
Interpretation:
Reaction between 1,3-Cyclopentadiene and cycloheptatrienone is suprafacial or antarafacial to give the product which is given below:
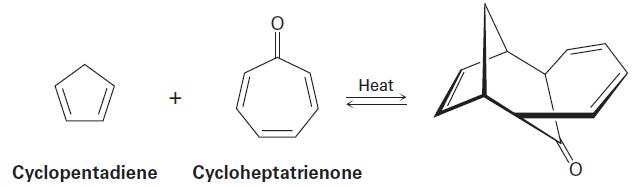
Concept introduction:
[6 + 4] Cycloaddition is a type of cycloaddition between a six-atom pi system and a four-atom pi system, leading to a ten-membered ring. It is a thermally allowed, higher-order cycloaddition process. Although most linear, acyclic trienes do not give [6 + 4] products selectively, cyclic trienes give high yields of [6 + 4] products in many cases.
A suprafacial cycloaddition occurs when like phases of the p orbitals of both reactants are on the same side of the pie system, so that two bonding interactions result.
An antarafacial cycloaddition occurs when one pie system must twist to align like phases of the p orbitals of the terminal carbons of the reactants.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 30 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- ΗΝ, cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Draw Enamine I I CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H3O+ I Drawing Draw Iminium Ionarrow_forward:0: :0: Select to Add Arrows :0: (CH3)2NH :0: ■ Select to Add Arrows :0: :0: (CH3)2NH ■ Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forwardDraw the product of the following H action sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings H Charges ㅁarrow_forward
- Please help me with this the problem is so confusingarrow_forward14 Question (1 point) Disiamylborane adds to a triple bond to give an alkenylborane. Upon oxidation with OH, H2O2, the alkenylborane will form an enol that tautomerizes to an aldehyde. In the first box below, draw the mechanism arrows for the reaction of disiamylborane with the alkyne, and in the last box draw the structure of the aldehyde. 4th attempt Feedback i > 3rd attempt OH, H2O2 i See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forwardanswer with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forward
- Hello I need some help with Smartwork. For drawing structure B, I know the correct answer is CH₃B₂, but when I try to type it in, it keeps giving me CH₄BH₃ instead. Do you know how I should write it properly? Should I use a bond or something else?arrow_forwardTrue or false, chemistryarrow_forwardanswer thse questions with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forward
- C app.aktiv.com Draw the product of the following reaction sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. H O 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Drawingarrow_forwardDraw the product of the following reaction sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. H O 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CHзBr Drawingarrow_forwardSeee the attached imaarrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

