
Concept explainers
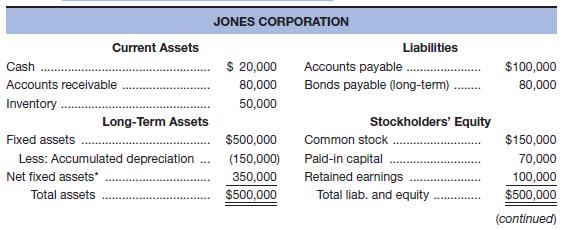
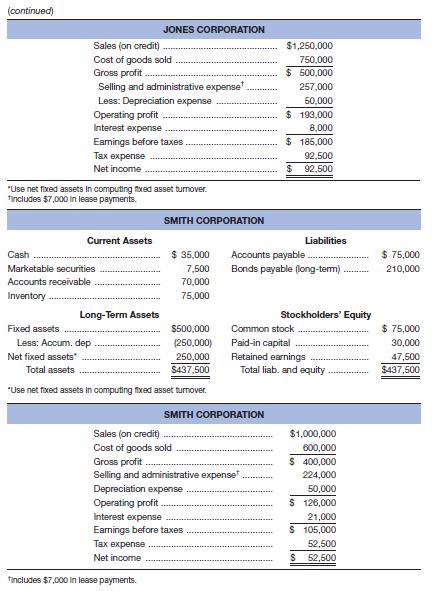
Given the financial statements for Jones Corporation and Smith Corporation shown here:
a. To which one would you, as credit manager for a supplier, approve the extension of (short-term) trade credit? Why? Compute all ratios before answering.
b. In which one would you buy stock? Why?
a.
To calculate: The relevant ratios so that the decision for the extension of short term trade credit can be taken.
Introduction:
Shortterm trade credit:
It is the type of credit that is granted to a business or an individual or a fixed loan for a period of not more than 12 months or 1 year.
Answer to Problem 37P
The Smith Corporation would get the extension of the short term trade credit as their liquidity ratios are better than those of the Jones Corporation; the suppliers and lenders are most concerned with the liquidity ratios.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of ratios for the Smith Corporation:
Calculation of current ratio:
Calculation of quick ratio:
Calculation of debt to total asset ratio:
Calculation of times interest ratio:
Calculation of fixed charge ratio:
Calculation of ratios for the Jones Corporation:
Calculation of current ratio:
Calculation of quick ratio:
Calculation of debt to total asset ratio:
Calculation of times interest ratio:
Calculation of fixed charge ratio:
b.
To determine: The company whose stock should be bought.
Introduction:
Stock:
Also termed as ordinary shares, it is a type of security that represents the corporate equity ownership. It is the best means to earn real rate of return ahead of inflation in the long run.
Answer to Problem 37P
The stocks of the Jones Corporation should be bought as their profit margin and return on assets are higher compared to the Smith Corporation; shareholders are mostly concerned with profitability.
But the return on equity is more for the Smith Corporation because it has taken a bigger financial risk. The times interest ratio and fixed charges ratio are higher for the Jones Corporation, which clearly reflects that their interest and fixed charges are well covered.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of ratios for the Smith Corporation:
Calculation of profit margin:
Calculation of return on assets:
Calculation of return on equity:
Calculation of debt to total asset ratio:
Calculation of times interest ratio:
Calculation of fixed charge ratio:
Calculation of ratios for the Jones Corporation:
Calculation of profit margin:
Calculation of return on assets:
Calculation of return on equity:
Calculation of debt to total asset ratio:
Calculation of times interest ratio:
Calculation of fixed charge ratio:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Foundations of Financial Management Format: Loose-leaf
- What are the six types of alternative case study compositional structures (formats)used for research purposes, such as: 1. Linear-Analytical, 2. Comparative, 3. Chronological, 4. Theory Building, 5. Suspense and 6. Unsequenced. Please explainarrow_forwardFor an operating lease, substantially all the risks and rewards of ownership remain with the _________. QuestFor an operating lease, substantially all the risks and rewards of ownership remain with the _________: A) Tenant b) Lessee lessor none of the above tenant lessee lessor none of the aboveLeasing allows the _________ to acquire the use of a needed asset without having to make the large up-front payment that purchase agreements require Question 4 options: lessor lessee landlord none of the abovearrow_forwardHow has AirBnb negatively affected the US and global economy? How has Airbnb negatively affected the real estate market? How has Airbnb negatively affected homeowners and renters market? What happened to Airbnb in the Tax Dispute in Italy?arrow_forward
- How has AirBnb positively affected the US and global economy? How has Airbnb positively affected the real estate market? How has Airbnb positively affected homeowners and renters market?arrow_forwardD. (1) Consider the following cash inflows of a financial product. Given that the market interest rate is 12%, what price would you pay for these cash flows? Year 0 1 2 3 4 Cash Flow 160 170 180 230arrow_forwardExplain why financial institutions generally engage in foreign exchange tradingactivities. Provide specific purposes or motivations behind such activities.arrow_forward
- A. In 2008, during the global financial crisis, Lehman Brothers, one of the largest investment banks, collapsed and defaulted on its corporate bonds, causing significant losses for bondholders. This event highlighted several risks that investors in corporate bonds might face. What are the key risks an investor would encounter when investing in corporate bonds? Explain these risks with examples or academic references. [15 Marks]arrow_forwardTwo companies, Blue Plc and Yellow Plc, have bonds yielding 4% and 5.3%respectively. Blue Plc has a credit rating of AA, while Yellow Plc holds a BB rating. If youwere a risk-averse investor, which bond would you choose? Explain your reasoning withacademic references.arrow_forwardB. Using the probabilities and returns listed below, calculate the expected return and standard deviation for Sparrow Plc and Hawk Plc, then justify which company a risk- averse investor might choose. Firm Sparrow Plc Hawk Plc Outcome Probability Return 1 50% 8% 2 50% 22% 1 30% 15% 2 70% 20%arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning





