
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781337553292
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 35, Problem 3P
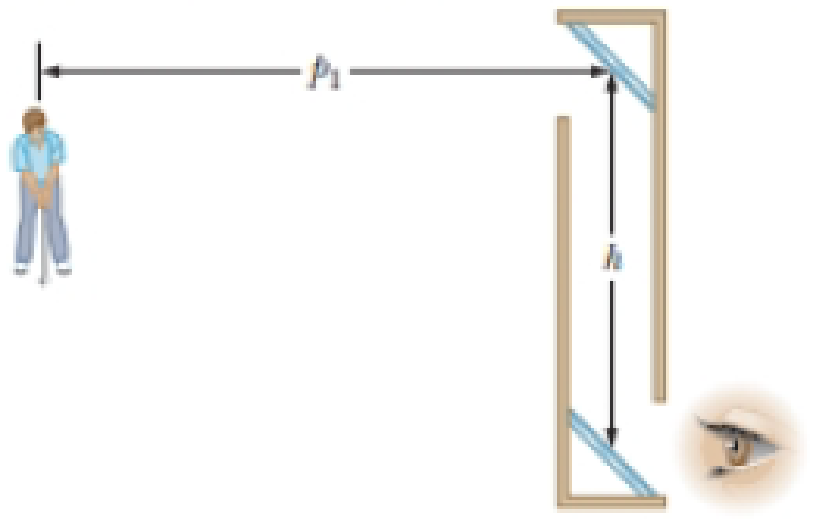
A periscope (Fig. P35.3) is useful for viewing objects that cannot be seen directly. It can be used in submarines and when watching golf matches or parades from behind a crowd of people. Suppose the object is a distance p1 from the upper mirror and the centers of the two flat mirrors are separated by a distance h. (a) What is the distance of the final image from the lower mirror? (b) Is the final image real or virtual? (c) Is it upright or inverted? (d) What is its magnification? (e) Does it appear to be left-right reversed?
Figure P35.3
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Please don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solution
how would i express force in vector form I keep getting a single number
please help me solve this questions. show all calculations and a good graph too :)
Chapter 35 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Ch. 35.1 - Prob. 35.1QQCh. 35.2 - You wish to start a fire by reflecting sunlight...Ch. 35.2 - Consider the image in the mirror in Figure 35.14....Ch. 35.3 - Prob. 35.4QQCh. 35.3 - Prob. 35.5QQCh. 35.4 - What is the focal length of a pane of window...Ch. 35.6 - Prob. 35.7QQCh. 35 - (a) Does your bathroom mirror show you older or...Ch. 35 - Two flat mirrors have their reflecting surfaces...Ch. 35 - A periscope (Fig. P35.3) is useful for viewing...
Ch. 35 - Prob. 4PCh. 35 - Prob. 5PCh. 35 - Prob. 6PCh. 35 - An object of height 2.00 cm is placed 30.0 cm from...Ch. 35 - Prob. 8PCh. 35 - Prob. 9PCh. 35 - A concave spherical mirror has a radius of...Ch. 35 - Prob. 11PCh. 35 - Prob. 12PCh. 35 - Prob. 13PCh. 35 - Prob. 14PCh. 35 - Prob. 15PCh. 35 - Prob. 16PCh. 35 - One end of a long glass rod (n = 1.50) is formed...Ch. 35 - Prob. 18PCh. 35 - Prob. 19PCh. 35 - Figure P35.20 (page 958) shows a curved surface...Ch. 35 - To dress up your dorm room, you have purchased a...Ch. 35 - You are working for a solar energy company. Your...Ch. 35 - Prob. 23PCh. 35 - An objects distance from a converging lens is 5.00...Ch. 35 - Prob. 25PCh. 35 - Prob. 26PCh. 35 - A converging lens has a focal length of 10.0 cm....Ch. 35 - Prob. 28PCh. 35 - Prob. 29PCh. 35 - In Figure P35.30, a thin converging lens of focal...Ch. 35 - Prob. 31PCh. 35 - Prob. 32PCh. 35 - Two rays traveling parallel to the principal axis...Ch. 35 - Prob. 34PCh. 35 - Prob. 35PCh. 35 - Prob. 36PCh. 35 - Prob. 37PCh. 35 - Prob. 38PCh. 35 - Prob. 39PCh. 35 - The intensity I of the light reaching the CCD in a...Ch. 35 - Prob. 41PCh. 35 - Prob. 42PCh. 35 - A simple model of the human eye ignores its lens...Ch. 35 - Prob. 44APCh. 35 - Prob. 45APCh. 35 - The distance between an object and its upright...Ch. 35 - Prob. 47APCh. 35 - Two converging lenses having focal lengths of f1 =...Ch. 35 - Two lenses made of kinds of glass having different...Ch. 35 - Prob. 50APCh. 35 - Prob. 51APCh. 35 - Prob. 52APCh. 35 - Prob. 53APCh. 35 - In many applications, it is necessary to expand or...Ch. 35 - Prob. 55APCh. 35 - A zoom lens system is a combination of lenses that...Ch. 35 - Prob. 57CPCh. 35 - Prob. 58CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the force (in N) on the 2.0 μC charge placed at the center of the square shown below? (Express your answer in vector form.) 5.0 με 4.0 με 2.0 με + 1.0 m 1.0 m -40 με 2.0 μCarrow_forwardWhat is the force (in N) on the 5.4 µC charge shown below? (Express your answer in vector form.) −3.1 µC5.4 µC9.2 µC6.4 µCarrow_forwardAn ideal gas in a sealed container starts out at a pressure of 8900 N/m2 and a volume of 5.7 m3. If the gas expands to a volume of 6.3 m3 while the pressure is held constant (still at 8900 N/m2), how much work is done by the gas? Give your answer as the number of Joules.arrow_forward
- The outside temperature is 25 °C. A heat engine operates in the environment (Tc = 25 °C) at 50% efficiency. How hot does it need to get the high temperature up to in Celsius?arrow_forwardGas is compressed in a cylinder creating 31 Joules of work on the gas during the isothermal process. How much heat flows from the gas into the cylinder in Joules?arrow_forwardThe heat engine gives 1100 Joules of energy of high temperature from the burning gasoline by exhausting 750 Joules to low-temperature . What is the efficiency of this heat engine in a percentage?arrow_forward
- L₁ D₁ L₂ D2 Aluminum has a resistivity of p = 2.65 × 10 8 2. m. An aluminum wire is L = 2.00 m long and has a circular cross section that is not constant. The diameter of the wire is D₁ = 0.17 mm for a length of L₁ = 0.500 m and a diameter of D2 = 0.24 mm for the rest of the length. a) What is the resistance of this wire? R = Hint A potential difference of AV = 1.40 V is applied across the wire. b) What is the magnitude of the current density in the thin part of the wire? Hint J1 = c) What is the magnitude of the current density in the thick part of the wire? J₂ = d) What is the magnitude of the electric field in the thin part of the wire? E1 = Hint e) What is the magnitude of the electric field in the thick part of the wire? E2 =arrow_forwardplease helparrow_forwardA cheetah spots a gazelle in the distance and begins to sprint from rest, accelerating uniformly at a rate of 8.00 m/s^2 for 5 seconds. After 5 seconds, the cheetah sees that the gazelle has escaped to safety, so it begins to decelerate uniformly at 6.00 m/s^2 until it comes to a stop.arrow_forward
- A projectile is fired with an initial speed of 40.2 m/s at an angle of 35.0 degree above the horizontal on a long flat firing range. Determine. please help and show work for them so i can understand.arrow_forwardpls helparrow_forwardJ K L The graph in the figure shows the position of an object as a function of time. The letters H-L represent particular moments of time. At which moments shown (H, I, etc.) is the speed of the object the greatest? + Position H I K Timearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Convex and Concave Lenses; Author: Manocha Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CJ6aB5ULqa0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY