
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305116399
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 33, Problem 33.71AP
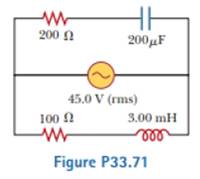
In Figure P33.71, find the rms current delivered by the 45.0-V (rms) power supply when (a) the frequency is very large and (b) the frequency is very small.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Solve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!
The spring in the figure has a spring constant of 1300 N/m. It is compressed 17.0 cm, then launches a 200 g block. The horizontal surface is frictionless, but the block’s coefficient of kinetic friction on the incline is 0.200. What distance d does the block sail through the air?
Solve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!
Chapter 33 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
Ch. 33 - Consider the voltage phasor in Figure 32.4, shown...Ch. 33 - Consider the AC circuit in Figure 32.8. The...Ch. 33 - Consider the AC circuit in Figure 32.11. The...Ch. 33 - Consider the AC circuit in Figure 32.12. The...Ch. 33 - Label each part of Figure 32.16, (a), (b), and...Ch. 33 - An AC source drives an RLC circuit with a fixed...Ch. 33 - What is the impedance of a series RLC circuit at...Ch. 33 - An inductor and a resistor are connected in series...Ch. 33 - (i) When a particular inductor is connected to a...Ch. 33 - A capacitor and a resistor are connected in series...
Ch. 33 - Prob. 33.4OQCh. 33 - Prob. 33.5OQCh. 33 - A sinusoidally varying potential difference has...Ch. 33 - A series RLCcircuit contains a 20.0- resistor, a...Ch. 33 - A resistor, a capacitor, and an inductor are...Ch. 33 - (a) Why does a capacitor act as a short circuit at...Ch. 33 - What is the plia.se angle in a series RLC circuit...Ch. 33 - Prob. 33.11OQCh. 33 - A 6.00-V battery is connected across the primary...Ch. 33 - Do AC ammeters and voltmeters read (a)...Ch. 33 - (a) Explain how the quality factor is related to...Ch. 33 - (a) Explain how the mnemonic ELI the ICE man can...Ch. 33 - Why is the sum of the maximum voltages across each...Ch. 33 - (a) Does the phase angle in an RLC series circuit...Ch. 33 - Prob. 33.5CQCh. 33 - As shown in Figure CQ33.6, a person pulls a vacuum...Ch. 33 - Prob. 33.7CQCh. 33 - Will a transformer operate if a battery is used...Ch. 33 - Prob. 33.9CQCh. 33 - Prob. 33.10CQCh. 33 - When an AC source is connected across a 12.0-...Ch. 33 - (a) What is the resistance of a lightbulb that...Ch. 33 - An AC power supply produces a maximum voltage Vmax...Ch. 33 - A certain lightbulb is rated at 60.0 W when...Ch. 33 - The current in the circuit shown in Figure P32.3...Ch. 33 - In the AC circuit shown in Figure P32.3, R = 70.0 ...Ch. 33 - An audio amplifier, represented by the AC I source...Ch. 33 - Figure P32.4 shows three lightbulbs connected to a...Ch. 33 - An inductor has a .54.0- reactance when connected...Ch. 33 - In a purely inductive AC circuit as shown in...Ch. 33 - Prob. 33.11PCh. 33 - An inductor is connected to an AC power supply...Ch. 33 - An AC source has an output rms voltage of 78.0 V...Ch. 33 - A 20.0-mH inductor is connected to a North...Ch. 33 - Review. Determine the maximum magnetic flux...Ch. 33 - The output voltage of an AC source is given by v =...Ch. 33 - A 1.00-mF capacitor is connected to a North...Ch. 33 - An AC source with an output rms voltage of 86.0 V...Ch. 33 - (a) For what frequencies does a 22.0-F capacitor...Ch. 33 - A source delivers an AC voltage of the form =...Ch. 33 - What maximum current is delivered by an AC source...Ch. 33 - A capacitor C is connected to a power supply that...Ch. 33 - What is the maximum current in a 2.20-F capacitor...Ch. 33 - An AC source with Vmax = 150 V and f = 50.0 Hz is...Ch. 33 - In addition to phasor diagrams showing voltages...Ch. 33 - A sinusoidal voltage = 40.0 sin 100t, where is...Ch. 33 - A series AC circuit contains a resistor, an...Ch. 33 - At what frequency does the inductive reactance of...Ch. 33 - An RLC circuit consists of a 150- resistor, a...Ch. 33 - Prob. 33.30PCh. 33 - An inductor (L = 400 mH), a capacitor (C = 4.43...Ch. 33 - A 60.0-ft resistor is connected in series with a...Ch. 33 - Review. In an RLC series circuit that includes a...Ch. 33 - Prob. 33.34PCh. 33 - A series RLC circuit has a resistance of 45.0 and...Ch. 33 - An AC voltage of the form = 100 sin 1 000t, where...Ch. 33 - A series RLC circuit has a resistance of 22.0 and...Ch. 33 - An AC voltage of the form v = 90.0 sin 350t, where...Ch. 33 - ln a certain series RLC circuit, Irms = 9.00 A,...Ch. 33 - Prob. 33.40PCh. 33 - Prob. 33.41PCh. 33 - A series RLC circuit has components with the...Ch. 33 - An RLC circuit is used in a radio to tune into an...Ch. 33 - The LC circuit of a radar transmitter oscillates...Ch. 33 - A 10.0- resistor, 10.0-mH inductor, and 100-F...Ch. 33 - A resistor R, inductor L, and capacitor C are...Ch. 33 - Review. A radar transmitter contains an LC circuit...Ch. 33 - A step-down transformer is used for recharging the...Ch. 33 - The primary coil of a transformer has N1 = 350...Ch. 33 - A transmission line that has a resistance per unit...Ch. 33 - In the transformer shown in Figure P33.51, the...Ch. 33 - A person is working near the secondary of a...Ch. 33 - The RC high-pass filter shown in Figure P33.53 has...Ch. 33 - Consider the RC high-pass filler circuit shown in...Ch. 33 - Prob. 33.55PCh. 33 - Consider the Filter circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 33 - A step-up transformer is designed to have an...Ch. 33 - Prob. 33.58APCh. 33 - Review. The voltage phasor diagram for a certain...Ch. 33 - Prob. 33.60APCh. 33 - Energy is to be transmitted over a pair of copper...Ch. 33 - Energy is to be transmitted over a pair of copper...Ch. 33 - A 400- resistor, an inductor, and a capacitor are...Ch. 33 - Show that the rms value for the sawtooth voltage...Ch. 33 - A transformer may be used to provide maximum power...Ch. 33 - A capacitor, a coil, and two resistors of equal...Ch. 33 - Marie Cornu, a physicist at the Polytechnic...Ch. 33 - A series RLC circuit has resonance angular...Ch. 33 - Review. One insulated conductor from a household...Ch. 33 - (a) Sketch a graph of the phase angle for an RLC...Ch. 33 - In Figure P33.71, find the rms current delivered...Ch. 33 - Review. In the circuit shown in Figure P32.44,...Ch. 33 - Prob. 33.73APCh. 33 - A series RLC circuit is operating at 2.00 103 Hz....Ch. 33 - A series RLC circuit consists of an 8.00-...Ch. 33 - A series RLC circuit in which R = l.00 , L = 1.00...Ch. 33 - The resistor in Figure P32.49 represents the...Ch. 33 - An 80.0- resistor and a 200-mH inductor are...Ch. 33 - Prob. 33.79CPCh. 33 - P33.80a shows a parallel RLC circuit. The...Ch. 33 - Prob. 33.81CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!arrow_forwardA 10-m-long glider with a mass of 680 kg (including the passengers) is gliding horizontally through the air at 28 m/s when a 60 kg skydiver drops out by releasing his grip on the glider. What is the glider's speed just after the skydiver lets go?arrow_forwardPROBLEM 2 A cube of mass m is placed in a rotating funnel. (The funnel is rotating around the vertical axis shown in the diagram.) There is no friction between the cube and the funnel but the funnel is rotating at just the right speed needed to keep the cube rotating with the funnel. The cube travels in a circular path of radius r, and the angle between the vertical and the wall of the funnel is 0. Express your answers to parts (b) and (c) in terms of m, r, g, and/or 0. (a) Sketch a free-body diagram for the cube. Show all the forces acting on it, and show the appropriate coordinate system to use for this problem. (b) What is the normal force acting on the cube? FN=mg58 (c) What is the speed v of the cube? (d) If the speed of the cube is different from what you determined in part (c), a force of friction is necessary to keep the cube from slipping in the funnel. If the funnel is rotating slower than it was above, draw a new free-body diagram for the cube to show which way friction…arrow_forward
- Circular turns of radius r in a race track are often banked at an angle θ to allow the cars to achieve higher speeds around the turns. Assume friction is not present. Write an expression for the tan(θ) of a car going around the banked turn in terms of the car's speed v, the radius of the turn r, and g so that the car will not move up or down the incline of the turn. tan(θ) =arrow_forwardThe character Min Min from Arms was a DLC character added to Super Smash Bros. Min Min’s arms are large springs, with a spring constant of 8.53 ⋅ 10^3 N/m, which she uses to punch and fling away her opponents. Min Min pushes her spring arm against Steve, who is not moving, compressing it 1.20 m as shown in figure A. Steve has a mass of 81.6 kg. Assuming she uses only the spring to launch Steve, how fast is Steve moving when the spring is no longer compressed? As Steve goes flying away he goes over the edge of the level, as shown in figure C. What is the magnitude of Steve’s velocity when he is 2.00 m below where he started?arrow_forwardSlinky dog whose middle section is a giant spring with a spring constant of 10.9 N/m. Woody, who has a mass of 0.412 kg, grabs onto the tail end of Slink and steps off the bed with no initial velocity and reaches the floor right as his velocity hits zero again. How high is the bed? What is Woody’s velocity halfway down? Enter just the magnitude of velocity.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardA positive charge of 91 is located 5.11 m to the left of a negative charge 92. The charges have different magnitudes. On the line through the charges, the net electric field is zero at a spot 2.90 m to the right of the negative charge. On this line there are also two spots where the potential is zero. (a) How far to the left of the negative charge is one spot? (b) How far to the right of the negative charge is the other?arrow_forwardA charge of -3.99 μC is fixed in place. From a horizontal distance of 0.0423 m, a particle of mass 7.31 x 103 kg and charge -9.76 µC is fired with an initial speed of 84.1 m/s directly toward the fixed charge. How far does the particle travel before its speed is zero?arrow_forward
- a) What is the minimum tension in N that the cable must be able to support without breaking? Assume the cable is massless. T = b) If the cable can only support a tension of 10,000 N what is the highest mass the ball can have in kg? mm =arrow_forwardCurve Fitter CURVE FITTER Open Update Fit Save New Exclusion Rules Select Validation Data Polynomial Exponential Logarithmic Auto Fourier Fit Fit Duplicate Data Manual FILE DATA FIT TYPE FIT Harmonic Motion X us 0.45 mi ce 0.4 0.35 0.3 0.25 0.2 Residuals Plot Contour Plot Plot Prediction Bounds None VISUALIZATION Colormap Export PREFERENCES EXPORT Fit Options COA Fourier Equation Fit Plot x vs. t -Harmonic Motion a0+ a1*cos(x*w) + b1*sin(x*w) Number of terms Center and scale 1 ▸ Advanced Options Read about fit options Results Value Lower Upper 0.15 a0 0.1586 0.1551 0.1620 a1 0.0163 0.0115 0.0211 0.1 b1 0.0011 -0.0093 0.0115 W 1.0473 0.9880 1.1066 2 8 10 t 12 14 16 18 20 Goodness of Fit Value Table of Fits SSE 0.2671 Fit State Fit name Data Harmonic Motion x vs. t Fit type fourier1 R-square 0.13345 SSE DFE 0.26712 296 Adj R-sq 0.12467 RMSE 0.030041 # Coeff Valic R-square 0.1335 4 DFE 296.0000 Adj R-sq 0.1247 RMSE 0.0300arrow_forwardWhat point on the spring or different masses should be the place to measure the displacement of the spring? For instance, should you measure to the bottom of the hanging masses?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
DC Series circuits explained - The basics working principle; Author: The Engineering Mindset;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VV6tZ3Aqfuc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY