
Concept explainers
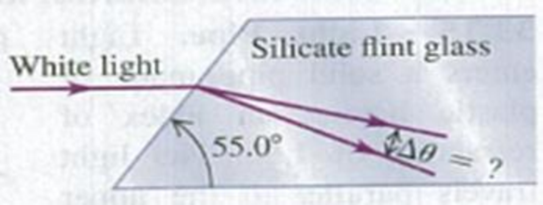
A narrow beam of white light strikes one face of a slab of silicate flint glass. The light is traveling parallel to the two adjoining faces,as shown in Fig. E33.23. For the transmitted light inside the glass, through what angle Δθ is the portion of the visible spectrum between 400 nm and 700 nm dispersed? (Consult the graph in Fig. 33.17.)
Figure E33.23
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 33 Solutions
University Physics with Modern Physics Plus Mastering Physics with eText -- Access Card Package (14th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
- Show that the units 1 v2/Q = 1 W, as implied by the equation P = V²/R. Starting with the equation P = V²/R, we can get an expression for a watt in terms of voltage and resistance. The units for voltage, V, are equivalent to [? v2 v2 A, are equivalent to J/C ✓ X . Therefore, 1 = 1 = 1 A V1 J/s Ω V-A X = 1 W. . The units for resistance, Q, are equivalent to ? The units for current,arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- According to the provided information answer the question accorrding to grade 11 physics Jerry has decided to give up his part-time job for a new career, cat-burglar! Jerry loves the idea of dressing up like a cat all day and of course the chance of meeting Cat Woman! On Jerry's first "job" he figures out his escape plan. He travels 3.0 km south for 15 minutes and then 8.0 km west for 1.5 hours before reaching his house. Draw a sketch diagram of the path he took with all the appropriate labels.arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer all parts of the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer this question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





