
Test your knowledge of the five major classes of plant hormones (auxins, cytokinins, gibberellins, abscisic acid, ethylene) by matching one hormone to each lettered box. (Note that some hormones will match up to more than one box.)
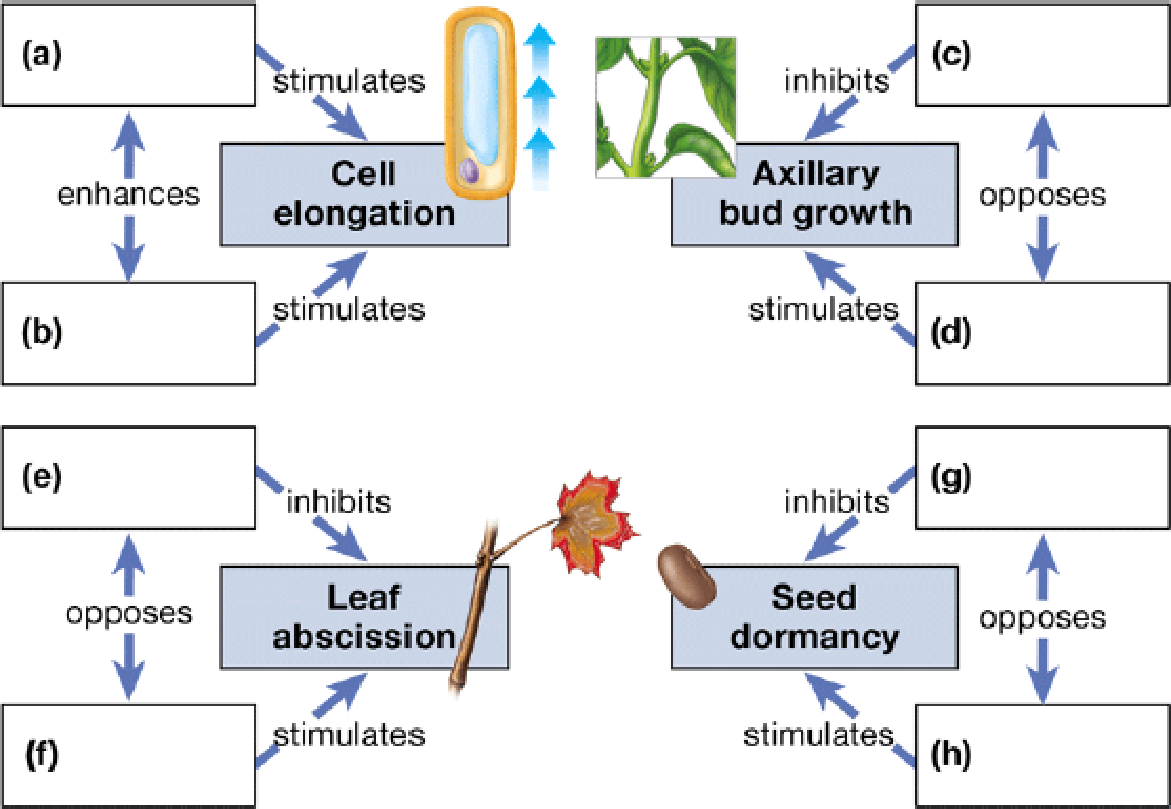
To complete: The given map of the five major classes of plant hormones.
Concept introduction:
Plant hormones are chemical messengers that are produced in trace amounts, but profoundly affect the growth and development of a plant. These include auxins, cytokinins, gibberellins, abscisic acid and ethylene.
The plant hormones perform various functions such as promoting growth, breaking dormancy, mediating fruit ripening and providing tolerance to stress.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows the completed map representing the five major classes of plant hormones.
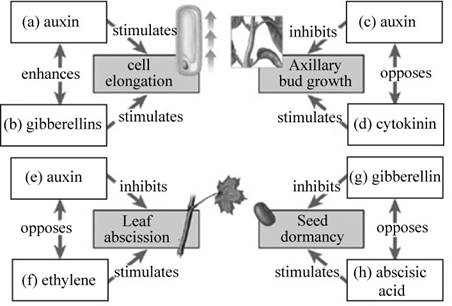
Fig.1: The five major classes of plant hormones.
(a)
Correct answer: Auxin.
Explanation: Auxins are a group of plant hormones that promotes cell elongation. They are produced by the apical meristems of shoot and root. They promote the growth of root and shoot of the plant. Hence the correct answer is auxin.
(b)
Correct answer: Gibberellins.
Explanation: The gibberellins are a group of plant hormones that stimulate the elongation of stem by promoting cell elongation. Hence the correct answer is gibberellins.
(c)
Correct answer: Auxin.
Explanation: Auxin is produced by the apical bud of the shoot and functions to inhibit the growth of axillary buds, a phenomenon called apical dominance. Hence, the correct answer is auxin.
(d)
Correct answer: cytokinin.
Explanation: The cytokinins are a group of plant hormones that stimulate rapid cell division in roots and shoots of the plant. It also promotes the growth of lateral buds, thereby nullifying the effects of auxin. Hence, the correct answer is cytokinin.
(e)
Correct answer: Auxin.
Explanation: In addition to cell elongation, the auxins also function to retard the abscission of leaves. It also plays a crucial role in nullifying the effects of ethylene. Hence, the correct answer is auxin.
(f)
Correct answer: Ethylene.
Explanation: Ethylene is a gaseous hormone that promotes ripening of fruit and abscission of leaves from trees. Hence, the correct answer is ethylene.
(g)
Correct answer: Gibberellin.
Explanation: The gibberellin is a plant hormone that promotes the germination of seed. It inhibits seed dormancy by nullifying the effects of abscisic acid. Hence the correct answer is gibberellin.
(h)
Correct answer: Abscisic acid.
Explanation: The abscisic acid is a plant hormone that is involved in the stress responses. It inhibits growth, promotes seed dormancy during winter or periods of drought. Hence, the correct answer is abscisic acid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 33 Solutions
CAMP.BIO:CONC...MOD.MAST+PRINT>I<
- the direct output from molecular replacement is a coordinate file showing the orientation of the unknown target protein in the unit cell. true or false?arrow_forwardDid your intake of vitamin C meet or come very close to the recommended amount? yes noarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements about hydration is true? Absence of thirst is a reliable indication that an individual is adequately hydrated. All of these statements are true. Although a popular way to monitor hydration status, weighing yourself before and after intensive physical activity is not a reliable method to monitor hydration. Urine that is the color of apple juice indicates dehydration. I don't know yetarrow_forward
- Three of the many recessive mutations in Drosophila melanogaster that affect body color, wing shape, or bristle morphology are black (b) body versus grey in wild type, dumpy (dp), obliquely truncated wings versus long wings in the male, and hooked (hk) bristles versus not hooked in the wild type. From a cross of a dumpy female with a black and hooked male, all of the F1 were wild type for all three of the characters. The testcross of an F1 female with a dumpy, black, hooked male gave the following results: Trait Number of individuals Wild type 169 Black 19 Black, hooked 301 Dumpy, hooked 21 Hooked, dumpy, black 172 Dumpy, black 6 Dumpy 305 Hooked 8 Determine the order of the genes and the mapping distance between genes. Determine the coefficient of confidence for the portion of the chromosome involved in the cross. How much interference takes place in the cross?arrow_forwardWhat happens to a microbes membrane at colder temperature?arrow_forwardGenes at loci f, m, and w are linked, but their order is unknown. The F1 heterozygotes from a cross of FFMMWW x ffmmww are test crossed. The most frequent phenotypes in the test cross progeny will be FMW and fmw regardless of what the gene order turns out to be. What classes of testcross progeny (phenotypes) would be least frequent if locus m is in the middle? What classes would be least frequent if locus f is in the middle? What classes would be least frequent if locus w is in the middle?arrow_forward
- 1. In the following illustration of a phospholipid... (Chemistry Primer and Video 2-2, 2-3 and 2-5) a. Label which chains contain saturated fatty acids and non-saturated fatty acids. b. Label all the areas where the following bonds could form with other molecules which are not shown. i. Hydrogen bonds ii. Ionic Bonds iii. Hydrophobic Interactions 12-6 HICIH HICIH HICHH HICHH HICIH OHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH C-C-C-C-C-c-c-c-c-c-c-c-c-c-c-c-C-C-H HH H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H HO H-C-O H-C-O- O O-P-O-C-H H T HICIH HICIH HICIH HICIH HHHHHHH HICIH HICIH HICIH 0=C HIC -C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-CC-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-H HHHHHHHHH IIIIIIII HHHHHHHH (e-osbiv)arrow_forwardAnswer this as a dental assistant studentarrow_forwardbuatkan judul skripsi tentang parasitologi yang sedang trendinharrow_forward
- Dental assistantarrow_forwardO Macmillan Learning Glu-His-Trp-Ser-Gly-Leu-Arg-Pro-Gly The pKa values for the peptide's side chains, terminal amino groups, and carboxyl groups are provided in the table. Amino acid Amino pKa Carboxyl pKa Side-chain pKa glutamate 9.60 2.34 histidine 9.17 1.82 4.25 6.00 tryptophan 9.39 2.38 serine 9.15 2.21 glycine 9.60 2.34 leucine 9.60 2.36 arginine 9.04 2.17 12.48 proline 10.96 1.99 Calculate the net charge of the molecule at pH 3. net charge at pH 3: Calculate the net charge of the molecule at pH 8. net charge at pH 8: Calculate the net charge of the molecule at pH 11. net charge at pH 11: Estimate the isoelectric point (pl) for this peptide. pl:arrow_forwardBiology Questionarrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





