
A radio station operating at 88.5 MHz broadcasts from two identical antennas at the same elevation but separated by a 9.0-m horizontal distance d. Fig. 34–28. A maximum signal is found along the midline, perpendicular to d at its midpoint and extending horizontally in both directions. If the midline is taken as 0°, at what other angle(s) θ is a maximum signal detected? A minimum signal? Assume all measurements are made much farther than 9.0 m from the antenna towers.
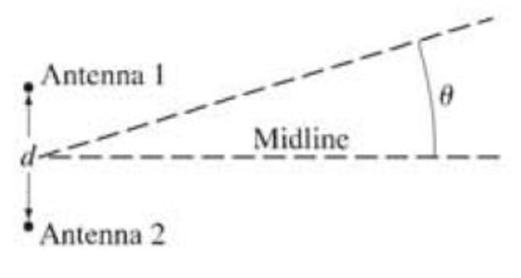
FIGURE 34–28
Problem 48.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 34 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
- Part 2 - Geometry and Trigonometry 1. Line B touches the circle at a single point. Line A extends radially through the center of the circle. A B (a) Which line is tangential to the circumference of the circle? (b) What is the angle between lines A and B. 2. In the figure below what is the angle C? 30 45 3. In the figure below what is the value of the angle 0? 30° 4. In the figure below what is the value of the angle 0? A 30°arrow_forwardDetails solution No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the problem correctly please.Thank you!!arrow_forward
- Will you please walk me through the calculations in more detail for solving this problem? I am a bit rusty on calculus and confused about the specific steps of the derivation: https://www.bartleby.com/solution-answer/chapter-3-problem-15e-modern-physics-2nd-edition/9780805303087/7cf8c31d-9476-46d5-a5a9-b897b16fe6fcarrow_forwardplease help with the abstract. Abstract - This document outlines the format of the lab report and describes the Excel assignment. The abstract should be a short paragraph that very briefly includes the experiment objective, method, result and conclusion. After skimming the abstract, the reader should be able to decide whether they want to keep reading your work. Both the format of the report and the error analysis are to be followed. Note that abstract is not just the introduction and conclusion combined, but rather the whole experiment in short including the results. I have attacted the theory.arrow_forwardUsing the Experimental Acceleration due to Gravity values from each data table, Data Tables 1, 2, and 3; determine the Standard Deviation, σ, mean, μ, variance, σ2 and the 95% Margin of Error (Confidence Level) Data: Ex. Acc. 1: 12.29 m/s^2. Ex. Acc. 2: 10.86 m/s^2, Ex. Acc. 3: 9.05 m/s^2arrow_forward
- In the Super Smash Bros. games the character Yoshi’s has a “ground pound” down special move where he launches himself downward to attack an enemy beneath him. A) If Yoshi flings himself downwards at 9.76 miles per hour to hit an enemy 10.5 m below him, how fast is Yoshi traveling when he hits the enemy? 1 mile = 1609 m B) How much time does it take Yoshi to hit the enemy beneath him?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardSolve No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- Can someone help me solve this thank you.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward1.62 On a training flight, a Figure P1.62 student pilot flies from Lincoln, Nebraska, to Clarinda, Iowa, next to St. Joseph, Missouri, and then to Manhattan, Kansas (Fig. P1.62). The directions are shown relative to north: 0° is north, 90° is east, 180° is south, and 270° is west. Use the method of components to find (a) the distance she has to fly from Manhattan to get back to Lincoln, and (b) the direction (relative to north) she must fly to get there. Illustrate your solutions with a vector diagram. IOWA 147 km Lincoln 85° Clarinda 106 km 167° St. Joseph NEBRASKA Manhattan 166 km 235° S KANSAS MISSOURIarrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning





