
Mechanics of Materials
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780137605460
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Pearson Education (US)
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.4, Problem 16P
Direct tension indicators are sometimes used instead of torque wrenches to ensure that a bolt has a prescribed tension when used for connections. If a nut on the bolt is tightened so that the six 3-mm high heads of the indicator are strained 0.1 mm/mm, and leave a contact area on each head of 1.5 mm2, determine the tension in the bolt shank. The material has the stress-strain diagram shown.
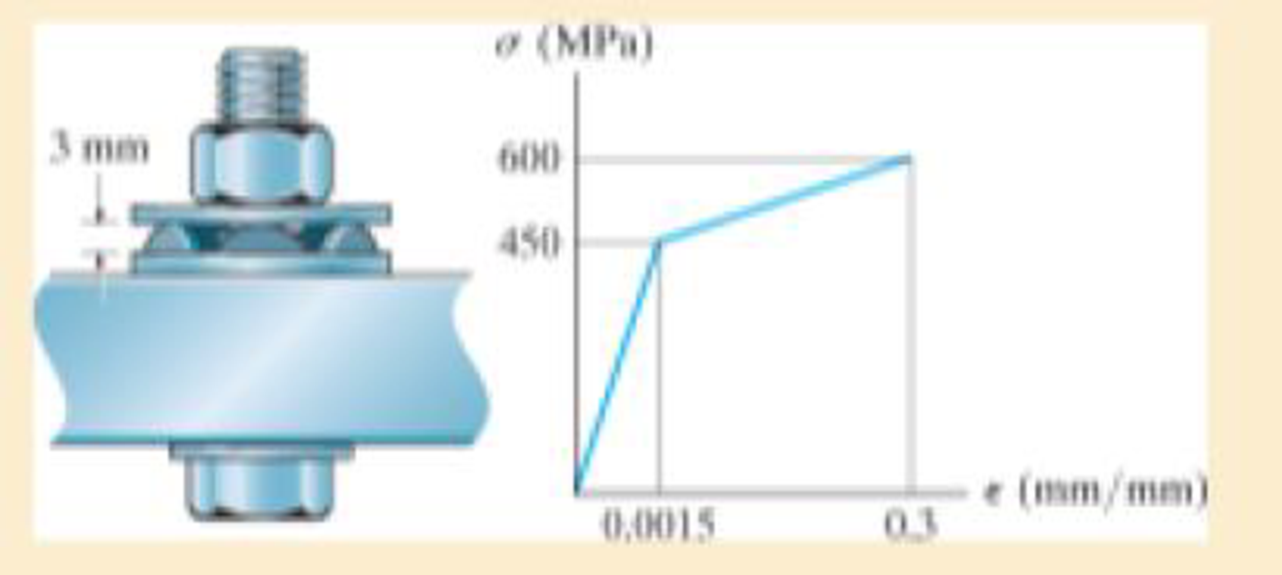
Prob. 3–16
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, publishing as Prentice Hall
2. Determine the force that the jaws J of the metal cutters exert on the smooth cable C if 100-N
forces are applied to the handles. The jaws are pinned at E and A, and D and B. There is also
a pin at F.
E
400 mm
15°
D
B
30 mm² 80 mm/
20 mm
15°
$15°
20 mm
400 mm
15°
100 N
100 N
15°
Draw for it make a match which direction
Q.1) Block A is connected to block B by a pulley
system as shown. The weights of blocks A and B
are 100 lbs and 70 lbs, respectively. Assume
negligible friction between the rope and all pulleys
as well as between block B and the incline and
neglect the mass of all pulleys and cables.
Determine the angle 0 required to keep the system
in equilibrium. (At least two FBDs must be drawn
for full credit)
B
Ꮎ
000
Chapter 3 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials
Ch. 3.4 - Define a homogeneous material.Ch. 3.4 - Indicate the points on the stress-strain diagram...Ch. 3.4 - Define the modulus of elasticity E.Ch. 3.4 - At room temperature, mild steel is a ductile...Ch. 3.4 - Engineering stress and strain are calculated using...Ch. 3.4 - As the temperature increases the modulus of...Ch. 3.4 - A 100-mm-long rod has a diameter of 15 mm. If an...Ch. 3.4 - A bar has a length of 8 in. and cross-sectional...Ch. 3.4 - A 10-mm-diameter rod has a modulus of elasticity...Ch. 3.4 - The material for the 50-mm-long specimen has the...
Ch. 3.4 - The material for the 50-mm-long specimen has the...Ch. 3.4 - If the elongation of wire BC is 0.2 mm after the...Ch. 3.4 - Data taken from a stress-strain test for a ceramic...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy having...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy having...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy having...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the elongation of the square hollow bar...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for an aluminum alloy...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for an aluminum alloy...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for an aluminum alloy...Ch. 3.4 - A structural member in a nuclear reactor is made...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid pipe is supported by a pin at A and an...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid pipe is supported by a pin at A and an...Ch. 3.4 - Direct tension indicators are sometimes used...Ch. 3.4 - A tension test was performed on a magnesium alloy...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a bone is shown and...Ch. 3.4 - The two bars are made of a material that has the...Ch. 3.4 - The two bars are made of a material that has the...Ch. 3.7 - A 100-mm-long rod has a diameter of 15 mm. If an...Ch. 3.7 - A solid circular rod that is 600 mm long and 20 mm...Ch. 3.7 - A 20-mm-wide block is firmly bonded to rigid...Ch. 3.7 - A 20-mm-wide block is bonded to rigid plates at...Ch. 3.7 - The acrylic plastic rod is 400mm long and 20mm in...Ch. 3.7 - The elastic portion of the stress-strain diagram...Ch. 3.7 - The elastic portion of the stress-strain diagram...Ch. 3.7 - The lap joint is connected together using a 1.25...Ch. 3.7 - The lap joint is connected together using a 1.25...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 32PCh. 3.7 - The thin-walled tube is subjected to an axial...Ch. 3 - The elastic portion of the tension stress-strain...Ch. 3 - The elastic portion of the tension stress-strain...Ch. 3 - The rigid beam rests in the horizontal position on...Ch. 3 - The wires each have a diameter of 12 in., length...Ch. 3 - Prob. 5RPCh. 3 - diameter steel bolts. If the clamping force in...Ch. 3 - The stress-strain diagram for polyethylene, which...Ch. 3 - The pipe with two rigid caps attached to its ends...Ch. 3 - The 8-mm-diameter bolt is made of an aluminum...Ch. 3 - An acetal polymer block is fixed to the rigid...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- pls solvearrow_forward+1. 0,63 fin r= 0.051 P The stepped rod in sketch is subjected to a tensile force that varies between 4000 and 7000 lb. The rod has a machined surface finish everywhere except the shoulder area, where a grinding operation has been performed to improve the fatigue resistance of the rod. Using a 99% probability of survival, determine the safety factor for infinite life if the rod is made of AISI 1080 steel, quenched and tempered at 800°c Use the Goodman line. Does the part fail at the fillet? Explainarrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward
- I need drawing solution,draw each one by one no Aiarrow_forwardQu. 17 Compute linear density values for [100] for silver (Ag). Express your answer in nm''. . Round off the answer to three significant figures. Qu. 18 Compute linear density value for [111] direction for silver (Ag). Express your answer in nm'. Round off the answer to three significant figures. Qu. 19 Compute planar density value for (100) plane for chromium (Cr). Express your answer in nm?. Round off the answer to two significant figures. Qu. 20 Compute planar density value for (110) plane for chromium (Cr). Express your answer in nm ≥ to four significant figures. show all work please in material engineeringarrow_forward3-142arrow_forward
- I need solutionsarrow_forward3-137arrow_forwardLarge wind turbines with a power capacity of 8 MW and blade span diameters of over 160 m areavailable for electric power generation. Consider a wind turbine with a blade span diameter of 120m installed at a site subjected to steady winds at 8.25 m/s. Taking the overall efficiency of thewind turbine to be 33 percent and the air density to be 1.25 kg/m3, determine the electric powergenerated by this wind turbine. Also, assuming steady winds of 8.25 m/s during a 24-h period,determine the amount of electric energy and the revenue generated per day for a unit price of$0.08/kWh for electricity.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Hand Tools; Author: UCI Media;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4o0tqF0jDdo;License: Standard Youtube License