
Concept explainers
(i) The x component of the velocity versus time
(ii) The y component of the velocity versus time
(iii) The y component of the acceleration versus time.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Magnitude of the initial velocity
Angle made by vi with x- axis
Magnitude of the final velocity
Angle made by vf with x axis
Time interval during which the velocity changes
Formula used:
The components of the velocity vectors along the x and the y directions are given by,
The change in velocity along the x and the y directions is given by,
The components of the acceleration along the x and y directions are given by,
The equation to determine the variation of
The equation to determine the variation of
Calculation:
Resolve the vectors vi and vf along the x and the y axes. This is shown in the diagram below.
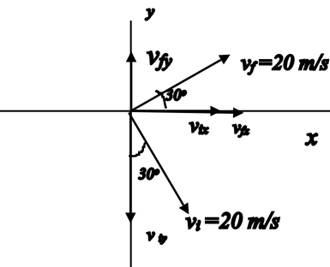
The components of the velocity vector vi are directed along +x and-y axes, hence the y component is assigned a negative sign. Calculate the magnitude of the components substituting the values of the variables in the equation,
The components of the final velocity vector vf are directed along the +x and +y directions, hence the components are positive. Calculate the magnitude of the components of the vector vf using the values of the variables.
Calculate the change in velocity along the x and the y directions.
Calculate the components of the acceleration along the x and the y directions.
Using the values of vix and ax in the equation
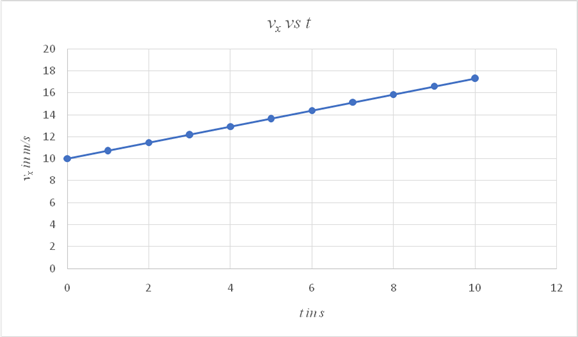
Plot a graph showing the variation of vx with time.
| t in s | vxin m/s |
| 0 | 10 |
| 1 | 10.732 |
| 2 | 11.464 |
| 3 | 12.196 |
| 4 | 12.928 |
| 5 | 13.66 |
| 6 | 14.392 |
| 7 | 15.124 |
| 8 | 15.856 |
| 9 | 16.588 |
| 10 | 17.32 |
Using the values of viy and ay in the equation
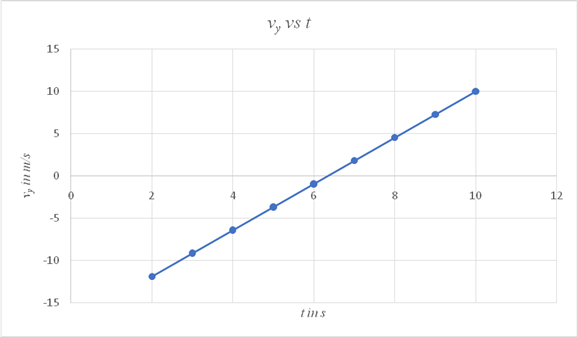
Use the equation in a spread sheet and plot the graph showing the variation of vy with time t.
| X-Values | Y-Values |
| 0 | -17.32 |
| 1 | -14.588 |
| 2 | -11.856 |
| 3 | -9.124 |
| 4 | -6.392 |
| 5 | -3.66 |
| 6 | -0.928 |
| 7 | 1.804 |
| 8 | 4.536 |
| 9 | 7.268 |
| 10 | 10 |
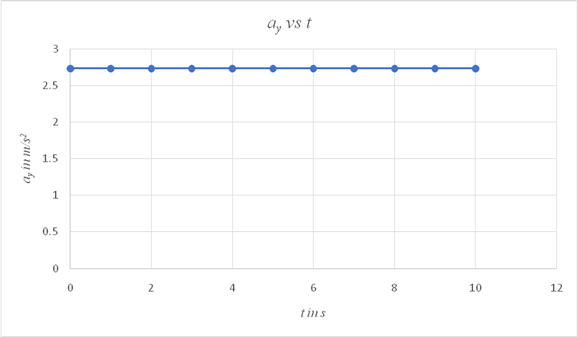
The y component of the acceleration ay is independent of time, since the object's acceleration remains constant during the time interval.
Plot a graph showing the variation of ay with time t.
| t in s | ayin m/s2 |
| 0 | 2.732 |
| 1 | 2.732 |
| 2 | 2.732 |
| 3 | 2.732 |
| 4 | 2.732 |
| 5 | 2.732 |
| 6 | 2.732 |
| 7 | 2.732 |
| 8 | 2.732 |
| 9 | 2.732 |
| 10 | 2.732 |
Conclusion:
The graph showing the variation of vx with time is linear and the value increases from 10 m/s to 17.32 m/s at the end of 10 s.
The graph showing the variation of vy with time is also linear and its value increases from -17.32 m/s to reach a value of 10 m/s at the end of 10 s.
The graph showing the variation of ay with time is a straight line parallel to the time axis, showing that its value is invariant with time.
Thus all the results are consistent with an object moving with a constant acceleration during the time interval of 10s.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS LL W/ 6 MONTH ACCESS
- An oil slick on water is 82.3 nm thick and illuminated by white light incident perpendicular to its surface. What color does the oil appear (what is the most constructively reflected wavelength, in nanometers), given its index of refraction is 1.43? (Assume the index of refraction of water is 1.33.) wavelength color 675 × nm red (1 660 nm)arrow_forwardA 1.50 μF capacitor is charging through a 16.0 Ω resistor using a 15.0 V battery. What will be the current when the capacitor has acquired 1/4 of its maximum charge? Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardIn the circuit shown in the figure (Figure 1), the 6.0 Ω resistor is consuming energy at a rate of 24 J/s when the current through it flows as shown. What are the polarity and emf of the battery E, assuming it has negligible internal resistance? Please explain all steps. I know you need to use the loop rule, but I keep getting the answer wrong.arrow_forward
- If you connect a 1.8 F and a 2.6 F capacitor in series, what will be the equivalent capacitance?arrow_forwardSuppose that a particular heart defibrillator uses a 1.5 x 10-5 Farad capacitor. If it is charged up to a voltage of 7300 volts, how much energy is stored in the capacitor? Give your answer as the number of Joules.arrow_forwardThe voltage difference across an 8.3 nanometer thick cell membrane is 6.5 x 10-5volts. What is the magnitude of the electric field inside this cell membrane? (Assume the field is uniform, and give your answer as the number of Volts per meter... which is the same as the number of Newtons per Coulomb.)arrow_forward
- Three identical capacitors are connected in parallel. When this parallel assembly of capacitors is connected to a 12 volt battery, a total of 3.1 x 10-5 coulombs flows through the battery. What is the capacitance of one individual capacitor? (Give your answer as the number of Farads.)arrow_forwardSuppose you construct your own capacitor by placing two parallel plates at a distance 0.27 meters apart. The plates each have a surface area of 0.64 square meters. What is the capacitance of this setup? (Give your answer as the number of Farads.)arrow_forwardDraw a diagram with the new arrows. No they do not point all towards the center.arrow_forward
- Example In Canada, the Earth has B = 0.5 mŢ, pointing north, 70.0° below the horizontal. a) Find the magnetic force on an oxygen ion (O2) moving due east at 250 m/s b) Compare the |FB| to |FE| due to Earth's fair- weather electric field (150 V/m downward).arrow_forwardFour charges, qa, qb, qa, and qd are fixed at the corners of a square. A charge q that is free to move located at the exact center of the square. Classify the scenarios described according to the force that would be exerted on the center charge q. Assume in each case that q is a positive charge. Do not assume that the fixed charges have equal magnitudes unless the scenario defines such an equality. qa Яс q %b Force is zero Force is to the left Force is to the right Force is undeterminedarrow_forwardCharge qi = -q is located at position (0, d). Charge q = −2q₁ is located at position (d,0). Charge q3 = located at position (2d, 2d). 5qi is y Determine the net electric field Ĕ net at the origin. Enter your expression using ij unit vector notation in terms of the given quantities, the permittivity of free space €0, and exact rational and irrational numbers. d 9₁ d TH net = 92 d d Xarrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill





