
Mechanics of Materials
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780137605460
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Pearson Education (US)
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.4, Problem 10FP
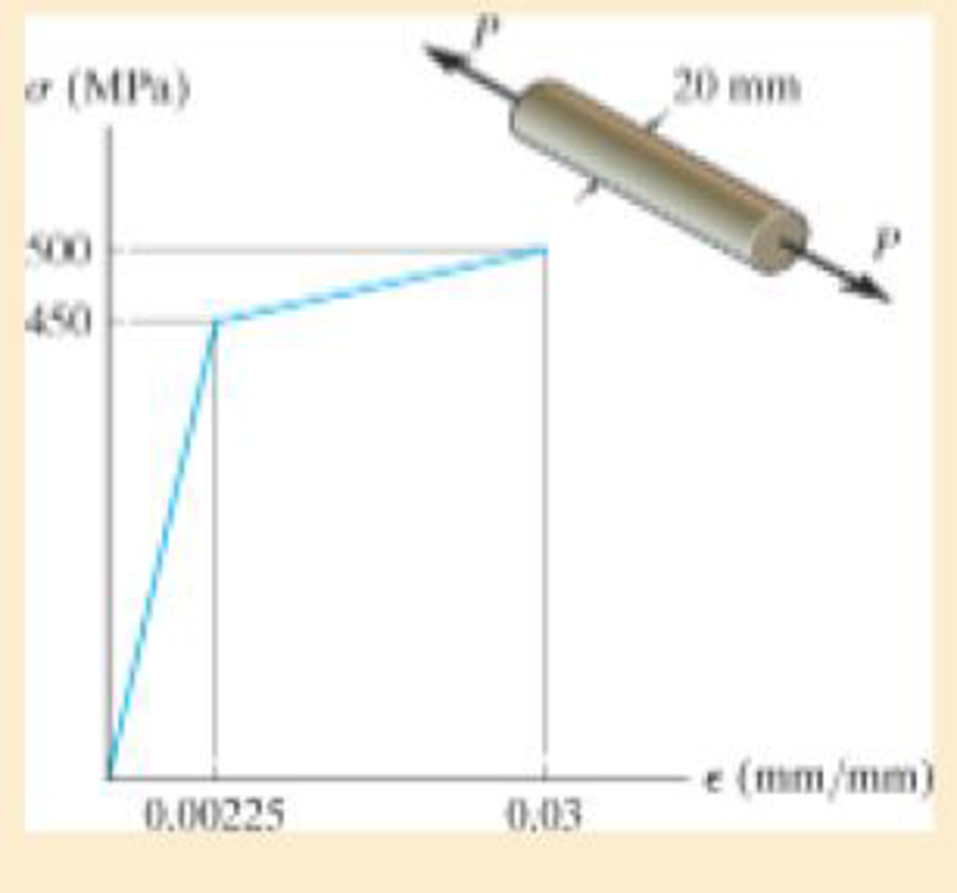
The material for the 50-mm-long specimen has the stress-strain diagram shown. If P = 100 kN, determine the elongation of the specimen.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule04:40
Students have asked these similar questions
Practise question need help on
Can you show explaination and working. The answer from the text book is Q=5.03 X 10^-3
practise question
Chapter 3 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials
Ch. 3.4 - Define a homogeneous material.Ch. 3.4 - Indicate the points on the stress-strain diagram...Ch. 3.4 - Define the modulus of elasticity E.Ch. 3.4 - At room temperature, mild steel is a ductile...Ch. 3.4 - Engineering stress and strain are calculated using...Ch. 3.4 - As the temperature increases the modulus of...Ch. 3.4 - A 100-mm-long rod has a diameter of 15 mm. If an...Ch. 3.4 - A bar has a length of 8 in. and cross-sectional...Ch. 3.4 - A 10-mm-diameter rod has a modulus of elasticity...Ch. 3.4 - The material for the 50-mm-long specimen has the...
Ch. 3.4 - The material for the 50-mm-long specimen has the...Ch. 3.4 - If the elongation of wire BC is 0.2 mm after the...Ch. 3.4 - Data taken from a stress-strain test for a ceramic...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy having...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy having...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy having...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the elongation of the square hollow bar...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for an aluminum alloy...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for an aluminum alloy...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for an aluminum alloy...Ch. 3.4 - A structural member in a nuclear reactor is made...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid pipe is supported by a pin at A and an...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid pipe is supported by a pin at A and an...Ch. 3.4 - Direct tension indicators are sometimes used...Ch. 3.4 - A tension test was performed on a magnesium alloy...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a bone is shown and...Ch. 3.4 - The two bars are made of a material that has the...Ch. 3.4 - The two bars are made of a material that has the...Ch. 3.7 - A 100-mm-long rod has a diameter of 15 mm. If an...Ch. 3.7 - A solid circular rod that is 600 mm long and 20 mm...Ch. 3.7 - A 20-mm-wide block is firmly bonded to rigid...Ch. 3.7 - A 20-mm-wide block is bonded to rigid plates at...Ch. 3.7 - The acrylic plastic rod is 400mm long and 20mm in...Ch. 3.7 - The elastic portion of the stress-strain diagram...Ch. 3.7 - The elastic portion of the stress-strain diagram...Ch. 3.7 - The lap joint is connected together using a 1.25...Ch. 3.7 - The lap joint is connected together using a 1.25...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 32PCh. 3.7 - The thin-walled tube is subjected to an axial...Ch. 3 - The elastic portion of the tension stress-strain...Ch. 3 - The elastic portion of the tension stress-strain...Ch. 3 - The rigid beam rests in the horizontal position on...Ch. 3 - The wires each have a diameter of 12 in., length...Ch. 3 - Prob. 5RPCh. 3 - diameter steel bolts. If the clamping force in...Ch. 3 - The stress-strain diagram for polyethylene, which...Ch. 3 - The pipe with two rigid caps attached to its ends...Ch. 3 - The 8-mm-diameter bolt is made of an aluminum...Ch. 3 - An acetal polymer block is fixed to the rigid...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Find the no-load value of υo in the circuit shown.
Find υo when RL is 150 Ω.
How much power is dissipated in th...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Find the Error 33. The following pseudocode algorithm has an error. It is supposed to use values input for a re...
Starting Out with C++: Early Objects (9th Edition)
Big data Big data describes datasets with huge volumes that are beyond the ability of typical database manageme...
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
What is the difference between main memory and secondary storage?
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Java programmers concentrate on creating, which contain fields and the set of methods that manipulate those fie...
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Why is it important to consider welded products as monolithic structures?
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can you provide steps and an explaination on how the height value to calculate the Pressure at point B is (-5-3.5) and the solution is 86.4kPa.arrow_forwardPROBLEM 3.46 The solid cylindrical rod BC of length L = 600 mm is attached to the rigid lever AB of length a = 380 mm and to the support at C. When a 500 N force P is applied at A, design specifications require that the displacement of A not exceed 25 mm when a 500 N force P is applied at A For the material indicated determine the required diameter of the rod. Aluminium: Tall = 65 MPa, G = 27 GPa. Aarrow_forwardFind the equivalent mass of the rocker arm assembly with respect to the x coordinate. k₁ mi m2 k₁arrow_forward
- 2. Figure below shows a U-tube manometer open at both ends and containing a column of liquid mercury of length l and specific weight y. Considering a small displacement x of the manometer meniscus from its equilibrium position (or datum), determine the equivalent spring constant associated with the restoring force. Datum Area, Aarrow_forward1. The consequences of a head-on collision of two automobiles can be studied by considering the impact of the automobile on a barrier, as shown in figure below. Construct a mathematical model (i.e., draw the diagram) by considering the masses of the automobile body, engine, transmission, and suspension and the elasticity of the bumpers, radiator, sheet metal body, driveline, and engine mounts.arrow_forward3.) 15.40 – Collar B moves up at constant velocity vB = 1.5 m/s. Rod AB has length = 1.2 m. The incline is at angle = 25°. Compute an expression for the angular velocity of rod AB, ė and the velocity of end A of the rod (✓✓) as a function of v₂,1,0,0. Then compute numerical answers for ȧ & y_ with 0 = 50°.arrow_forward
- 2.) 15.12 The assembly shown consists of the straight rod ABC which passes through and is welded to the grectangular plate DEFH. The assembly rotates about the axis AC with a constant angular velocity of 9 rad/s. Knowing that the motion when viewed from C is counterclockwise, determine the velocity and acceleration of corner F.arrow_forward500 Q3: The attachment shown in Fig.3 is made of 1040 HR. The static force is 30 kN. Specify the weldment (give the pattern, electrode number, type of weld, length of weld, and leg size). Fig. 3 All dimension in mm 30 kN 100 (10 Marks)arrow_forward(read image) (answer given)arrow_forward
- A cylinder and a disk are used as pulleys, as shown in the figure. Using the data given in the figure, if a body of mass m = 3 kg is released from rest after falling a height h 1.5 m, find: a) The velocity of the body. b) The angular velocity of the disk. c) The number of revolutions the cylinder has made. T₁ F Rd = 0.2 m md = 2 kg T T₂1 Rc = 0.4 m mc = 5 kg ☐ m = 3 kgarrow_forward(read image) (answer given)arrow_forward11-5. Compute all the dimensional changes for the steel bar when subjected to the loads shown. The proportional limit of the steel is 230 MPa. 265 kN 100 mm 600 kN 25 mm thickness X Z 600 kN 450 mm E=207×103 MPa; μ= 0.25 265 kNarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Material Properties 101; Author: Real Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BHZALtqAjeM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY