subsets of X that are members of are called the open sets of the topological space.arrow_forwardDefinition: A topology on a set X is a collection T of subsets of X having the following properties. (1) Both the empty set and X itself are elements of T. (2) The union of an arbitrary collection of elements of T is an element of T. (3) The intersection of a finite number of elements of T is an element of T. A set X with a specified topology T is called a topological space. The subsets of X that are members of are called the open sets of the topological space.arrow_forward
- 3) Let a1, a2, and a3 be arbitrary real numbers, and define an = 3an 13an-2 + An−3 for all integers n ≥ 4. Prove that an = 1 - - - - - 1 - - (n − 1)(n − 2)a3 − (n − 1)(n − 3)a2 + = (n − 2)(n − 3)aı for all integers n > 1.arrow_forwardDefinition: A topology on a set X is a collection T of subsets of X having the following properties. (1) Both the empty set and X itself are elements of T. (2) The union of an arbitrary collection of elements of T is an element of T. (3) The intersection of a finite number of elements of T is an element of T. A set X with a specified topology T is called a topological space. The subsets of X that are members of are called the open sets of the topological space.arrow_forwardDefinition: A topology on a set X is a collection T of subsets of X having the following properties. (1) Both the empty set and X itself are elements of T. (2) The union of an arbitrary collection of elements of T is an element of T. (3) The intersection of a finite number of elements of T is an element of T. A set X with a specified topology T is called a topological space. The subsets of X that are members of are called the open sets of the topological space.arrow_forward
- Definition: A topology on a set X is a collection T of subsets of X having the following properties. (1) Both the empty set and X itself are elements of T. (2) The union of an arbitrary collection of elements of T is an element of T. (3) The intersection of a finite number of elements of T is an element of T. A set X with a specified topology T is called a topological space. The subsets of X that are members of are called the open sets of the topological space.arrow_forward1) If f(x) = g¹ (g(x) + a) for some real number a and invertible function g, show that f(x) = (fo fo... 0 f)(x) = g¯¹ (g(x) +na) n times for all integers n ≥ 1.arrow_forwardimage belowarrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning


