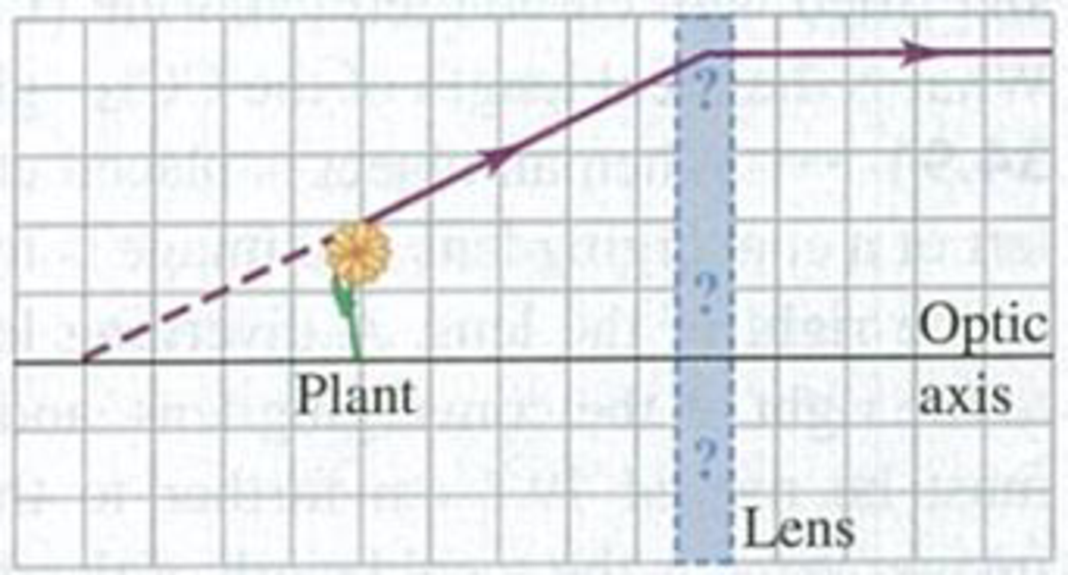
Problem Q34.1DQ: A spherical mirror is cut in half horizontally. Will an image be formed by the bottom half of the... Problem Q34.2DQ: For the situation shown in Fig. 34.3, is the image distance s positive or negative? Is the image... Problem Q34.3DQ: The laws of optics also apply to electromagnetic waves invisible to the eye. A satellite TV dish is... Problem Q34.4DQ: Explain why the focal length of a plane mirror is infinite, and explain what it means for the focal... Problem Q34.5DQ: If a spherical mirror is immersed in water, does its focal length change? Explain. Problem Q34.6DQ: For what range of object positions does a concave spherical mirror form a real image? What about a... Problem Q34.7DQ: When a room has mirrors on two opposite walls, an infinite series of reflections can be seen.... Problem Q34.8DQ: For a spherical mirror, if s = f, then s = , and the lateral magnification m is infinite. Does this... Problem Q34.9DQ: You may have noticed a small convex mirror next to your banks ATM. Why is this mirror convex, as... Problem Q34.10DQ: A student claims that she can start a fire on a sunny day using just the suns rays and a concave... Problem Q34.11DQ: A person looks at his reflection in the concave side of a shiny spoon. Is it right side up or... Problem Q34.12DQ: In Example 34.4 (Section 34.2), there appears to be an ambiguity for the case s = 10 cm as to... Problem Q34.13DQ: Suppose that in the situation of Example 34.7 of Section 34.3 (see Fig. 34.26) a vertical arrow 2.00... Problem Q34.14DQ: The bottom of the passenger-side mirror on your car notes, Objects in mirror are closer than they... Problem Q34.15DQ: How could you very quickly make an approximate measurement of the focal length of a converging lens?... Problem Q34.16DQ: The focal length of a simple lens depends on the color (wavelength) of light passing through it.... Problem Q34.17DQ: When a converging lens is immersed in water, does its focal length increase or decrease in... Problem Q34.18DQ: A spherical air bubble in water can function as a lens. Is it a converging or diverging lens? How is... Problem Q34.19DQ: Can an image formed by one reflecting or refracting surface serve as an object for a second... Problem Q34.20DQ: If a piece of photographic film is placed at the location of a real image, the film will record the... Problem Q34.21DQ: According to the discussion in Section 34.2, light rays are reversible. Are the formulas in the... Problem Q34.22DQ: Youve entered a survival contest that will include building a crude telescope. You are given a large... Problem Q34.23DQ: BIO You cant see clearly underwater with the naked eye, but you can if you wear a face mask or... Problem Q34.24DQ Problem 34.1E: A candle 4.85 cm tall is 39.2 cm to the left of a plane mirror. Where is the image formed by the... Problem 34.2E: The image of a tree just covers the length of a plane mirror 4.00 cm tall when the mirror is held... Problem 34.3E: A pencil that is 9.0 cm long is held perpendicular to the surface of a plane mirror with the tip of... Problem 34.4E: A concave mirror has a radius of curvature of 34.0 cm. (a) What is its focal length? (b) If the... Problem 34.5E: An object 0.600 cm tall is placed 16.5 cm to the left of the vertex of a concave spherical mirror... Problem 34.6E: An object 0.600 cm tall is placed 16.5 cm to the left of the vertex of a concave spherical mirror... Problem 34.7E: The diameter of Mars is 6794 km, and its minimum distance from the earth is 5.58 107 km. When Mars... Problem 34.8E: An object is 18.0 cm from the center of a spherical silvered-glass Christmas tree ornament 6.00 cm... Problem 34.9E Problem 34.10E: You hold a spherical salad bowl 60 cm in front of your face with the bottom of the bowl facing you.... Problem 34.11E: A spherical, concave shaving mirror has a radius of curvature of 32.0 cm. (a) What is the... Problem 34.12E: For a concave spherical mirror that has focal length f = +18.0 cm, what is the distance of an object... Problem 34.13E: Dental Mirror. A dentist uses a curved mirror to view teeth on the upper side of the mouth. Suppose... Problem 34.14E: For a convex spherical mirror that has focal length f = 12.0 cm, what is the distance of an object... Problem 34.15E: The thin glass shell shown in Fig. E34.15 has a spherical shape with a radius of curvature of 12.0... Problem 34.16E: A tank whose bottom is a minor is filled with water to a depth of 20.0 cm. A small fish floats... Problem 34.17E: A speck of dirt is embedded 3.50 cm below the surface of a sheet of ice (n = 1.309). What is its... Problem 34.18E: A transparent liquid fills a cylindrical tank to a depth of 3.60 m. There is air above the liquid.... Problem 34.19E: A person swimming 0.80 m below the surface of the water in a swimming pool looks at the diving board... Problem 34.20E Problem 34.21E: A Spherical Fish Bowl. A small tropical fish is at the center of a water-tilled, spherical fish bowl... Problem 34.22E: The left end of a long glass rod 6.00 cm in diameter has a convex hemispherical surface 3.00 cm in... Problem 34.23E Problem 34.24E: The left end of a long glass rod 8.00 cm in diameter, with an index of refraction of 1.60, is ground... Problem 34.25E: Repeat Exercise 34.24 for the case in which the end of the rod is ground to a concave hemispherical... Problem 34.26E: The glass rod of Exercise 34.25 is immersed in a liquid. An object 14.0 cm from the vertex of the... Problem 34.27E: An insect 3.75 mm tall is placed 22.5 cm to the left of a thin planoconvex lens. The left surface of... Problem 34.28E: A lens forms an image of an object. The object is 16.0 cm from the lens. The image is 12.0 cm from... Problem 34.29E: A converging meniscus lens (see Fig. 34.32a) with a refractive index of 1.52 has spherical surfaces... Problem 34.30E: A converging lens with a focal length of 70.0 cm forms an image of a 3.20-cm-tall real object that... Problem 34.31E: A converging lens forms an image of an 8.00-mm-tall real object. The image is 12.0 cm lo the left of... Problem 34.32E: A photographic slide is to the left of a lens. The lens projects an image of the slide onto a wall... Problem 34.33E: A double-convex thin lens has surfaces with equal radii of curvature of magnitude 2.50 cm. Using... Problem 34.34E: A converging lens with a focal length of 9.00 cm forms an image of a 4.00-mm-tall real object that... Problem 34.35E: BIO The Cornea As a Simple Lens. The cornea behaves as a thin lens of focal length approximately 1.8... Problem 34.36E: A lensmaker wants to make a magnifying glass from glass that has an index of refraction n = 1.55 and... Problem 34.37E: For each thin lens shown in Fig. E34.37, calculate the location of the image of an object that is... Problem 34.38E: A converging lens with a focal length of 12.0 cm forms a virtual image 8.00 mm tall, 17.0 cm to the... Problem 34.39E: Repeat Exercise 34.38 for the case in which the lens is diverging, with a focal length of 48.0 cm. Problem 34.40E: An object is 16.0 cm to the left of a lens. The lens forms an image 36.0 cm to the right of the... Problem 34.41E: Combination of Lenses I. A 1.20-cm-tall object is 50.0 cm to the left of a converging lens of focal... Problem 34.42E: Combination of Lenses II. Repeat Exercise 34.41 using the same lenses except for the following... Problem 34.43E: Combination of Lenses III. Two thin lenses with a focal length of magnitude 12.0 cm, the first... Problem 34.44E: BIO The Lens or the Eye. The crystalline lens of the human eye is a double-convex lens made of... Problem 34.45E: A camera lens has a focal length of 200 mm. How far from the