
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The hybridization of each non-hydrogen atom in Octocrylene is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
A hybrid atomic orbital is a cross between two or more pure AOs from the valence shell of a single atom. Typically
Answer to Problem 3.54P
Atoms shown in blue color are
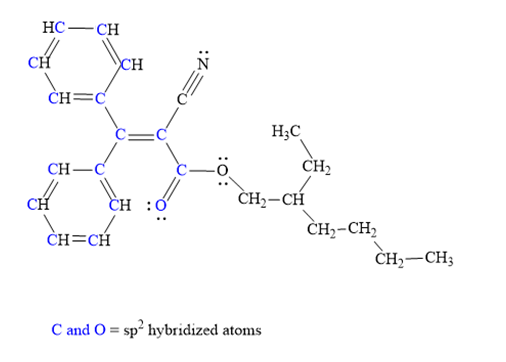
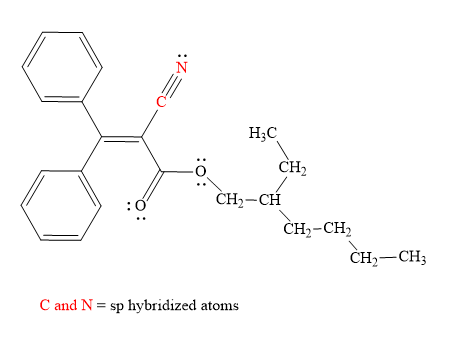
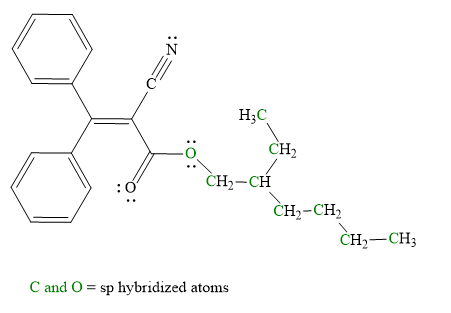
Explanation of Solution
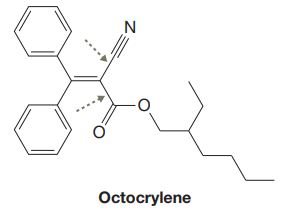
The given structure for Octocrylene is:
The above molecule has two benzene rings. Each carbon atom in the benzene ring has three electron groups: two single bonds and one double bond. Thus, the geometry for all these carbon atoms must be trigonal planar and hybridization must be

The triple bonded carbon atom has two electron groups: one single bond and one triple bond. Thus, the hybridization of this carbon atom must be

The single bonded oxygen atom and each carbon atom in the alkyl chain has four electrons groups. Thus, its geometry must be tetrahedral and hybridization must be

Hybridization of all non-hydrogen atoms is shown in three figures as above.
(b)
Interpretation:
All the atoms bonded to the acyclic
Concept introduction:
Free rotation can occur about single bonds but not about double bonds. According to the VSEPR theory, if an atom has three electron groups: three bonds, or two bonds and one pair of electrons then, the atom is said to be
Answer to Problem 3.54P
Explanation of Solution
The given structure for Octocrylene is:
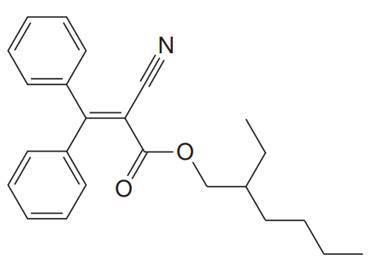
In the above structure, the
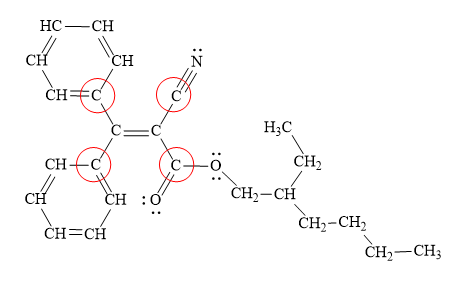
All the atoms bonded to the acyclic
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined if there are two unique configurations possible about the acyclic
Concept introduction:
No free rotation takes place about the double bonds. Hence, in such compounds, molecules that differ by the exchange of two groups on one of the doubly bonded atoms are said to have different configurations. It is a cis configuration if the two non-hydrogen substituents are on present the same side of the double bond, and it is trans if they are on the opposite sides.
Answer to Problem 3.54P
It is not possible to have two unique configurations about the acyclic
Explanation of Solution
The given structure for Octocrylene is:
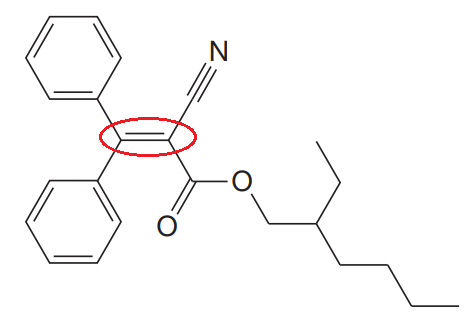
In the structure above, the acyclic
Thus, it is not possible to have two unique configurations about the acyclic
For a
(d)
Interpretation:
Out of the two indicated
Concept introduction:
The bond distance decrease and bond energies increase as the hybridization of the atom goes changes
Answer to Problem 3.54P
The
Explanation of Solution
The given structure for Octocrylene is:
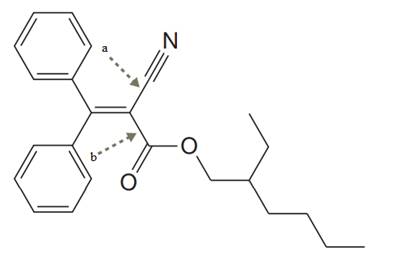
In the structure above, the two
The two carbon atoms involved in ‘a’ type of are
The two carbon atoms involved in ‘b’ type of bond are both
The bond distance decrease and bond energies increase as the hybridization of the atom goes changes
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
ORG CHEM W/ EBOOK & SW5 + STUDY GUIDE
- Nonearrow_forwardPart II. Given below are the 'H-NMR spectrum at 300 MHz in CDC13 and mass spectrum using electron ionization of compound Brian. The FTIR of the said compound showed a strong peak at 1710 cm"). Determine the following: (a) molecular Formula and Degree of unsaturation of compound Brian (b) Basing on the given H-NMR spectrum tabulate the following (i) chemical shifts (ii) integration, ciii) multiplicity and (iv) interferences made for each signal (c) Draw the structure of compound Brian. ) ΕΙ 43 41 27 71 114 (M+) Hmmm 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 1H NMR spectrum 300 MHz in CDCl3 2.0 alle 1.0arrow_forwardThe iron-iron carbide phase diagram. In the diagram, the letter L indicates that it is a liquid. Indicate what its components are. Temperature (°C) 1600 10 Composition (at% C) 15 25 1538°C -1493°C 8 1400 1200 1394°C y+L L 2500 1147°C y. Austenite 2.14 4.30 2000 1000 912°C y + Fe3C 800ㅏ 0.76 0.022 600 a, Ferrite a + Fe3C 400 0 (Fe) Composition (wt% C) 727°C 1500 Cementite (Fe3C) 1000 6 6.70 Temperature (°F)arrow_forward
- Part V. Choose which isomer would give the 1H-NMR spectrum below. Justify your reasoning by assigning important signals to the Corresponding protons of the correct molecule. A D on of of of H H 88 2 90 7.8 7.6 7.4 80 5 6 [ppm] 7.2 6.8 6.6 6.4 ō [ppm]arrow_forwardShow work with explanation. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardQ7. a. Draw the line-bond structure of the major product for the following reaction, if a reaction occurs, assume monohalogenation. b. Calculate the product ratios using the following information (hint: use the number of hydrogens in each category present to calculate the ratios). Chlorination: 1° Reactivity=1 2° Reactivity=4 Heat + Cl2 3° Reactivity=5arrow_forward
- Please correct answer and don't use hand rating and don't use Ai solutionarrow_forwardQ10: Alkane halogenation a. Give the name and structures of the five isomeric hexanes. Page 4 of 5 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 Recitations b. For each isomer, give all the free radical monochlorination and monobromination products that are structurally isomeric.arrow_forwardQ9. The insecticide DDT (in the box below) is useful in controlling mosquito populations and has low toxicity to humans, but is dangerous to birds and fish. Hoping to alleviate the dangers, little Johnny Whizbang, an aspiring chemist, proposes a new version of DDT ("Bromo-DDT") and shows his synthesis to his boss. Will Johnny Whizbang's synthesis work? Or will he be fired? Assume there is an excess of bromine and polybrominated products can be separated. Explain why. CH3 Br2, light CBR3 ok-ok Br Br Br Br CI "Bromo-DDT" CCl 3 DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) CIarrow_forward
- Differentiate the terms Monotectic, Eutectic, Eutectoid, Peritectic, Peritectoid.arrow_forwardQ5. Predict the organic product(s) for the following transformations. If no reaction will take place (or the reaction is not synthetically useful), write "N.R.". Determine what type of transition state is present for each reaction (think Hammond Postulate). I Br₂ CH3 F2, light CH3 Heat CH3 F₂ Heat Br2, light 12, light CH3 Cl2, lightarrow_forwarda. For the following indicated bonds, rank them in order of decreasing AH° for homolytic cleavage. Based on your answer, which bond would be most likely to break homolytically? (a) (c) H3C CH3 .CH3 CH3 CH3 (b) Page 1 of 5 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 Recitations b. Draw all the possible radical products for 2-methylbutane, and determine which bond is most likely to be broken.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

