
Certain solid substances, known as hydrated compounds, have well-defined molecular ratios of water to some other species. For example, calcium sulfate dihydrate (commonly known as gypsum, CaSO42H2O), has 2 moles of water per mole of calcium sulfate; alternatively, it may be said that 1 mole of gypsum consists of 1 mole of calcium sulfate and 2 moles of water. The water in such substances is called water of hydration. (More information about hydrated salts is given in Chapter 6.)
In order to eliminate the discharge of sulfuric acid into the environment, a process has been developed in which the acid is reacted with aragonite (CaCO3) to produce calcium sulfate. The calcium sulfate then comes out of solution in a crystallizer to form a slurry (a suspension of solid particles in a liquid) of solid gypsum particles suspended in an aqueous CaSO4 solution. The slurry flows front tlte crystallizer to a filter in which the particles arc collected as a filter cake. The filter cake, which is 95.0 wt% solid gypsum and the remainder CaSO4 solution, is fed to a dryer in which all water (including the water of hydration in the crystals) is driven off to yield anhydrous (water-free) CaSO4 as product A flowchart and relevant process data arc given below.
Solids content of slurry leaving crystallizer 0.35 kg CaSO4-2H2O/L slurry CaSO4 content of slurry liquid: 0.209g CaSO4/100g H2O Specific gravities: CaSO4-2H2O(s), 2.32; liquid solutions, 1.05
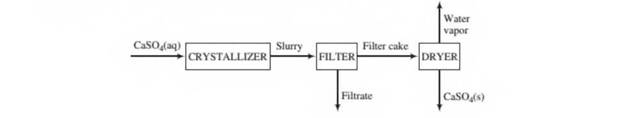
- Briefly explain in your own words the functions of the three units (crystallizer, filter, and dryer).
- Take a basis of one liter of solution leaving the crystallizer and calculate tlte mass (kg) and volume (L) of solid gypsum, the mass of CaSO4 in the gypsum, and the mass of CaSO4 in the liquid solution.
- Calculate the percentage recovery of CaSO4—that is, the percentage of the total CaSO4(precipitated plus dissolved) leaving the crystallizer recovered as solid anhydrous CaSO4.
- List five potential negative consequences of discharging H2SO4 into the river passing the plant.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
ELEM PRIN OF CHEMICAL PROC(LL)+NEXTGEN
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- Problem 1 Marks: 60 Section: 1a): 30 marks, Section 1b):30 marks A laboratory scale fluidized bed is considered for studying a catalytic ozone decomposition. a) It is requested to derive model equations under the following assumptions: ■ Operation of the catalytic reactor under steady state conditions, There is no influence of thermal ozone decomposition reactions. The fluidized bed includes bubbles and dense phase. □ The dense phase can be simulated using a CSTR The fluidized bed bubbles contain catalyst particles and can be simulated as a DSTR (batch). □ The jets contain particles and can be simulated with a PFR. The influence of the freeboard has to be considered using a PFR model. The available catalytic reaction rate model is r (moles/gcat.s)= -k CA b) Same than on a) under unsteady state conditions, using an absorbable and reactive tracer. Note: A step-by step derivation of the model equations is required here. A quick answer will not do. Problem 2 Marks: 40 Section 2a: 30 marks,…arrow_forwardPenicillin process Penicillium chrysogenum is used to produce penicillin in a 90,000-litre fermenter. The volumetric rate of oxygen uptake by the cells ranges from 0.45 to 0.85 mmol l^−1 min^−1 depending on time during the culture. Power input by stirring is 2.9 W l^−1. Estimate the cooling requirements.arrow_forwardProduction of bakers’ yeast Bakers’ yeast is produced in a 50,000-litre fermenter under aerobic conditions. The carbon substrate is sucrose; ammonia is provided as the nitrogen source. The average biomass composition is CH_1.83O_0.55N_0.17 with 5% ash. Under conditions supporting efficient growth, biomass is the only major product and the biomass yield from sucrose is 0.5 g g^−1. If the specific growth rate is 0.45 h^−1, estimate the rate of heat removal required to maintain constant temperature in the fermenter when the yeast concentration is 10 g l^−1.arrow_forward
- Sensible energy change Calculate the enthalpy change associated with the following processes:(a) m-Cresol is heated from 25°C to 100°C(b) Ethylene glycol is cooled from 20°C to 10°C(c) Succinic acid is heated from 15°C to 120°C(d) Air is cooled from 150°C to 65°Carrow_forward▼ Enzyme conversion An immobilised enzyme process is used in an ice-cream factory to hydrolyse lactose (C12H22O11) to glucose (C6H12O6) and galactose (C6H1206): C12H22O11 + H2O →→ C6H12O + C6H12O6 Gel beads containing ß-galactosidase are packed into a column reactor; 2500 kg of lactose enters the reactor per day as a 10% solution in water at 25°C. The reactor operates at steady state and 32°C; all of the lactose is converted. Because the heat of reaction for enzyme conversions is not as great as for cell culture, sensible heat changes and heats of mixing cannot be ignored. Lactose Water Ah (kJ gmol¹) C, (cal g¹ ºC-¹) Ahm (kcal gmol¹) 3.7 -5652.5 0.30 1.0 Glucose -2805.0 0.30 5.6 Galactose -2805.7 0.30 5.6 (a) What is the standard heat of reaction for this enzyme conversion? (b) Estimate the heating or cooling requirements for this process. State explicitly whether heating or cooling is needed.arrow_forwardBacterial production of alginate Azotobacter vinelandii is investigated for production of alginate from sucrose. In a continuous fermenter at 28°C with ammonia as nitrogen source, the yield of alginate was found to be 4 g g^−1 oxygen consumed. It is planned to produce alginate at a rate of 5 kg h^−1. Since the viscosity of alginate in aqueous solution is considerable, energy input due to mixing the broth cannot be neglected. The fermenter is equipped with a flat-blade disc turbine; at a satisfactory mixing speed and air flow rate, the power requirements are estimated at 1.5 kW. Calculate the cooling requirements.arrow_forward
- Preheating nutrient medium Steam is used to heat nutrient medium in a continuous-flow process. Saturated steam at 150°C enters a coil on the outside of the heating vessel and is completely condensed. Liquid medium enters the vessel at 15°C and leaves at 44°C. Heat losses from the jacket to the surroundings are estimated as 0.22 kW. If the flow rate of medium is 3250 kg h^−1 and its heat capacity is 0.9 cal g^−1 °C^−1, how much steam is required?arrow_forwardQ3] Determine the optimal operating conditions (XA, t, and CR) in a mixed flow reactor to maximize the concentration of R (CR) in the effluent, where an aqueous feed A with an initial concentration of CA0-40 mol/m³ enters the reactor, undergoes decomposition, and exits as a mixture containing A, R, and S. K₁ AR, FR = k₁C, k₁ = 0.4 m³/(mol min) SA AS, rs = k₂CA, k₂ = 2(min), CA0 = 40 mol/m³arrow_forwardConsider the parallel decomposition of A of different orders with FR = 1, rs = 2CA and IT = C. Determine the maximum concentration of desired product obtainable in mixed flow reactor and plug flow reactor. (1) R is desired product and CA0 = 2. (2) S is desired product and CA0 = 4. R S Tarrow_forward
- 1. Copper is known to be toxic to fish, and in particular, the free ion Cu²+ species typically shows greatest toxicity. a. Calculate the speciation of Cu(II) for freshwater at a pH value of 8.3 as the hardness increases from 20 (soft) to 100 (moderately hard) to 200 (very hard) mg/L as CaCO3. Assume that the total divalent Cu(II) concentration is 10 µg/L. b. Based on your findings in part (a), do you think it is appropriate to set a single regulatory limit or should it depend on variables such as pH and hardness? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardMaterial Sciencearrow_forwardElectronic devices found in integrated circuits are composed of very high purity silicon to which has been added small and very controlled concentrations of elements found in Groups IIIA and VA of the periodic table. For Si that has had added 9.1 × 1021 atoms per cubic meter of antimony compute (a) the weight percent and (b) the atom percent of Sb present. (Hint: use Equation 100 C₁ = 1 + NAP2 N1A₁ P2 P1 (a) 0.00636 %wt (b) i 0.0182 %atarrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





