
Concept explainers
(a)
The time taken by the rock thrown from the edge of a cliff to reach the ground.
(a)
Answer to Problem 50P
The rock takes 2.93 s to reach the ground.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The depth of the ground from the top of the cliff,
Velocity of projection
,
Angle of projection,
Formula used:
The time taken to reach the ground is determined using the expression
Here,
Calculation:
The path of the rock is shown in the diagram below:
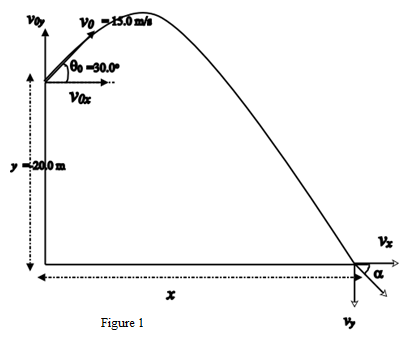
Calculate the value of
Substitute the values of variables in equation (1).
Rewrite the equation as follows:
Solve the quadratic equation.
Take the positive root, since time cannot have a negative value.
Conclusion:
Thus, the rock takes 2.93 s to reach the ground.
(b)
The horizontal distance between the point of projection and the point where the rock lands on the ground.
(b)
Answer to Problem 50P
The rock lands at a horizontal distance of 38.1 m from the point of projection.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Velocity of projection,
Angle of projection,
Time of flight of the rock,
Formula used:
The horizontal component of the rock’s velocity is constant, since no force acts on the rock in the horizontal direction in the absence of air resistance.
The horizontal distance travelled by the rock in a time t is given by,
Here, the horizontal component
Calculation:
Substitute the given values in equation (4) and calculate the value of
Substitute the values of
Conclusion:
Thus, the rock lands at a horizontal distance of 38.1 m from the point of projection.
(c)
The velocity of the rock when it lands on the ground.
(c)
Answer to Problem 50P
The velocity of the rock when it lands on the ground is found to have a magnitude
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The horizontal component of the rock’s initial velocity,
The vertical component of the rock’s initial velocity,
Time of flight of the rock,
Formula used:
The vertical component of the rock’s velocity when it reaches the ground is given by the expression,
The horizontal component of the rock’s velocity when it reaches the ground remains unchanged during its motion. Therefore,
The magnitude of the velocity of the particle when it reaches the ground is given by,
The angle made by the velocity vector to the horizontal is given by the expression,
Calculation:
Calculate the vertical component of the rock’s velocity when it reaches the ground by substituting the values of the variables in equation (5).
Since
Substitute the values of
Substitute the values of
Conclusion:
Thus the velocity of the rock when it lands on the ground is found to have a magnitude
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Physics Fundamentals
- (Figure 1)In each case let w be the weight of the suspended crate full of priceless art objects. The strut is uniform and also has weight w Find the direction of the force exerted on the strut by the pivot in the arrangement (a). Express your answer in degrees. Find the tension Tb in the cable in the arrangement (b). Express your answer in terms of w. Find the magnitude of the force exerted on the strut by the pivot in the arrangement (b). Express your answer in terms of w.arrow_forward(Figure 1)In each case let ww be the weight of the suspended crate full of priceless art objects. The strut is uniform and also has weight w. Find the direction of the force exerted on the strut by the pivot in the arrangement (b). Express your answer in degrees.arrow_forwardA 70.0 cm, uniform, 40.0 N shelf is supported horizontally by two vertical wires attached to the sloping ceiling (Figure 1). A very small 20.0 N tool is placed on the shelf midway between the points where the wires are attached to it. Find the tension in the left-hand wire. Express your answer with the appropriate units.arrow_forward
- Find the total bind Mev. binding energy for 13 Carbon, 6C (atomic mass = 13.0033554)arrow_forwardWhat is the 27 energy absorbed in this endothermic Auclear reaction 2] Al + 'n → 27 Mg + ! H? (The atom mass of "Al is 26.981539u. and that of 11 Mg is 26.984341u) MeVarrow_forwardWhat is the energy released in this nuclear reaction 1 F + "', H-1 O+ He? 19 19 16 (The atomic mass of 1F is 18.998403 u, and that of 20 is 15.9949154) MeV.arrow_forward
- What is the energy released in this B+ nuclear reaction خالد 2½ Al w/ Mg + ie? (The atomic mass of 11 Al is 23.9999394 and that > of 12 Mg is 23.985041 u) MeV.arrow_forwardWhat is the energy released / absorbed in this nuclear reaction 14 N+ & He → » O + ! N? (The atomic mass of 14 N is 14.003074u. 17N+ and that of 10 is 16.9991324). MeVarrow_forwardCan someone help me answer this question thanks.arrow_forward
- Can someone help me with this question thanks.arrow_forward4B. Four electrons are located on the corners of a square, one on each corner, with the sides of the square being 25 cm long. a) Draw a sketch of the scenario and use your sketch to b) Determine the total force (magnitude and direction) on one of the electrons from the other three?arrow_forwardPortfolio Problem 3. A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a speed vo from the floor of a room of height h. It hits the ceiling and then returns to the floor, from which it rebounds, managing just to hit the ceiling a second time. Assume that the coefficient of restitution between the ball and the floor, e, is equal to that between the ball and the ceiling. Compute e.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





