
EBK THE ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF LINEAR C
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781119140320
Author: Toussaint
Publisher: VST
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 3.91P
Design two interface circuits in Figure P3-91 so that the power delivered to the load is 100 mW. In one case use a series interface resistor, and in the second case use a parallel resistor to attain the same result. Evaluate your interface circuits and determine which one results in the source delivering less power.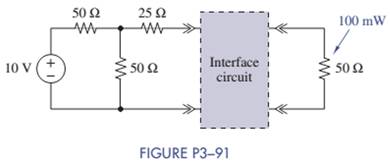
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Don't use ai to answer I will report you answer
The former expert solved the question, but I didn't
understand how he simplified the fractions.
A communication satellite is in stationary (synchronous) orbit about the carch (assume
altitude of 22.300 statute miles). Its transmitter generates 8.0 W. Assume the transmit-
ting antenna is isotropic. Its signal is received by the 210-ft diameter tracking parabo-
loidal antenna on the earth at the NASA tracking station at Goldstone, California. Also
assume no resistive loss in either antenna, perfect polarization match, and perfect
impedance match at both antennas. At a frequency of 2 GHz, determine the:
(a) power density (in watts/m²) incident on the receiving antenna.
(b) power received by the ground-based antenna whose gain is 60 dB.
Don't use ai to answer I will report you answer
Chapter 3 Solutions
EBK THE ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF LINEAR C
Ch. 3 - Formulate node-voltage equations for the circuit...Ch. 3 - (a) Formulate node-voltage equations for the...Ch. 3 - (a) Formulate node-voltage equations for the...Ch. 3 - Formulate node-voltage equations for the circuit...Ch. 3 - (a) Formulate node-voltage equations for the...Ch. 3 - Choose a ground wisely and formulate node-voltage...Ch. 3 - The following are a set of node-voltage equations;...Ch. 3 - Choose a ground wisely and formulate node-voltage...Ch. 3 - Formulate node-voltage equations for the circuit...Ch. 3 - Formulate node-voltage equations for the circuit...
Ch. 3 - (a) Formulate mesh-current equations for the...Ch. 3 - (a) Formulate mesh-current equations for the...Ch. 3 - (a) Formulate mesh-current equations for the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.16PCh. 3 - Formulate mesh-current equations for the circuit...Ch. 3 - For the circuit of figure P3-19 solve for iA,iB,...Ch. 3 - Formulate mesh-current equations for the circuit...Ch. 3 - The circuit in Figure P3-21 seems to require two...Ch. 3 - Formulate mesh-current equations for the circuit...Ch. 3 - Use simple engineering intuition to find the input...Ch. 3 - In Figure P3-24 all of the resistors are 1k and...Ch. 3 - Use Figure P3-24 and MATLAB to solve the following...Ch. 3 - Formulate mesh-current equations for the circuit...Ch. 3 - Find vO for the block diagram shown in figure...Ch. 3 - Design a voltage-divider circuit that will realize...Ch. 3 - Design a current-divider circuit that will realize...Ch. 3 - Using a single resistor, design a circuit that...Ch. 3 - Find the proportionality constant K=vO/vS for the...Ch. 3 - Find the proportionality constant K=iO/vS for the...Ch. 3 - Find the proportionality constant K=vO/iS for the...Ch. 3 - Find the proportionality constant K=iO/iS for the...Ch. 3 - Find the proportionality constant K=vO/vS for the...Ch. 3 - Use the unit output method to find K and vO in...Ch. 3 - Use the unit output method to find K and vO in...Ch. 3 - Use the unit output method to find K in Figure...Ch. 3 - Use the superposition principle to find vO in...Ch. 3 - Use the superposition principle to find vO in...Ch. 3 - Use the superposition principle to find vO in...Ch. 3 - (a) Use the superposition principle to find vO in...Ch. 3 - A linear circuit containing two sources drives a...Ch. 3 - A block diagram of a linear circuit is shown in...Ch. 3 - A certain linear circuit has four input voltages...Ch. 3 - When the current source is turned off in the...Ch. 3 - For the circuit in Figure P3—51, find the Thévenin...Ch. 3 - For the circuit in Figure P3—52, find the Thévenin...Ch. 3 - For the circuit of Figure P3—53, find the Thévenin...Ch. 3 - Find the Thévenin or Norton equivalent circuit...Ch. 3 - Find the Thévenin or Norton equivalent circuit...Ch. 3 - Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit seen by RL in...Ch. 3 - Find the Norton equivalent seen by RL in Figure...Ch. 3 - You need to determine the Thévenin equivalent...Ch. 3 - Find the Thévenin equivalent seen by RL in figure...Ch. 3 - The purpose of this problem is to use Thévenin...Ch. 3 - The circuit in Figure P3-62 was solved earlier...Ch. 3 - Assume that Figure P3-63 represents a model of the...Ch. 3 - The iv characteristic of the active circuit...Ch. 3 - You have successfully completed the first course...Ch. 3 - The Thévenin equivalent parameters of a practical...Ch. 3 - Use a sequence of source transformations to find...Ch. 3 - The circuit in Figure P3-68 provides power to a...Ch. 3 - A nonlinear resistor is connected across a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.71PCh. 3 - Find the Norton equivalent seen by RL in Figure...Ch. 3 - Find the Thévenin equivalent seen by RL in Figure...Ch. 3 - Find the Thévenin equivalent seen by RL in Figure...Ch. 3 - For the circuit of Figure P3-75, find the value of...Ch. 3 - For the circuit of Figure P3-76, find the value of...Ch. 3 - The resistance R in Figure P3-77 is adjusted until...Ch. 3 - When a 5-k resistor is connected across a...Ch. 3 - Find the value of R in the circuit of Figure P3-79...Ch. 3 - For the circuit of Figure P3-80, find the value of...Ch. 3 - A 1-k load needs 10 mA to operate correctly....Ch. 3 - A practical source delivers 25 mA to a load. The...Ch. 3 - A 10-V source is shown in Figure P3-83 that is...Ch. 3 - (a)Select RL and design an interface circuit for...Ch. 3 - The source in Figure P3-85 has a 100-mA output...Ch. 3 - Figure P3-86 shows an interface circuit connecting...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.87PCh. 3 - In this problem, you will design two interface...Ch. 3 - Two teams are competing to design the interface...Ch. 3 - The bridge-T attenuation pad shown in FigureP3-90...Ch. 3 - Design two interface circuits in Figure P3-91 so...Ch. 3 - Design the interface circuit in Figure P3-91 so...Ch. 3 - Design the interface circuit in Figure P3-93 so...Ch. 3 - It is claimed that both interface circuits in...Ch. 3 - Audio Speaker Resistance-Matching Network A...Ch. 3 - Interface Circuit Design Using no more than three...Ch. 3 - Battery Design A satellite requires a battery with...Ch. 3 - Design Interface Competition The output of a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.106IP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A communication satellite is in stationary (synchronous) orbit about the earch (assume altitude of 22.300 statute miles). Its transmitter generates 8.0 W. Assume the transmit- ting antenna is isotropic. Its signal is received by the 210-ft diameter tracking parabo- loidal antenna on the earth at the NASA tracking station at Goldstone, California. Also assume no resistive loss in either antenna, perfect polarization match, and perfect impedance match at both antennas. At a frequency of 2 GHz. determine the: (a) power density (in watts/m²) incident on the receiving antenna. (b) power received by the ground-based antenna whose gain is 60 dB.arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardA plane wave traveling in z-direction through a medium with &=8, μ-2 and has the electric and magnetic field intensity at z=0 shown in Fig. 6.1 and Fig. 6.2, respectively. Utilize the provided information to find the following: (a) w (b) The intrinsic impedance of the medium © B (d) a (e) The expression of the magnetic field intensity, H (f) The time-average power carried by the wave Magnetic Field Intensity (mA/m) Electric Field Intensity (V/m) 0.5 0.4- 0.3 0.2 ཧཱུྃ༔ཤྲུསྦྱ ཌུ ཋ ; སྟྲི " ° ཝཱ 0.1 -0.5 Ex -2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 Fig 6.2 Hy 2.0 Time (ns)². -2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0; 0.5 1.0 Time (ns) 2.0 0.083 ns or 0.0415 Tarrow_forward
- Please help mearrow_forwardPlease help mearrow_forward3.7 The AM signal s(t) = Ac[1+kam(t)] cos(2nfct) is applied to the system shown in Figure P3.7. Assuming that |kam(t) 2W, show that m(t) can be obtained from the square-rooter output U3(t). s(t) Squarer v1(t) Low-pass 12(t) Square- filter ra(t) rooter V₁ (t) = 5² (t) 13(1)=√√12 (1) Figure P3.7arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Nodal Analysis for Circuits Explained; Author: Engineer4Free;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f-sbANgw4fo;License: Standard Youtube License