
Concept explainers
Lara’s Landscaping Service has the following chart of accounts:
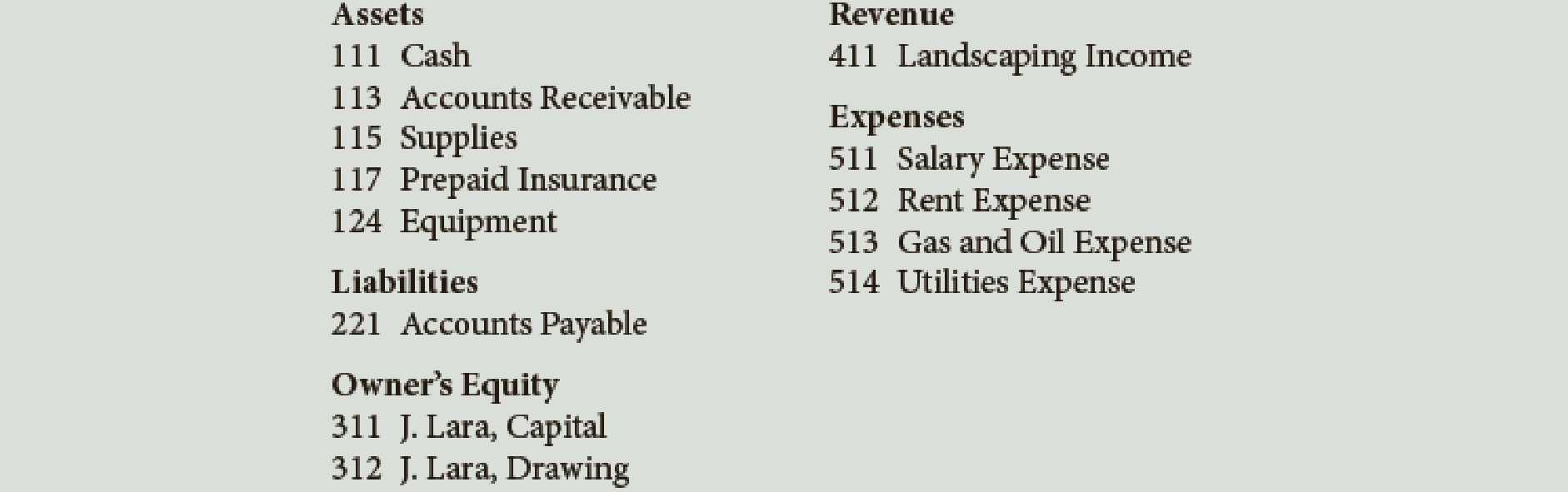
The following transactions were completed by Lara’s Landscaping Service:

Required
- 1. Journalize the transactions in the general journal. Provide a brief explanation for each entry.
- 2. If you are using working papers, write the name of the owner on the Capital and Drawing accounts. (Skip this step if you are using CLGL.)
- 3.
Post the journal entries to the general ledger accounts. (Skip this step if you are using CLGL.) - 4. Prepare a
trial balance dated March 31, 20–.
*If you are using CLGL, use the year 2020 when recording transaction! and preparing reports.
1.
Prepare journal entries for the given transactions.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Debit and credit rules:
- ■ Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in stockholders’ equity accounts.
- ■ Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Prepare journal entries for the given transactions.
Transaction on March 1:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| March | 1 | Cash | 111 | 35,000 | ||
| JL, Capital | 311 | 35,000 | ||||
| (Record cash invested in the business by JL) | ||||||
Table (1)
Description:
- ■ Cash is an asset account. Since cash is invested in the business, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- ■ JL, Capital is an equity account. Since cash is contributed as capital by the owner, equity value increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Transaction on March 4:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| March | 4 | Equipment | 124 | 1,325 | ||
| JL, Capital | 311 | 1,325 | ||||
| (Record equipment invested in the business by JL) | ||||||
Table (2)
Description:
- ■ Equipment is an asset account. Since equipment is invested in the business, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- ■ JL, Capital is an equity account. Since equipment is contributed as capital by the owner, equity value increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Transaction on March 6:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| March | 6 | Equipment | 124 | 915 | ||
| Accounts Payable | 221 | 915 | ||||
| (Record purchase of equipment) | ||||||
Table (3)
Description:
- ■ Equipment is an asset account. Since equipment is bought, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- ■ Accounts Payable is a liability account. Since the payable increased, the liability increased, and an increase in liability is credited.
Transaction on March 7:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| March | 7 | Rent Expense | 512 | 950 | ||
| Cash | 111 | 950 | ||||
| (Record payment of rent expense) | ||||||
Table (4)
Description:
- ■ Rent Expense is an expense account. An increase in expense reduces the equity value, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- ■ Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Transaction on March 9:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| March | 9 | Equipment | 124 | 5,300 | ||
| Cash | 111 | 3,000 | ||||
| Accounts Payable | 221 | 2,300 | ||||
| (Record purchase of equipment) | ||||||
Table (5)
Description:
- ■ Equipment is an asset account. Since equipment is bought, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- ■ Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
- ■ Accounts Payable is a liability account. Since the payable increased, the liability increased, and an increase in liability is credited.
Transaction on March 10:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| March | 10 | Prepaid Insurance | 117 | 1,800 | ||
| Cash | 111 | 1,800 | ||||
| (Record payment of insurance in advance) | ||||||
Table (6)
Description:
- ■ Prepaid Insurance is an asset account. Since insurance is paid in advance, it is recorded as asset until it is consumed. So, asset value is increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- ■ Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Transaction on March 13:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| March | 13 | Accounts Receivable | 113 | 2,832 | ||
| Landscaping Income | 411 | 2,832 | ||||
| (Record services performed on account) | ||||||
Table (7)
Description:
- ■ Accounts Receivable is an asset account. The amount is increased because amount to be received increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- ■ Landscaping Income is a revenue account. Since gains and revenues increase equity, and an increase in equity is credited, Landscaping Income account is credited.
Transaction on March 14:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| March | 14 | Supplies | 113 | 380 | ||
| Accounts Payable | 411 | 380 | ||||
| (Record supplies bought on account) | ||||||
Table (8)
Description:
- ■ Supplies is an asset account. Since store supplies are bought, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- ■ Accounts Payable is a liability account. Since the payable increased, the liability increased, and an increase in liability is credited.
Transaction on March 15:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| March | 15 | Accounts Receivable | 113 | 2,832 | ||
| Landscaping Income | 411 | 2,832 | ||||
| (Record services performed on account) | ||||||
Table (9)
Description:
- ■ Accounts Receivable is an asset account. The amount is increased because amount to be received increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- ■ Landscaping Income is a revenue account. Since gains and revenues increase equity, and an increase in equity is credited, Landscaping Income account is credited.
Transaction on March 17:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| March | 17 | Gas and Oil Expense | 513 | 180 | ||
| Cash | 111 | 180 | ||||
| (Record payment of oil and gas expense) | ||||||
Table (10)
Description:
- ■ Gas and Oil Expense is an expense account. An increase in expense reduces the equity value, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- ■ Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Transaction on March 19:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| March | 19 | Cash | 111 | 1,864 | ||
| Landscaping Income | 411 | 1,864 | ||||
| (Record revenue earned and received) | ||||||
Table (11)
Description:
- ■ Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- ■ Landscaping Income is a revenue account. Since gains and revenues increase equity, and an increase in equity is credited, Landscaping Income account is credited.
Transaction on March 22:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| March | 22 | Accounts Payable | 221 | 500 | ||
| Cash | 111 | 500 | ||||
| (Record cash paid on account) | ||||||
Table (12)
Description:
- ■ Accounts Payable is a liability account. Since the payable decreased, the liability decreased, and a decrease in liability is debited.
- ■ Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Transaction on March 24:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| March | 24 | Cash | 111 | 800 | ||
| Accounts Receivable | 113 | 800 | ||||
| (Record cash received on account) | ||||||
Table (13)
Description:
- ■ Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- ■ Accounts Receivable is an asset account. Since amount to be received has decreased, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Transaction on March 28:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| March | 28 | Accounts Receivable | 113 | 1,400 | ||
| Landscaping Income | 411 | 1,400 | ||||
| (Record services performed on account) | ||||||
Table (14)
Description:
- ■ Accounts Receivable is an asset account. The amount is increased because amount to be received increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- ■ Landscaping Income is a revenue account. Since gains and revenues increase equity, and an increase in equity is credited, Landscaping Income account is credited.
Transaction on March 29:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| March | 29 | Utilities Expense | 514 | 260 | ||
| Cash | 111 | 260 | ||||
| (Record payment of utilities expense) | ||||||
Table (15)
Description:
- ■ Utilities Expense is an expense account. An increase in expense reduces the equity value, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- ■ Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Transaction on March 30:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| March | 30 | Salary Expense | 511 | 1,850 | ||
| Cash | 111 | 1,850 | ||||
| (Record payment of salary expense) | ||||||
Table (16)
Description:
- ■ Salary Expense is an expense account. An increase in expense reduces the equity value, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- ■ Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Transaction on March 31:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| March | 31 | JL, Drawing | 312 | 1,500 | ||
| Cash | 111 | 1,500 | ||||
| (Record cash withdrawn by JL for personal use) | ||||||
Table (17)
Description:
- ■ JL, Drawing is a contra-capital account. The contra-capital accounts decrease the equity value, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- ■ Cash is an asset account. Since cash is withdrawn, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
2.
Indicate the names of owner above the Capital and Drawing accounts.
Explanation of Solution
Owners’ equity: The financial interest of the owners to invest in the business is referred to as owners’ equity or capital. Owners’ equity comprises of capital, drawings, revenues and expenses.
Write the name of owner, JL before the capital and drawings terms and name those accounts as JL, Capital account and JL, Drawing account.
3.
Post the journalized transactions in the ledger accounts.
Explanation of Solution
Ledger: Ledger is a book in which the accounts are summarized and grouped from the transactions recorded in the journal.
Post the journalized transactions in the ledger accounts.
| ACCOUNT Cash ACCOUNT NO. 111 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| March | 1 | 1 | 35,000 | 35,000 | |||
| 7 | 1 | 950 | 34,050 | ||||
| 9 | 1 | 3,000 | 31,050 | ||||
| 10 | 1 | 1,800 | 29,250 | ||||
| 17 | 1 | 180 | 29,070 | ||||
| 19 | 1 | 1,864 | 30,934 | ||||
| 22 | 1 | 500 | 30,434 | ||||
| 24 | 1 | 800 | 31,234 | ||||
| 29 | 1 | 260 | 30,974 | ||||
| 30 | 1 | 1,850 | 29,124 | ||||
| 31 | 1 | 1,500 | 27,624 | ||||
Table (18)
| ACCOUNT Accounts Receivable ACCOUNT NO. 113 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| March | 13 | 1 | 3,895 | 3,895 | |||
| 15 | 1 | 2,832 | 6,727 | ||||
| 24 | 1 | 800 | 5,927 | ||||
| 28 | 1 | 1,830 | 7,757 | ||||
Table (19)
| ACCOUNT Supplies ACCOUNT NO. 115 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| March | 14 | 1 | 380 | 380 | |||
Table (20)
| ACCOUNT Prepaid Insurance ACCOUNT NO. 117 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| March | 10 | 1 | 1,800 | 1,800 | |||
Table (21)
| ACCOUNT Equipment ACCOUNT NO. 124 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| March | 4 | 1 | 1,325 | 1,325 | |||
| 6 | 1 | 915 | 2,240 | ||||
| 9 | 1 | 5,300 | 7,540 | ||||
Table (22)
| ACCOUNT Accounts Payable ACCOUNT NO. 221 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| March | 6 | 1 | 915 | 915 | |||
| 9 | 1 | 2,300 | 3,215 | ||||
| 14 | 1 | 380 | 3,595 | ||||
| 22 | 1 | 500 | 3,095 | ||||
Table (23)
| ACCOUNT JL, Capital ACCOUNT NO. 311 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| March | 1 | 1 | 35,000 | 35,000 | |||
| 4 | 1 | 1,325 | 36,325 | ||||
Table (24)
| ACCOUNT JL, Drawing ACCOUNT NO. 312 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| March | 31 | 1 | 1,500 | 1,500 | |||
Table (25)
| ACCOUNT Landscaping Income ACCOUNT NO. 411 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| March | 13 | 1 | 3,895 | 3,895 | |||
| 15 | 1 | 2,832 | 6,727 | ||||
| 19 | 1 | 1,864 | 8,591 | ||||
| 28 | 1 | 1,830 | 10,421 | ||||
Table (26)
| ACCOUNT Salary Expense ACCOUNT NO. 511 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| March | 30 | 1 | 1,850 | 1,850 | |||
Table (27)
| ACCOUNT Rent Expense ACCOUNT NO. 512 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| March | 7 | 1 | 950 | 950 | |||
Table (28)
| ACCOUNT Gas and Oil Expense ACCOUNT NO. 513 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| March | 17 | 1 | 180 | 180 | |||
Table (29)
| ACCOUNT Utilities Expense ACCOUNT NO. 514 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| March | 29 | 1 | 260 | 260 | |||
Table (30)
4.
Prepare the trial balance for L’s Landscaping Service as at March 31, 20--.
Explanation of Solution
Trial balance: Trial balance is a summary of all the asset, liability, and equity accounts and their balances.
Prepare the trial balance for L’s Landscaping Service as at March 31, 20--.
| L’s Landscaping Service | ||
| Trial Balance | ||
| March 31, 20-- | ||
| Account Title | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | $27,624 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 7,757 | |
| Supplies | 380 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 1,800 | |
| Equipment | 7,540 | |
| Accounts Payable | $3,095 | |
| JL, Capital | 36,325 | |
| JL, Drawing | 1,500 | |
| Landscaping Income | 10,421 | |
| Salary Expense | 1,850 | |
| Rent Expense | 950 | |
| Gas and Oil Expense | 180 | |
| Miscellaneous Expense | 260 | |
| Total | $49,841 | $49,841 |
Table (31)
Hence, the debit and credit total of trial balance of L’s Landscaping Service at March 31, 20-- is 49,841.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career Approach
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
Intermediate Accounting (2nd Edition)
Marketing: An Introduction (13th Edition)
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains (12th Edition) (What's New in Operations Management)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
- Please give me true answer this financial accounting questionarrow_forwardRK Co. sells snowboards. Each snowboard requires direct materials for $140, direct labor for $55, and variable overhead of $64. The company expects fixed overhead costs of $673,000 and fixed selling and administrative costs of $160,000 for the next year. It expects to produce and sell 11,900 snowboards in the next year. What will be the selling price per unit if RK uses a mark-up of 17% of the total cost?arrow_forwardWhat amount should watch of the three assets ne recorded?arrow_forward
 College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





