
(a)
Interpretation:
The wavelength (in nanometres) and the frequency (in hertz) of light should be calculated using the relation between speed, wavelength and frequency of a wave.
Concept Introduction:
A wave is a disturbance or variation that travels through a medium transporting energy without transporting matter. The wavelength is defined as the distance between the two similar points on consecutive waves. The frequency is defined as the number of waves which move through any particular point in one second.
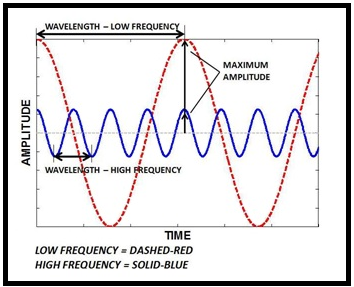
Figure.1
The speed, wavelength and frequency of a wave are interrelated by
(b)
Interpretation:
The frequency (in hertz) of light should be calculated using the relation between speed, wavelength and frequency of a wave.
Concept Introduction:
A wave is a disturbance or variation that travels through a medium transporting energy without transporting matter. The wavelength is defined as the distance between the two similar points on consecutive waves. The frequency is defined as the number of waves which move through any particular point in one second.

Figure.1
The speed, wavelength and frequency of a wave are interrelated by
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Chemistry: Atoms First V1
- Answe Answer A and B pleasearrow_forward3. Refer to the data below to answer the following questions: Isoelectric point Amino Acid Arginine 10.76 Glutamic Acid 3.22 Tryptophan 5.89 A. Define isoelectric point. B. The most basic amino acid is C. The most acidic amino acid is sidizo zoarrow_forward3. A gas mixture contains 50 mol% H2 and 50 mol% He. 1.00-L samples of this gas mixture are mixed with variable volumes of O2 (at 0 °C and 1 atm). A spark is introduced to allow the mixture to undergo complete combustion. The final volume is measured at 0 °C and 1 atm. Which graph best depicts the final volume as a function of the volume of added O2? (A) 2.00 1.75 Final Volume, L 1.50 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.25 0.50 2.00 (B) 1.75 1.50 Final Volume, L 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50- 0.25 0.00 0.75 1.00 0.00 0.25 Volume O₂ added, L 2 0.50 0.75 1.00 Volume O₂ added, L 2 2.00 2.00 (C) (D) 1.75 1.75 1.50 1.50 Final Volume, L 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 Final Volume, L 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.00 0.00 0.25 Volume O₂ added, L 0.50 0.75 1.00 Volume O₂ added, L 2arrow_forward
- Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid. It has pai 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60. H2N-C(R)H-COOH and R is -CH2-CH(CH3)2 A. Draw the condensed structure for leucine, and label all chirality centers with an asterisk. B. How many possible stereoisomers of leucine are there? C. Draw a Fischer projection of L-leucine and label the chirality center(s) as R or S. D. What is the p/ of leucine? E. Draw the structure of the predominant form of leucine at 10.00. F. Draw the structure of the predominant form of leucine at pH = 1.50. G. Leucine is described as an essential amino acid. What does this mean? H. Show the alkyl halide you would use to prepare leucine by the amidomalonate method. =arrow_forwarda) Write out 6 completely different reactions of acetophenone (reagent, product). b) Write out 3 preparations of 1-methylcyclohexanol, using a different starting material for each one. You may use preps where you just change the functional group, and/or preps where you construct the carbon chain. c) Write out 3 preparations of 2-ethoxybenzoic acid, a different starting material for each one. You may use preps where you just change the functional group, and/or preps where you construct the carbon chain.arrow_forward12. CH3 OH OH H&C CH3 H₂C N OH H₂C CH3 H&C CH3 H₂C' CH3 H.C CH3OH H.C CH2CH3OH CH3CEN Which one of these 17 compounds is represented by this IR and this 'H NMR spectrum? IR Spectrum 3000 4000 3000 NMR Spectrum 2000 £500 RAVENUMBER 2000 1500 9 8 6 5 10 HP-00-290 ppm m 1000 500 1000 4 °arrow_forward
- Draw the structure of (E,6R) 6-methoxy-4-hepten-2-one. Give the IUPAC name of this compound, including stereochemistry. Draw the most stable chair conformation of (cis) 1,3-isobutylcyclohexane. H HC=CCH₂ CH2CH3 EN(CH3)2 -CN(CH3)2arrow_forward10. Write out the mechanism (intermediate/transition state) for this reaction; indicate stereochemistry in product. H3C CH₂OH CH3 SN1 Harrow_forwardWrite "most" under the member of each trio which is most stable. Write "least under the member of each trio which is least stable. b) Draw a Fischer projection of a pair of enantiomers with three chiral carbons. Which of these two would you expect to be more soluble in water? Why? 1-butanol 1-heptanol Which of these two would you expect to have the higher boiling point? Why? hexyl methyl ether 1-heptanolarrow_forward
- Write "most" under the most acidic compound. Write "least" under the least acidic compound. OH NO₂ OCH3 Br 9. Compound X, C50H84F2, reacts with excess H2/Pd to give a C50H88F2 compound. How many rings are in X? How many double bonds are in X? Show your work.arrow_forward4. State whether these two are: a) the same molecule b) c) d) different compounds that are not isomers constitutional isomers diastereomers e) enantiomers CH3 CH₁₂ H OH HO H H OH HO H CH, CH₂ 5. a) How many stereocenters does this compound have? b) How many stereoisomers are possible for this compound? CH₂ OH CHCHarrow_forwardCalculating the pH at equivalence of a titration A chemist titrates 210.0 mL of a 0.1003 M hydrobromic acid (HBr) solution with 0.7550M KOH solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of KOH solution added. pH = ] ☑ o0o 18 Ararrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





