
Intermediate Accounting
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781259722660
Author: J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 3.20E
Effect of management decisions on ratios
• LO3–8
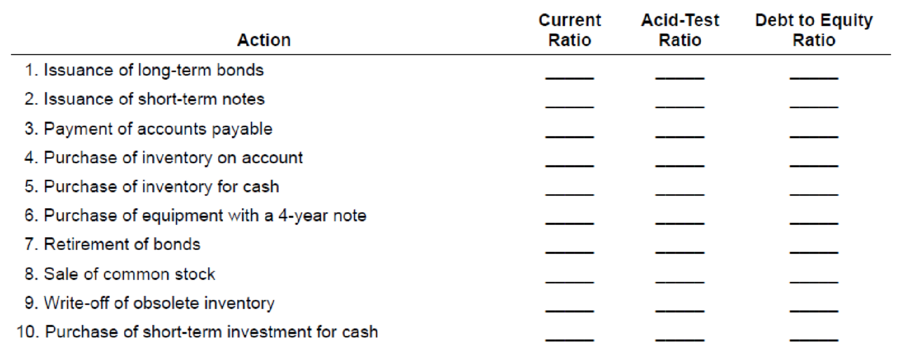
Most decisions made by management impact the ratios analysts use to evaluate performance. Indicate (by letter) whether each of the actions listed below will immediately increase (I), decrease (D), or have no effect (N) on the ratios shown. Assume each ratio is less than 1.0 before the action is taken.

Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Can you help me solve this financial accounting problem using the correct accounting process?
Please explain the correct approach for solving this general accounting question
Can you solve this general accounting question with accurate accounting calculations?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting
Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.1QCh. 3 - Prob. 3.2QCh. 3 - Define current assets and list the typical asset...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.4QCh. 3 - Prob. 3.5QCh. 3 - Prob. 3.6QCh. 3 - Describe the common characteristics of assets...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.8QCh. 3 - Prob. 3.9QCh. 3 - Define the terms paid-in-capital and retained...
Ch. 3 - Disclosure notes are an integral part of the...Ch. 3 - A summary of the companys significant accounting...Ch. 3 - Define a subsequent event.Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.14QCh. 3 - Prob. 3.15QCh. 3 - Prob. 3.16QCh. 3 - Prob. 3.17QCh. 3 - Show the calculation of the following solvency...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.19QCh. 3 - Prob. 3.20QCh. 3 - (Based on Appendix 3) Segment reporting...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.22QCh. 3 - Prob. 3.23QCh. 3 - Current versus long-term classification LO32,...Ch. 3 - Balance sheet classification LO32, LO33 The trial...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.3BECh. 3 - Balance sheet classification LO32, LO33 Refer to...Ch. 3 - Balance sheet classification LO32, LO33 The...Ch. 3 - Balance sheet classification LO32, LO33 You have...Ch. 3 - Balance sheet preparation; missing elements LO32,...Ch. 3 - Financial statement disclosures LO34 For each of...Ch. 3 - Calculating ratios LO38 Refer to the trial...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.10BECh. 3 - Calculating ratios; solving for unknowns LO38 The...Ch. 3 - Balance sheet; missing elements LO32, LO33, LO38...Ch. 3 - Balance sheet classification LO32, LO33 The...Ch. 3 - Balance sheet classification LO32, LO33 The...Ch. 3 - Balance sheet preparation LO32, LO33 The...Ch. 3 - Balance sheet preparation LO32, LO33 The...Ch. 3 - Balance sheet; Current versus long-term...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.7ECh. 3 - Prob. 3.8ECh. 3 - Balance sheet preparation LO32, LO33 The...Ch. 3 - Financial statement disclosures LO34 The...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.11ECh. 3 - Prob. 3.12ECh. 3 - Prob. 3.13ECh. 3 - FASB codification research LO32, LO34 Access the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.15ECh. 3 - Prob. 3.16ECh. 3 - Prob. 3.17ECh. 3 - Calculating ratios; solve for unknowns LO38 The...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.19ECh. 3 - Effect of management decisions on ratios LO38...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.21ECh. 3 - Prob. 3.22ECh. 3 - Balance sheet preparation LO32, LO33 Presented...Ch. 3 - Balance sheet preparation; missing elements LO32,...Ch. 3 - Balance sheet preparation LO32, LO33 The...Ch. 3 - Balance sheet preparation LO32, LO33 The...Ch. 3 - Balance sheet preparation LO32, LO33 The...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.6PCh. 3 - Balance sheet preparation; errors LO32, LO33 The...Ch. 3 - Balance sheet; errors; missing amounts LO32, LO33...Ch. 3 - Balance sheet preparation LO32 , LO33 Presented...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.10PCh. 3 - Communication Case 31 Current versus long-term...Ch. 3 - Analysis Case 32 Current versus long- term...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.4BYPCh. 3 - Judgment Case 35 Balance sheet; errors LO32...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.6BYPCh. 3 - Real World Case 37 Balance sheet and significant...Ch. 3 - Judgment Case 38 Post fiscal year-end e vents ...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.9BYPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.10BYPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.11BYPCh. 3 - Analysis Case 314 Balance sheet information LO32...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.15BYPCh. 3 - Ethics Case 316 Segment reporting Appendix 3 You...Ch. 3 - Prob. 1CCTC
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please explain the correct approach for solving this general accounting question.arrow_forwardGlobal Fitness LLC reported a debt-to-equity ratio of 1.5 times at the end of 2024. If the firm's total assets at year-end were $36.8 million, how much of their assets are financed with equity?a. $14.72 millionb. $22.08 millionc. $9.2 milliond. $55.2 million i need helparrow_forwardPlease provide the accurate answer to this financial accounting problem using valid techniques.arrow_forward
- Can you help me solve this general accounting problem with the correct methodology?arrow_forwardGlobal Fitness LLC reported a debt-to-equity ratio of 1.5 times at the end of 2024. If the firm's total assets at year-end were $36.8 million, how much of their assets are financed with equity?a. $14.72 millionb. $22.08 millionc. $9.2 milliond. $55.2 million helparrow_forwardPlease help me solve this financial accounting problem with the correct financial process.arrow_forward
- Please provide answer accurate of this Financial Accounting Question without any problemarrow_forwardI need help finding the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forwardPlease provide the answer to this financial accounting question using the right approach.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781285866307Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781285866307Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning

Financial & Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781285866307
Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Financial ratio analysis; Author: The Finance Storyteller;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MTq7HuvoGck;License: Standard Youtube License