
Concept explainers
How long after the ball is released from the balcony, the friend has to wait, to start running so that she'll be able to catch the ball exactly 1.00 m above the floor of the court.
Answer to Problem 63QAP
The friend has to wait for 0.25 s after the ball is released and then start running so as to catch the ball at the height of 1.00 m above the floor.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The height of the balcony above the court
y0=7.00 m
Initial velocity of the ball
v0=9.00 m/s
Angle at which the ball is released
θ=33.0°
Distance of the initial position of the friend from the balcony
x1=11.0 m
Friend's initial velocity
u0=0 m/s
Friend's acceleration
a=1.80 m/s2
Height at which the ball is caught
y=1.00 m
Formula used:
The equations of motion for vertical and horizontal motion of the ball can be used to find the time the friend needs to wait.
For vertical motion,
Δy=v0yt+12ayt2......(1)
Here, Δy is the vertical displacement of the ball, v0y is the vertical component of the ball's velocity, t is the time of flight of the ball and ay is the vertical component of the acceleration.
For horizontal motion of the ball,
Δx=v0xt+12axt2......(2)
Here, Δx is the horizontal displacement of the ball in time t, v0x is the horizontal component of the ball's velocity and ax is the acceleration in the horizontal direction.
The friend's motion can be analyzed using the equation,
Δx=u0t1+12at21......(3)
Here, Δx is the displacement made by the friend, u0 her initial velocity, a her acceleration and t1 is the time she takes to make the displacement.
Calculation:
Assume the origin A to be located at the point just below the balcony, with the x axis parallel to the ground and the positive y axis directed upwards. The height of the balcony from the ground is OA. The friend stands at B initially, and then catches the ball at the point C at a height CD from the ground. This is represented by the diagram shown below.
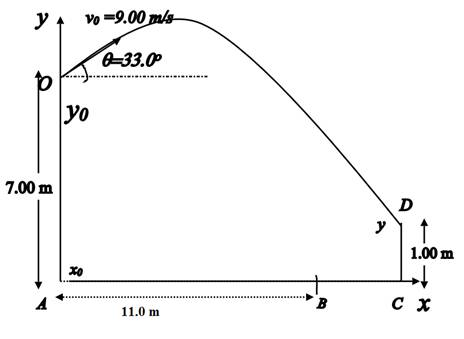
The ball is released with an initial velocity v0 at an angle θ to the horizontal. Calculate the horizontal and vertical components of the ball's velocity.
v0x=v0cosθ=(9.00 m/s)(cos33.0°)=7.55 m/sv0y=v0sinθ=(9.00 m/s)(sin33.0°)=4.90 m/s
The vertical motion of the ball is governed by the gravitational force. The acceleration of the ball in the vertical direction is equal to the acceleration of free fall.
Therefore,
ay=g=−9.80 m/s2
The ball makes a vertical displacement from the initial position y0 to the final position y.
Therefore,
Δy=y−y0......(4)
Rewrite the equation (1) using the above expression, equation (4).
y−y0=v0yt+12ayt2
Substitute the values of the variables in the equation and calculate the value of time of flight t.
y−y0=v0yt+12ayt2(1.00 m)−(7.00 m)=(4.90 m/s)t+12(−9.80 m/s2)t2−6.00 m=(4.90 m/s)t−(4.90 m/s2)t2
Rewrite the equation as a quadratic for t.
(4.90 m/s2)t2−(4.90 m/s)t−6.00 m=0
Solve for t.
t=−(−4.90 m/s)±√(−4.90 m/s)2−4(4.90 m/s2)(−6.00 m)2(4.90 m/s2)=(4.90 m/s)±(11.90 m/s)(9.80 m/s2)
Take the positive root alone.
t=1.71 s
The ball is in flight for 1.71 s. During this time, the ball travels a horizontal distance Δx, from the position x0 to a position x.
Therefore,
Δx=x−x0......(5)
Since point A is directly below the balcony, its x coordinate is x0=0 m. No force acts on the ball in the horizontal direction, hence no acceleration acts on the ball in the horizontal direction.
Therefore, ax=0 m/s2.
Use equation (5) and the values of the variables in the equation (2) and calculate the value of x.
Δx=v0xt+12axt2x−x0=v0xt+12axt2x−(0 m)=(7.55 m/s)(1.71 s)+12(0 m/s2)(1.71 s)2x=12.91 m
The friend stands at the position x1 and she needs to make a displacement of Δx to reach the position x, with an acceleration a. She takes a time t1 to cover this distance.
The horizontal displacement the friend needs to make is given by,
Δx=x−x1
In equation (3), substitute the known values of the variables and calculate the time t1 she takes to cover the distance.
Δx=u0t1+12at21x−x1=u0t1+12at21(12.91 m)−(11.0 m)=(0 m/s)t1+12(1.80 m/s2)t21
Simplify the expression and solve for t1.
t1=√2(1.91 m)1.80 m/s2=1.46 s
The ball takes a time t=1.71 s to reach point D and the friend needs a time of t1=1.46 s to reach the point C. Therefore, she needs to start at a time Δt=t−t1 after the ball is released so that she would be able to catch the ball.
Calculate the time Δt.
Δt=t−t1=(1.71 s)−(1.46 s)=0.25 s
Conclusion:
Thus, the friend has to wait for 0.25 s after the ball is released and then start running so as to catch the ball at the height of 1.00 m above the floor.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS LL W/ 6 MONTH ACCESS
- Pls help ASAParrow_forwardFind the integral expression for the magnetic force on a wire carrying 3.5 amps current on the z axis with length2 meters on end at the origin and the other at z=4. Magnetic field is B = 4(zy+4) i - (z-3) j + 20(x+2)/(z-3) k.Don’t take the integral. Integral should contain only x-y-z as variables not rarrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward
- 9. Light of wavelength 442 nm is sent through a single slit with a width of 884 nm. At what angle does the first dark fringe occur? a. 30.0° b. 45.0° C. 60.0° d. 90.0° 10. Light travels through a single-slit and forms an interference pattern. The spacing of the dark fringes on one side of the pattern is 1.44 cm. What is the width of the central maximum? a. 0.720 cm 1.44 cm b. C. 2.88 cm d. 4.32 cmarrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forwardd. when the index of refraction of medium A is equal to the index of refraction of medium B 7. What is the term for the bending of a wave front as it passes an obstacle? a. interference b. reflection C. d. diffraction refraction 8. A ray of light travels from air into a soap film on a layer of glass, as shown right. Which statement about ray 1 is true? a. There is no inversion at either surface. b. There is an inversion the surface between air and soap, but not soap and glass. C. There is no inversion at the surface between air and soap, incident light ray 1 ray 2 ray 3 but there is one at the surface between soap and glass. d. There is an inversion at both surfaces. air = nair 1.00 soap film nfilm = 1.35 glass = nglass 1.50arrow_forward
- A circular wire with radius 0.4 meters in on x-y plane. There is a constant Magnetic field with 14T strengthtowards z-axis. Find the magnitude of the electromotive force and the direction of the current for a) B decreasesto 10T in 5 seconds. B) B is rotated by 45 degrees and the area doubles in 4 seconds.arrow_forwardWrite the expression for the magnetic flux inside a region om x-z plane at y=0 bounded by z=3x z=0 x=5 x=7due to a magnetic field B = f(x,y,z) i +g(x,y,z) j + h(x,y,z) karrow_forwardExplain mutual inductance of two loops facing one another and compare with one loop inside the other.arrow_forward
- Two very long wires carry each 3 amps current in the same direction along the z-axis (outward). First is at x=0y=0 current is upward. Second at x=0 y=3 current is also upward. Find the net magnetic field at x=4 y=3.arrow_forwardFind the integral expression for the magnetic field at x=5 y=6 due to a wire on the x axis with length 5 meters onend at x=0 and the other at x=5. Don’t take the integralarrow_forwardTwo very long wires carry current along y-axis. First is at x=0 0.45 amps current is upward. Second at x=5 currentwith 0.65 amps current downward. Find the net magnetic a) Two meters to the left of the first wire. b) Twometers to the right of the first wire. a) Two meters to the right of the second wire. b) Two meters to the right ofthe second wire.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