lens should the subject for the photo... Problem 34.46E: You wish to project the image of a slide on a screen 9.00 m from the lens of a slide projector. (a)... Problem 34.47E: When a camera is focused, the lens is moved away from or toward the digital image sensor. If you... Problem 34.48E: Zoom Lens. Consider the simple model of the zoom lens shown in Fig. 34.43a. The converging lens has... Problem 34.49E: A camera lens has a focal length of 180.0 mm and an aperture diameter of 16.36 mm. (a) What is the... Problem 34.50E: BIO Curvature of the Cornea. In a simplified model of the human eye, the aqueous and vitreous humors... Problem 34.51E: BIO (a) Where is the near point of an eye for which a contact lens with a power of +2.75 diopters is... Problem 34.52E: BIO Contact Lenses. Contact lenses are placed right on the eyeball, so the distance from the eye to... Problem 34.53E: BIO Ordinary Glasses. Ordinary glasses are worn in front of the eye and usually 2.0 cm in front of... Problem 34.54E: BIO A person can see clearly up close but cannot focus on objects beyond 75.0 cm. She opts for... Problem 34.55E: BIO If the person in Exercise 34.54 chooses ordinary glasses over contact lenses, what power lens... Problem 34.56E: A thin lens with a focal length of 6.00 cm is used as a simple magnifier. (a) What angular... Problem 34.57E: The focal length of a simple magnifier is 8.00 cm. Assume the magnifier is a thin lens placed very... Problem 34.58E: You want to view through a magnifier an insect that is 2.00 mm long. If the insect is to be at the... Problem 34.59E: The focal length of the eyepiece of a certain microscope is 18.0 mm. The focal length of the... Problem 34.60E: Resolution of a Microscope. The image formed by a microscope objective with a focal length of 5.00... Problem 34.61E: A telescope is constructed from two lenses with focal lengths of 95.0 cm and 15.0 cm, the 95.0-cm... Problem 34.62E: The eyepiece of a refracting telescope (see Fig. 34.53) has a focal length of 9.00 cm. The distance... Problem 34.63E: A reflecting telescope (Fig. E34.63) is to be made by using a spherical mirror with a radius of... Problem 34.64P: What is the size of the smallest vertical plane mirror in which a woman of height h can see her... Problem 34.65P: If you run away from a plane mirror at 3.60 m/s, at what speed does your image move away from you? Problem 34.66P: Where must you place an object in front of a concave mirror with radius R so that the image is erect... Problem 34.67P Problem 34.68P: A light bulb is 3.00 m from a wall. You are to use a concave mirror to project an image of the bulb... Problem 34.69P: CP CALC You are in your car driving on a highway at 25 m/s when you glance in the passenger-side... Problem 34.70P: A layer of benzene (n = 1.50) that is 4.20 cm deep floats on water (n = 1.33) that is 5.70 cm deep.... Problem 34.71P: Rear-View Mirror. A mirror on the passenger side of your car is convex and has a radius of curvature... Problem 34.72P: Figure P34.72 shows a small plant near a thin lens. The ray shown is one of the principal rays for... Problem 34.73P: Pinhole Camera. A pinhole camera is just a rectangular box with a tiny hole in one face. The film is... Problem 34.74P: A microscope is focused on the upper surface of a glass plate. A second plate is then placed over... Problem 34.75P: What should be the index of refraction of a transparent sphere in order for paraxial rays from an... Problem 34.76P: A Glass Rod. Both ends of a glass rod with index of refraction 1.60 are ground and polished to... Problem 34.77P: (a) You want to use a lens with a focal length of 35.0 cm to produce a real image of an object, with... Problem 34.78P: Autocollimation. You place an object alongside a white screen, and a plane mirror is 60.0 cm to the... Problem 34.79P: A lens forms a real image that is 214 cm away from the object and 223 times its height. What kind of... Problem 34.80P: Figure P34.80 shows an object and its image formed by a thin lens. (a) What is the focal length of... Problem 34.81P: Figure P34.81 shows an object and its image formed by a thin lens. (a) What is the focal length of... Problem 34.82P: A transparent rod 30.0 cm long is cut flat at one end and rounded to a hemispherical surface of... Problem 34.83P: BIO Focus of the Eye. The cornea of the eye has a radius of curvature of approximately 0.50 cm. and... Problem 34.84P: The radii of curvature of the surfaces of a thin converging meniscus lens are R1 = +12.0 cm and R2 =... Problem 34.85P: An object to the left of a lens is imaged by the lens on a screen 30.0 cm to the right of the lens.... Problem 34.86P: An object is placed 22.0 cm from a screen. (a) At what two points between object and screen may a... Problem 34.87P: A convex mirror and a concave mirror are placed on the same optic axis, separated by a distance L =... Problem 34.88P: A screen is placed a distance d to the right of an object. A converging lens with focal length f is... Problem 34.89P: As shown in Fig. P34.89, the candle is at the center of curvature of the concave mirror, whose focal... Problem 34.90P: Two Lenses in Contact. (a) Prove that when two thin lenses with focal lengths f1, and f2 are placed... Problem 34.91P: When an object is placed at the proper distance to the left of a converging lens, the image is... Problem 34.92P: (a) Repeat the derivation of Eq. (34.19) for the case in which the lens is totally immersed in a... Problem 34.93P: A convex spherical mirror with a focal length of magnitude 24.0 cm is placed 20.0 cm to the left of... Problem 34.94P: BIO What Is the Smallest Thing We Can See? The smallest object we can resolve with our eye is... Problem 34.95P: Three thin lenses, each with a focal length of 40.0 cm, are aligned on a common axis; adjacent... Problem 34.96P: A camera with a 90-mm-focal-length lens is focused on an object 1.30 m from the lens. To refocus on... Problem 34.97P: BIO In one form of cataract surgery the persons natural lens, which has become cloudy, is replaced... Problem 34.98P: BIO A Nearsighted Eye. A certain very nearsighted person cannot focus on anything farther than 36.0... Problem 34.99P: BIO A person with a near point of 85 cm, but excellent distant vision, normally wears corrective... Problem 34.100P: The Galilean Telescope. Figure P34.100 is a diagram of a Galilean telescope, or opera glass, with... Problem 34.101P: Focal Length of a Zoom Lens. Figure P34.101 shows a simple version of a zoom lens. The converging... Problem 34.102P: DATA In setting up an experiment for a high school biology lab, you use a concave spherical mirror... Problem 34.103P: DATA It is your first day at work as a summer intern at an optics company. Your supervisor hands you... Problem 34.104P Problem 34.105CP: CALC (a) For a lens with focal length f, find the smallest distance possible between the object and... Problem 34.106CP: An Object at an Angle. A 16.0-cm-long pencil is placed at a 45.0 angle, with its center 15.0 cm... Problem 34.107CP: BIO People with normal vision cannot focus their eyes underwater if they arent wearing a face mask... Problem 34.108PP: BIO AMPHIBIAN VISION. The eyes of amphibians such as frogs have a much flatter cornea but a more... Problem 34.109PP: BIO AMPHIBIAN VISION. The eyes of amphibians such as frogs have a much flatter cornea but a more... Problem 34.110PP: Given that frogs are nearsighted in air, which statement is most likely to be true about their... Problem 34.111PP: BIO AMPHIBIAN VISION. The eyes of amphibians such as frogs have a much flatter cornea but a more... format_list_bulleted


 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill




