
Concept explainers
Magnesium ribbon reacts with acid to produce hydro- gen gas and magnesium ions. Different masses of magnesium ribbon are added to 10 mL of the acid. The volume of the hydrogen gas obtained is a measure of the number of moles of hydrogen produced by the reaction. Various measurements are given in the table below.
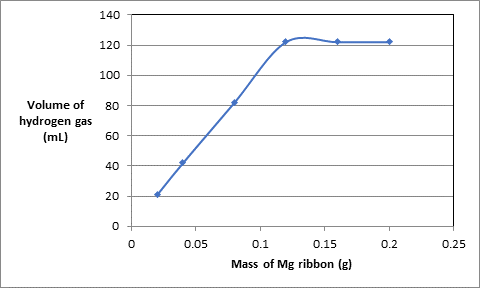
(a) Draw a graph of the results by plotting the mass of Mg versus the volume of the hydrogen gas.
(b) What is the limiting reactant in experiment 1?
(c) What is the limiting reactant in experiment 3?
(d) What is the limiting reactant in experiment 6?
(e) Which experiment uses stoichiometric amounts of each reactant?
(f) What volume of gas would be obtained if 0.300 g of Mg ribbon were used? If 0.010 g were used?
(a)
Interpretation:.
The graph between mass of Mg versus the volume of hydrogen gas should be plotted..
Concept introduction:.
The number of moles of a substance is related to mass and molar mass as follows:.
Here,mis mass andMis molar mass of the substance..
The density of solution can be calculated as follow:.
Here, m is mass and V is volume.
Answer to Problem 74QAP

Explanation of Solution
The data of mass of Mg ribbon in grams and volume of hydrogen gas produced in experiments is as follows:.
| Experiment | Mass of Mg ribbon (g) | Volume of acid used (mL) | Volume of hydrogen gas (mL) |
| 1 | 0.020 | 10.0 | 21 |
| 2 | 0.040 | 10.0 | 42 |
| 3 | 0.080 | 10.0 | 82 |
| 4 | 0.120 | 10.0 | 122 |
| 5 | 0.160 | 10.0 | 122 |
| 6 | 0.200 | 10.0 | 122 |
To plot put the data of mass of Mg ribbon on x-axis and volume of hydrogen gas at y-axis:.
(b)
Interpretation:
The limiting reactant in experiment 1 should be determined..
Concept introduction:.
The number of moles of a substance is related to mass and molar mass as follows:.
Here,mis mass andMis molar mass of the substance..
The density of solution can be calculated as follow:.
Here, m is mass and V is volume.
Answer to Problem 74QAP
Mg is limiting reactant.
Explanation of Solution
The balanced chemical reaction will be as follows:.
According to experiment 1, mass of Mg ribbon is 0.020 g, volume of acid used is 10.0 mL and volume of
The density of
Putting the values,
Molar mass of
From the balanced chemical reaction, 1 mol of hydrogen gas is produced from 1 mol of Mg thus, number of moles of Mg required to produce
The mass of Mg is 0.020 g and molar mass of Mg is 24.305 g/mol thus, number of moles of Mg will be:.
Since, number of moles of Mg required is
(c)
Interpretation:
The limiting reactant in experiment 3 should be determined..
Concept introduction:.
The number of moles of a substance is related to mass and molar mass as follows:.
Here,mis mass andMis molar mass of the substance..
The density of solution can be calculated as follow:.
Here, m is mass and V is volume.
Answer to Problem 74QAP
Mg is limiting reactant.
Explanation of Solution
The balanced chemical reaction will be as follows:.
According to experiment 3, mass of Mg ribbon is 0.080 g, volume of acid used is 10.0 mL and volume of
The density of
Putting the values,
Molar mass of
From the balanced chemical reaction, 1 mol of hydrogen gas is produced from 1 mol of Mg thus, number of moles of Mg required to produce
The mass of Mg is 0.080 g and molar mass of Mg is 24.305 g/mol thus, number of moles of Mg will be:.
Since, number of moles of Mg required is
(d)
Interpretation:
The limiting reactant in experiment 6 should be determined..
Concept introduction:.
The number of moles of a substance is related to mass and molar mass as follows:.
Here,mis mass andMis molar mass of the substance..
The density of solution can be calculated as follow:.
Here, m is mass and V is volume.
Answer to Problem 74QAP
Acid is limiting reactant.
Explanation of Solution
The balanced chemical reaction will be as follows:.
According to experiment 6, mass of Mg ribbon is 0.200 g, volume of acid used is 10.0 mL and volume of
The density of
Putting the values,
Molar mass of
From the balanced chemical reaction, 1 mol of hydrogen gas is produced from 1 mol of Mg thus, number of moles of Mg required to produce
The mass of Mg is 0.200 g and molar mass of Mg is 24.305 g/mol thus, number of moles of Mg will be:.
Since, number of moles of Mg required is
(e)
Interpretation:
The experiment that uses stoichiometric amounts of each reactant should be determined..
Concept introduction:.
The number of moles of a substance is related to mass and molar mass as follows:.
Here,mis mass andMis molar mass of the substance..
The density of solution can be calculated as follow:.
Here, m is mass and V is volume.
Answer to Problem 74QAP
Experiment 4.
Explanation of Solution
According to balance chemical reaction, 1 mol of Mg gives 1 mol of hydrogen gas thus, the experiment in which same number of moles of Mg reacts with acid to form hydrogen gas that experiment uses stoichiometric amounts of each reactant..
This cannot be experiment 1, 3 and 6 because ratio of number of moles of Mg and hydrogen gas is not 1:1 in these experiments..
Check experiment 2: mass of Mg is 0.040 g and molar mass of Mg is 24.305 g/mol thus, number of mol of Mg will be:
The volume of
The density of
Putting the values,
Molar mass of
The number of moles of Mg and hydrogen gas is not same thus, it is not experiment 2..
Check experiment 4: mass of Mg is 0.120 g and molar mass of Mg is 24.305 g/mol thus, number of mol of Mg will be:
The volume of
The density of
Putting the values,
Molar mass of
The number of moles of Mg and hydrogen gas is approximately same thus, it is experiment 4..
Check experiment 5: mass of Mg is 0.160 g and molar mass of Mg is 24.305 g/mol thus, number of mol of Mg will be:
The volume of
The density of
Putting the values,
Molar mass of
The number of moles of Mg and hydrogen gas is not same thus, it is not experiment 4..
Therefore, experiment 4 uses stoichiometric amounts of each reactant.
(f)
Interpretation:
The volume of the gas for 0.300 g and 0.010 g of Mg ribbon should be calculated.
Concept introduction:.
The number of moles of a substance is related to mass and molar mass as follows:.
Here,mis mass andMis molar mass of the substance..
The density of solution can be calculated as follow:.
Here, m is mass and V is volume.
Answer to Problem 74QAP
The volume of hydrogen gas produced from 0.120 g of Mg and 0.010 g of Mg is 122 mL and 11.32 mL respectively.
Explanation of Solution
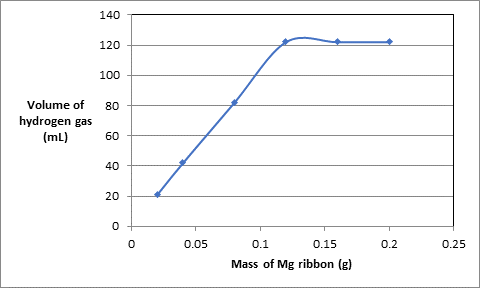
The graph between mass of Mg ribbon and volume of hydrogen gas is as follows:.

According to the graph, above the mass of Mg 0.120 g, the volume of hydrogen gas becomes constant at 122 mL thus, the volume of hydrogen gas produced if 0.120 g of Mg is burned will be 122 mL.
Considering only the straight line in the graph,.
| Experiment | Mass of Mg ribbon (g) | Volume of acid used (mL) | Volume of hydrogen gas (mL) |
| 1 | 0.020 | 10.0 | 21 |
| 2 | 0.040 | 10.0 | 42 |
| 3 | 0.080 | 10.0 | 82 |
| 4 | 0.120 | 10.0 | 122 |
The plot will be as follows:.

Comparing this with equation of straight line
For the mass of ribbon 0.010 g, the volume of hydrogen gas can be calculated as follows:.
Therefore, the volume of hydrogen gas is 11.32 mL.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
OWLV2 FOR MASTERTON/HURLEY'S CHEMISTRY:
- Briefly indicate the coordination forms of B and Si in borates and silicates, respectively.arrow_forwardCan you please draw out the Lewis structure for these two formulasarrow_forwardIn a rotational Raman spectrum of a diatomic molecule it is correct to say that:a) anti-Stokes lines occur at frequencies higher than the excitatory oneb) Stokes lines occur at frequencies higher than the excitatory onec) Rayleigh scattering is not observedd) Rayleigh scattering corresponds to delta J = 0arrow_forward
- Of the molecules: H2, N2, HCl, CO2, indicate which ones can give Raman vibration-rotation spectra:a) H2, N2 and HClb) H2, N2, HCl and CO2c) H2 and N2d) all of themarrow_forwardCan you please help me with drawing the Lewis structure of each molecular formula?I truly appreciate you!arrow_forwardCan you please help me with drawing the Lewis structure of each molecular formula?I truly appreciate you!arrow_forward
- Describe each highlighted bond in terms of the overlap of atomic orbitals. (a) Н Н H H [References] HIC H H C H H-C-CC-N: H σ character n character (b) HIC H H H H-C-C-C HIC H Н H O-H σ character n character Submit Answer Try Another Version 3 item attempts remainingarrow_forward11 Naming and drawing alcohols Write the systematic (IUPAC) name for each of the following organic molecules: structure OH HO OH Explanation Check name ☐arrow_forwardwhat is the drawn mechanism for diethyl carbonate and 4 - bromo - N, N -dimethylaniline to create crystal violet?arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





