
College Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781938168000
Author: Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher: OpenStax College
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 34, Problem 13PE
The average particle energy needed to observe uni?cation of forces is estimated to be 1019 GeV. (a) What is the rest mass in kilograms of a particle that has a rest mass of 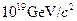 (b) How many times the mass of a hydrogen atom is this?
(b) How many times the mass of a hydrogen atom is this?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Three slits, each separated from its neighbor by d = 0.06 mm, are illuminated by a coherent light source of
wavelength 550 nm. The slits are extremely narrow. A screen is located L = 2.5 m from the slits. The
intensity on the centerline is 0.05 W. Consider a location on the screen x = 1.72 cm from the centerline.
a) Draw the phasors, according to the phasor model for the addition of harmonic waves, appropriate for this
location.
b) From the phasor diagram, calculate the intensity of light at this location.
A Jamin interferometer is a device for measuring or for comparing the indices of refraction of gases. A beam
of monochromatic light is split into two parts, each of which is directed along the axis of a separate cylindrical
tube before being recombined into a single beam that is viewed through a telescope. Suppose we are given the
following,
•
Length of each tube is L = 0.4 m.
• λ= 598 nm.
Both tubes are initially evacuated, and constructive interference is observed in the center of the field of view. As
air is slowly let into one of the tubes, the central field of view changes dark and back to bright a total of 198
times.
(a) What is the index of refraction for air?
(b) If the fringes can be counted to ±0.25 fringe, where one fringe is equivalent to one complete cycle of
intensity variation at the center of the field of view, to what accuracy can the index of refraction of air be
determined by this experiment?
1. An arrangement of three charges is shown below where q₁ = 1.6 × 10-19 C, q2 = -1.6×10-19 C,
and q3 3.2 x 10-19 C.
2 cm
Y
93
92
91
X
3 cm
(a) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the net force on q₁.
(b) Sketch the direction of the forces on qi
Chapter 34 Solutions
College Physics
Ch. 34 - Explain why it only appears that we are at the...Ch. 34 - If there is no observable edge to the universe,...Ch. 34 - If the universe is infinite, does it have a...Ch. 34 - Another known cause of red shift in light is the...Ch. 34 - If some unknown cause of red shiftsuch as light...Ch. 34 - Olbers’s paradox poses an interesting question: If...Ch. 34 - If the cosmic microwave background radiation...Ch. 34 - The decay of one type of Kmeson is cited as...Ch. 34 - Distances to local galaxies are determined by...Ch. 34 - Distances to very remote galaxies are estimated...
Ch. 34 - If the smallest meaningful time interval is...Ch. 34 - Quantum gravity, if developed, would be an...Ch. 34 - Does observed gravitational lensing correspond to...Ch. 34 - Suppose you measure the red shifts of all the...Ch. 34 - What are gravitational waves, and have they yet...Ch. 34 - Is the event horizon of a black hole the actual...Ch. 34 - Suppose black holes radiate their mass away and...Ch. 34 - Discuss the possibility that star velocities at...Ch. 34 - How does relativistic time dilation prohibit...Ch. 34 - If neutrino oscillations do occur, will they...Ch. 34 - Lacking direct evidence of WIMPs as dark matter,...Ch. 34 - Must a complex system be adaptive to be of...Ch. 34 - State a necessary condition for a System to be...Ch. 34 - What is critical temperature Tc? Do all materials...Ch. 34 - Explain how good thermal contact with liquid...Ch. 34 - Not only is liquid nitrogen a cheaper coolant than...Ch. 34 - For experimental evidence particularly of...Ch. 34 - Discuss whether you think there are limits to what...Ch. 34 - Find the approximate mass of the luminous matter...Ch. 34 - Find the approximate mass of the dark and luminous...Ch. 34 - (a) Estimate the mass of the luminous matter in...Ch. 34 - If a galaxy is 500 Mly away from us, how fast do...Ch. 34 - On average, how far away are galaxies mat are...Ch. 34 - Our solar system orbits the center of the Milky...Ch. 34 - (a) What is the approximate speed relative to us...Ch. 34 - (a) Calculate The approximate age of the universe...Ch. 34 - Assuming a circular orbit for the Sun about the...Ch. 34 - (a) What is the approximate force of gravity on a...Ch. 34 - Andromeda galaxy is the closest large galaxy and...Ch. 34 - (a) A particle and its antiparticle are at rest...Ch. 34 - The average particle energy needed to observe...Ch. 34 - The peak intensity of the CMBR occurs at a...Ch. 34 - (a) What Hubble constant corresponds to an...Ch. 34 - Show that the velocity of a star orbiting its...Ch. 34 - The core of a star collapses during a supernova,...Ch. 34 - Using data from the previous problem, find the...Ch. 34 - Distances to the nearest stars (up to 500 by away)...Ch. 34 - (a) Use the Heisenberg uncertainty principle to...Ch. 34 - Construct Your Own Problem Consider a star moving...Ch. 34 - What is the Schwarzschild radius of a blank hole...Ch. 34 - Black holes with masses smaller than muse formed...Ch. 34 - Supermassive black holes are thought to exist at...Ch. 34 - Construct Your Own Problem Consider a supermassive...Ch. 34 - The characteristic length of entities in...Ch. 34 - If the dark matter in the Milky Way were composed...Ch. 34 - The critical mass density needed to just halt the...Ch. 34 - Assume the average density of the universe is 0.1...Ch. 34 - To get an idea of how empty deep spam is on the...Ch. 34 - A section of superconducting wire carries a...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Your bore cells, muscle cells, and skin cells look different because a. different kinds of genes are present in...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
In mice, a short-tailed mutant was discovered. When it was crossed to a normal long-tailed mouse, 4 offspring w...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Fill in the blanks: a. The wrist is also known as the _________ region. b. The arm is also known as the _______...
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Endospore formation is called (a) _____. It is initiated by (b) _____. Formation of a new cell from an endospor...
Microbiology: An Introduction
1. Why is the quantum-mechanical model of the atom important for understanding chemistry?
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
123. A sample contains both KBr and KI in unknown qualities. If the sample has a total mass of and contains , ...
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (Figure 1)In each case let w be the weight of the suspended crate full of priceless art objects. The strut is uniform and also has weight w Find the direction of the force exerted on the strut by the pivot in the arrangement (a). Express your answer in degrees. Find the tension Tb in the cable in the arrangement (b). Express your answer in terms of w. Find the magnitude of the force exerted on the strut by the pivot in the arrangement (b). Express your answer in terms of w.arrow_forward(Figure 1)In each case let ww be the weight of the suspended crate full of priceless art objects. The strut is uniform and also has weight w. Find the direction of the force exerted on the strut by the pivot in the arrangement (b). Express your answer in degrees.arrow_forwardA 70.0 cm, uniform, 40.0 N shelf is supported horizontally by two vertical wires attached to the sloping ceiling (Figure 1). A very small 20.0 N tool is placed on the shelf midway between the points where the wires are attached to it. Find the tension in the left-hand wire. Express your answer with the appropriate units.arrow_forward
- Find the total bind Mev. binding energy for 13 Carbon, 6C (atomic mass = 13.0033554)arrow_forwardWhat is the 27 energy absorbed in this endothermic Auclear reaction 2] Al + 'n → 27 Mg + ! H? (The atom mass of "Al is 26.981539u. and that of 11 Mg is 26.984341u) MeVarrow_forwardWhat is the energy released in this nuclear reaction 1 F + "', H-1 O+ He? 19 19 16 (The atomic mass of 1F is 18.998403 u, and that of 20 is 15.9949154) MeV.arrow_forward
- What is the energy released in this B+ nuclear reaction خالد 2½ Al w/ Mg + ie? (The atomic mass of 11 Al is 23.9999394 and that > of 12 Mg is 23.985041 u) MeV.arrow_forwardWhat is the energy released / absorbed in this nuclear reaction 14 N+ & He → » O + ! N? (The atomic mass of 14 N is 14.003074u. 17N+ and that of 10 is 16.9991324). MeVarrow_forwardCan someone help me answer this question thanks.arrow_forward
- Can someone help me with this question thanks.arrow_forward4B. Four electrons are located on the corners of a square, one on each corner, with the sides of the square being 25 cm long. a) Draw a sketch of the scenario and use your sketch to b) Determine the total force (magnitude and direction) on one of the electrons from the other three?arrow_forwardPortfolio Problem 3. A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a speed vo from the floor of a room of height h. It hits the ceiling and then returns to the floor, from which it rebounds, managing just to hit the ceiling a second time. Assume that the coefficient of restitution between the ball and the floor, e, is equal to that between the ball and the ceiling. Compute e.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning

Modern Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781111794378
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning
