
Concept explainers
Define each of the following terms:
- supertype
- subtype
- specialization
- entity cluster
- completeness constraint
- enhanced entity-relationship (EER) model
- supertype/subtype hierarchy
- total specialization rule
- generalization
- disjoint rule
- overlap rule
- partial specialization rule
- universal data model
(a)
Definition of supertype
Explanation of Solution
Supertype is an entity that has relationship with one or more subtypes and contains some common subtype attributes. For example, when we are designing a data model for the employee, then we can have employee as a supertype, and its attributes like salary employee and contracted employee are taken as subtype.
(b)
Subtype
Explanation of Solution
Subtypes are the subgroups of the supertype entities. Each subtype consists of some unique attributes and is different from each other. For example, when we are creating a data model for the employee details, here we have one supertype entity employee with many subtype entities like part time employee, full time employee, and salaried employee, etc.
(c)
Specialization
Explanation of Solution
It is an opposite approach of the generalization. It is used to break down the higher level of the entity into the subgroups of lower level entity. Specialization is used to identify the subset entity that is sharing some common and distinguished characters.
Example:
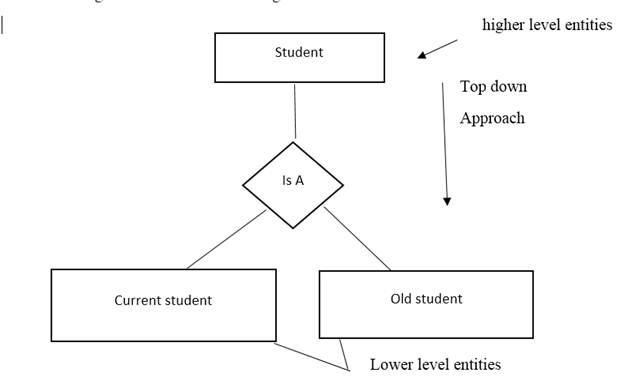
(d)
Entity cluster
Explanation of Solution
Entity cluster is a useful way to represent the data model for large and complex organization. Entity cluster is a collection of various entities that are combined to form one common entity. An entity can be considered as virtual in the entity cluster. These entities are developed with the purpose of the reliability and simplification of data. EER diagram of an entity cluster is given below:
(e)
Completeness constraints
Explanation of Solution
Completeness constraints are used to check that the supertype entity must have an occurrence of the subtype entity. It is basically used to check the common attributes among the supertype and the subtype. There are two types of completeness constraints:
- Partial specialization: In Partial specialization, it is not necessary that all the subtype and the supertype entities are related to each other totally. There might be some cases where a partial relationship between the entities is possible. It can be represented by using a single line. Consider the below given diagram.
- Total specialization: In total specialization, it is necessary that all the subtype and the supertype entities are related to each other totally. It can be represented by using a single line. Consider the below given diagram.
Here, a person has a license. Suppose we have 5 people among which only 2 have license and rest do not. Then, it is a case of partial specialization. Here, it not necessary that all the people have license, there might be some persons who do not possess a license.
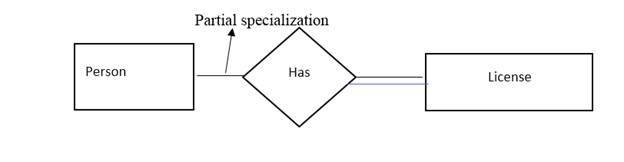
Here, the license should always belong to a particular person, i.e., there is no license without a person. This is a case of total specialization.
(f)
Enhanced entity-relationship (EER) model.
Explanation of Solution
Enhanced entity-relationship (EER) model is the enhanced model form of entity relational data model. It is a higher-level conceptual model of the computer science that is used to develop the advance databases, complex software designs, and geographic information systems (GIS), etc. Enhanced entity-relationship (EER) model reflects the data properties and constraints more precisely. It also consists of all the concepts of the entity relation diagram, specialization, and generalization.
(g)
Supertype/subtype hierarchy.
Explanation of Solution
Supertype/subtype hierarchy is the structure in which the supertype and the subtype entities are leveled according to their order. This organization of data make the data more modular and easier to understand and use.
(h)
Total specialization rule
Explanation of Solution
Total specialization rule is used to ensure that every entity of the subtype belongs to the supertype entity, i.e., there must be no entity of superclass which is not belongs to the subtype.
(i)
Generalization.
Explanation of Solution
Generalization is a process of extracting common features from multiple entities source in order to create a new entity. it helps in reducing the size of schema. Generalization provide one entity from multiple entity. Bottom − up designing strategies are used in the Generalization.
In Generalization entity all the all higher-level entities have the lower level entity. There is no higher entity without the lower level entity.
(j)
Disjoint rules
Explanation of Solution
The disjoint rule specifies that the entity object of supertype can only be the member of any of the subtype. For example, let’s consider animal as a supertype. Then it can have subtype entities like dog, cat, etc., In disjoint rule, the supertype class animal can be associated with the dog or cat at one time. i.e., the animal can be either dog or cat.
(k)
Overlap rule
Explanation of Solution
In the overlap rule, the supertype can be associated with more than one subtype entities. For example, consider a supertype entity student that can be associated with many subjects like math, English, Hindi and many more.
(l)
Partial specialization rules
Explanation of Solution
Partial specialization rules allow that the entity of supertype must not always need to belong to the subtype entity. Consider a supertype entity vehicle having subtypes entities car and truck. Here motorcycle is also subtype of vehicles, but it is not specified as subtype in the data model. Thus, if a vehicle is a car, then it must appear in the object of car and if the vehicle is a truck, it must appear in the object of truck. But if the vehicle is a motorcycle, then it cannot appear in any of the subtypes.
(m)
Universal data model
Explanation of Solution
Universal data model can be used as a starting point for the data modeling project. It is also known as a data model pattern. Advantages of using the Universal data model:
- Project takes less time and efforts to develop as all the essential components and structures are already designed and need only to be customized according to the requirement.
- Data models of the existing database are easier to read by the data modeler and other data management experts, as it is based on the common components seen in the other situations.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Modern Database Management
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
- Obtain the MUX design for the function F(X,Y,Z) = (0,3,4,7) using an off-the-shelf MUX with an active low strobe input (E).arrow_forwardI cannot program smart home automation rules from my device using a computer or phone, and I would like to know how to properly connect devices such as switches and sensors together ? Cisco Packet Tracer 1. Smart Home Automation:o Connect a temperature sensor and a fan to a home gateway.o Configure the home gateway so that the fan is activated when the temperature exceedsa set threshold (e.g., 30°C).2. WiFi Network Configuration:o Set up a wireless LAN with a unique SSID.o Enable WPA2 encryption to secure the WiFi network.o Implement MAC address filtering to allow only specific clients to connect.3. WLC Configuration:o Deploy at least two wireless access points connected to a Wireless LAN Controller(WLC).o Configure the WLC to manage the APs, broadcast the configured SSID, and applyconsistent security settings across all APs.arrow_forwardusing r language for integration theta = integral 0 to infinity (x^4)*e^(-x^2)/2 dx (1) use the density function of standard normal distribution N(0,1) f(x) = 1/sqrt(2pi) * e^(-x^2)/2 -infinity <x<infinity as importance function and obtain an estimate theta 1 for theta set m=100 for the estimate whatt is the estimate theta 1? (2)use the density function of gamma (r=5 λ=1/2)distribution f(x)=λ^r/Γ(r) x^(r-1)e^(-λx) x>=0 as importance function and obtain an estimate theta 2 for theta set m=1000 fir the estimate what is the estimate theta2? (3) use simulation (repeat 1000 times) to estimate the variance of the estimates theta1 and theta 2 which one has smaller variance?arrow_forward
- using r language A continuous random variable X has density function f(x)=1/56(3x^2+4x^3+5x^4).0<=x<=2 (1) secify the density g of the random variable Y you find for the acceptance rejection method. (2) what is the value of c you choose to use for the acceptance rejection method (3) use the acceptance rejection method to generate a random sample of size 1000 from the distribution of X .graph the density histogram of the sample and compare it with the density function f(x)arrow_forwardusing r language a continuous random variable X has density function f(x)=1/4x^3e^-(pi/2)^4,x>=0 derive the probability inverse transformation F^(-1)x where F(x) is the cdf of the random variable Xarrow_forwardusing r language in an accelerated failure test, components are operated under extreme conditions so that a substantial number will fail in a rather short time. in such a test involving two types of microships 600 chips manufactured by an existing process were tested and 125 of them failed then 800 chips manufactured by a new process were tested and 130 of them failed what is the 90%confidence interval for the difference between the proportions of failure for chips manufactured by two processes? using r languagearrow_forward
- I want a picture of the tools and the pictures used Cisco Packet Tracer Smart Home Automation:o Connect a temperature sensor and a fan to a home gateway.o Configure the home gateway so that the fan is activated when the temperature exceedsa set threshold (e.g., 30°C).2. WiFi Network Configuration:o Set up a wireless LAN with a unique SSID.o Enable WPA2 encryption to secure the WiFi network.o Implement MAC address filtering to allow only specific clients to connect.3. WLC Configuration:o Deploy at least two wireless access points connected to a Wireless LAN Controller(WLC).o Configure the WLC to manage the APs, broadcast the configured SSID, and applyconsistent security settings across all APs.arrow_forwardA. What will be printed executing the code above?B. What is the simplest way to set a variable of the class Full_Date to January 26 2020?C. Are there any empty constructors in this class Full_Date?a. If there is(are) in which code line(s)?b. If there is not, how would an empty constructor be? (create the code lines for it)D. Can the command std::cout << d1.m << std::endl; be included after line 28 withoutcausing an error?a. If it can, what will be printed?b. If it cannot, how could this command be fixed?arrow_forwardCisco Packet Tracer Smart Home Automation:o Connect a temperature sensor and a fan to a home gateway.o Configure the home gateway so that the fan is activated when the temperature exceedsa set threshold (e.g., 30°C).2. WiFi Network Configuration:o Set up a wireless LAN with a unique SSID.o Enable WPA2 encryption to secure the WiFi network.o Implement MAC address filtering to allow only specific clients to connect.3. WLC Configuration:o Deploy at least two wireless access points connected to a Wireless LAN Controller(WLC).o Configure the WLC to manage the APs, broadcast the configured SSID, and applyconsistent security settings across all APs.arrow_forward
- Transform the TM below that accepts words over the alphabet Σ= {a, b} with an even number of a's and b's in order that the output tape head is positioned over the first letter of the input, if the word is accepted, and all letters a should be replaced by the letter x. For example, for the input aabbaa the tape and head at the end should be: [x]xbbxx z/z,R b/b,R F ① a/a,R b/b,R a/a, R a/a,R b/b.R K a/a,R L b/b,Rarrow_forwardGiven the C++ code below, create a TM that performs the same operation, i.e., given an input over the alphabet Σ= {a, b} it prints the number of letters b in binary. 1 #include 2 #include 3 4- int main() { std::cout > str; for (char c : str) { if (c == 'b') count++; 5 std::string str; 6 int count = 0; 7 char buffer [1000]; 8 9 10 11- 12 13 14 } 15 16- 17 18 19 } 20 21 22} std::string binary while (count > 0) { binary = std::to_string(count % 2) + binary; count /= 2; std::cout << binary << std::endl; return 0;arrow_forwardConsidering the CFG described below, answer the following questions. Σ = {a, b} • NT = {S} Productions: P1 S⇒aSa P2 P3 SbSb S⇒ a P4 S⇒ b A. List one sequence of productions that can accept the word abaaaba; B. Give three 5-letter words that can be accepted by this CFG; C. Create a Pushdown automaton capable of accepting the language accepted by this CFG.arrow_forward
 Principles of Information Systems (MindTap Course...Computer ScienceISBN:9781285867168Author:Ralph Stair, George ReynoldsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Information Systems (MindTap Course...Computer ScienceISBN:9781285867168Author:Ralph Stair, George ReynoldsPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Information SystemsComputer ScienceISBN:9781305082168Author:Ralph Stair, George ReynoldsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Information SystemsComputer ScienceISBN:9781305082168Author:Ralph Stair, George ReynoldsPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Information Systems (MindTap Course...Computer ScienceISBN:9781305971776Author:Ralph Stair, George ReynoldsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Information Systems (MindTap Course...Computer ScienceISBN:9781305971776Author:Ralph Stair, George ReynoldsPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781305627482Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781305627482Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781285196145Author:Steven, Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel, Carlos, Coronel, Carlos; Morris, Carlos Coronel and Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel; Steven Morris, Steven Morris; Carlos CoronelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781285196145Author:Steven, Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel, Carlos, Coronel, Carlos; Morris, Carlos Coronel and Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel; Steven Morris, Steven Morris; Carlos CoronelPublisher:Cengage Learning





