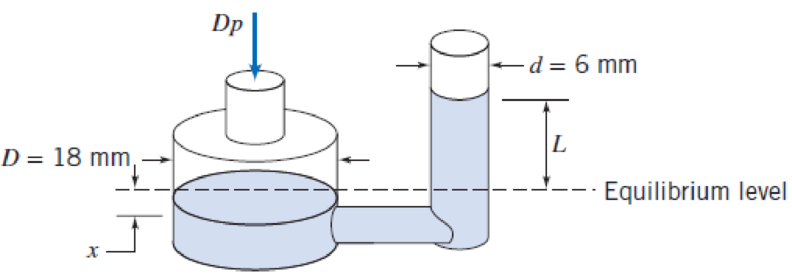
Problem 1P: Because the pressure falls, water boils at a lower temperature with increasing altitude.... Problem 2P: Ear popping is an unpleasant phenomenon sometimes experienced when a change in pressure occurs, for... Problem 3P: When you are on a mountain face and boil water, you notice that the water temperature is 195F. What... Problem 4P: Your pressure gauge indicates that the pressure in your cold tires is 0.25 MPa gage on a mountain at... Problem 5P: A 125-mL cube of solid oak is held submerged by a tether as shown. Calculate the actual force of the... Problem 6P: The tube shown is filled with mercury at 20C. Calculate the force applied to the piston. P3.6 Problem 7P: Calculate the absolute and gage pressure in an open tank of crude oil 2.4 m below the liquid... Problem 8P: An open vessel contains carbon tetrachloride to a depth of 6 ft and water on the carbon... Problem 9P: A hollow metal cube with sides 100 mm floats at the interface between a layer of water and a layer... Problem 10P: Compressed nitrogen (140 lbm) is stored in a spherical tank of diameter D = 2.5 ft at a temperature... Problem 11P: If at the surface of a liquid the specific weight is o, with z and p both zero, show that, if E =... Problem 12P: In the deep ocean the compressibility of seawater is significant in its effect on and p. If E =2.07... Problem 13P: Assuming the bulk modulus is constant for sea water, derive an expression for the density variation... Problem 14P: An inverted cylindrical container is lowered slowly beneath the surface of a pool of water. Air... Problem 15P: A water tank filled with water to a depth of 16 ft has an inspection cover (1 in. 1 in.) at its... Problem 16P: A partitioned tank as shown contains water and mercury. What is the gage pressure in the air trapped... Problem 17P: Consider the two-fluid manometer shown. Calculate the applied pressure difference. P3.17 Problem 18P: The manometer shown contains water and kerosene. With both tubes open to the atmosphere, the... Problem 19P: Determine the gage pressure in kPa at point a, if liquid A has SG = 1.20 and liquid B has SG = 0.75.... Problem 20P: With the manometer reading as shown, calculate px. P3.20 Problem 21P: Calculate px py for this inverted U-tube manometer. Problem 22P: An inclined gauge having a tube of 3-mm bore, laid on a slope of 1:20, and a reservoir of... Problem 23P: Water flows downward along a pipe that is inclined at 30 below the horizontal, as shown. Pressure... Problem 24P: A reservoir manometer has vertical tubes of diameter D = 18 mm and d = 6 mm. The manometer liquid is... Problem 25P: A rectangular tank, open to the atmosphere, is filled with water to a depth of 2.5 m as shown. A... Problem 26P: The sketch shows a sectional view through a submarine. Calculate the depth of submergence, y. Assume... Problem 27P: The manometer reading is 6 in. when the funnel is empty (water surface at A). Calculate the... Problem 28P: A reservoir manometer is calibrated for use with a liquid of specific gravity 0.827. The reservoir... Problem 29P: The inclined-tube manometer shown has D = 96 mm and d = 8 mm. Determine the angle, , required to... Problem 30P: The inclined-tube manometer shown has D = 76 mm and d = 8 mm, and is filled with Meriam red oil.... Problem 31P: A barometer accidentally contains 6.5 inches of water on top of the mercury column (so there is also... Problem 32P: A water column stands 50 mm high in a 2.5-mm diameter glass tube. What would be the column height if... Problem 33P: Consider a small-diameter open-ended tube inserted at the interface between two immiscible fluids of... Problem 34P: Compare the height due to capillary action of water exposed to air in a circular tube of diameter D... Problem 37P: If atmospheric pressure at the ground is 101.3 kPa and temperature is 15C, calculate the pressure... Problem 38P: If the temperature in the atmosphere is assumed to vary linearly with altitude so T = To z where To... Problem 40P: A hydropneumatic elevator consists of a piston-cylinder assembly to lift the elevator cab. Hydraulic... Problem 41P: Semicircular plane gate AB is hinged along B and held by horizontal force FA applied at A. The... Problem 42P: A circular gate 3 m in diameter has its center 2.5 m below a water surface and lies in a plane... Problem 43P: For the situation shown, find the air pressure in the tank in psi. Calculate the force exerted on... Problem 44P: What is the pressure at A? Draw a free body diagram of the 10-ft wide gate showing all forces and... Problem 45P: A plane gate of uniform thickness holds back a depth of water as shown. Find the minimum weight... Problem 46P: A rectangular gate (width w = 2 m) is hinged as shown, with a stop on the lower edge. At what depth... Problem 47P: Gates in the Poe Lock at Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan, close a channel W = 34 m wide, L = 360 m long,... Problem 48P: Calculate the minimum force P necessary to hold a uniform 12 ft square gate weighing 500 lb closed... Problem 49P: Calculate magnitude and location of the resultant force of water on this annular gate. Problem 50P: Calculate magnitude and location of the resultant force of water on this annular gate. Problem 51P: A window in the shape of an isosceles triangle and hinged at the top is placed in the vertical wall... Problem 52P: A large open tank contains water and is connected to a 6-ft-diameter conduit as shown. A circular... Problem 53P: The circular access port in the side of a water standpipe has a diameter of 0.6 m and is held in... Problem 54P: The gate AOC shown is 6 ft wide and is hinged along O. Neglecting the weight of the gate, determine... Problem 55P: The gate shown is hinged at H. The gate is 3 m wide normal to the plane of the diagram. Calculate... Problem 57P: For the dam shown, what is the vertical force of the water on the dam? Problem 58P: The parabolic gate shown is 2 m wide and pivoted at O; c = 0.25 m1, D = 2 m, and H = 3 m. Determine... Problem 59P: An open tank is filled with water to the depth indicated. Atmospheric pressure acts on all outer... Problem 60P: A dam is to be constructed using the cross-section shown. Assume the dam width is w = 160 ft. For... Problem 61P: The quarter cylinder AB is 10 ft long. Calculate magnitude, direction, and location of the resultant... Problem 62P: Calculate the magnitude, direction (horizontal and vertical components are acceptable), and line of... Problem 63P: A hemispherical shell 1.2 m in diameter is connected to the vertical wall of a tank containing... Problem 65P: A cylindrical weir has a diameter of 3 m and a length of 6 m. Find the magnitude and direction of... Problem 67P: If you throw an anchor out of your canoe but the rope is too short for the anchor to rest on the... Problem 69P: A hydrometer is a specific gravity indicator, the value being indicated by the level at which the... Problem 70P: A cylindrical can 76 mm in diameter and 152 mm high, weighing 1.11 N, contains water to a depth of... Problem 71P: If the 10-ft-long box is floating on the oil-water system, calculate how much the box and its... Problem 72P: The timber weighs 40 lb/ft3 and is held in a horizontal position by the concrete (150 lb/ft3)... Problem 73P: Find the specific weight of the sphere shown if its volume is 0.025m3. State all assumptions. What... Problem 74P: The fat-to-muscle ratio of a person may be determined from a specific gravity measurement. The... Problem 75P: An open tank is filled to the top with water. A steel cylindrical container, wall thickness = 1 mm,... Problem 76P: If the timber weighs 670 N, calculate its angle of inclination when the water surface is 2.1 m above... Problem 77P: The barge shown weighs 40 tons and carries a cargo of 40 tons. Calculate its draft in freshwater. Problem 78P: Quantify the experiment performed by Archimedes to identify the material content of King Hieros... Problem 79P: Hot-air ballooning is a popular sport. According to a recent article, hot-air volumes must be large... Problem 80P: It is desired to use a hot air balloon with a volume of 320,000 ft3 for rides planned in summer... Problem 81P: The opening in the bottom of the tank is square and slightly less than 2 ft on each side. The... Problem 82P: A balloon has a weight (including crew but not gas) of 2.2 kN and a gas-bag capacity of 566 m3. At... Problem 83P: A helium balloon is to lift a payload to an altitude of 40 km, where the atmospheric pressure and... Problem 84P: The stem of a glass hydrometer used to measure specific gravity is 5 mm in diameter. The distance... Problem 85P: A sphere of radius R is partially immersed to depth d in a liquid of specific gravity SG. Obtain an... Problem 86P: A sphere of 1-in.-radius made from material of specific gravity of SG = 0.95, is submerged in a tank... Problem 87P: You are in the Bermuda Triangle when you see a bubble plume eruption (a large mass of air bubbles,... Problem 88P: Three steel balls (each about half an inch in diameter) lie at the bottom of a plastic shell... Problem 89P: A proposed ocean salvage scheme involves pumping air into bags placed within and around a wrecked... format_list_bulleted


 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY




