
1.
Record the
1.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entries for given transactions are as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| 2021 | Prepaid rent | 6,000 | |
| January 2 | Cash | 6,000 | |
| (To record advance rent received for one year) | |||
| 2021 | Supplies | 3,500 | |
| January 9 | Accounts payable | 3,500 | |
| (To record purchase of additional supplied) | |||
| 2021 | 25,500 | ||
| January 13 | Service revenue | 25,500 | |
| (To record service provided on account) | |||
| 2021 | Cash | 3,700 | |
| January 17 | Deferred revenue | 3,700 | |
| (To record cash received from customer for future service) | |||
| 2021 | Salaries expense | 11,500 | |
| January 20 | Cash | 11,500 | |
| (To record incurred of salaries expense) | |||
| 2021 | Cash | 24,100 | |
| January 22 | Accounts receivable | 24,100 | |
| (To record cash received from customer) | |||
| 2021 | Accounts payable | 4,000 | |
| January 29 | Cash | 4,000 | |
| (To record cash paid to suppliers) | |||
Table (1)
2.a.
Record the adjusting entry for prepaid rent.
2.a.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries refers to the entries that are made at the end of an accounting period in accordance with revenue recognition principle, and expenses recognition principle. The purpose of adjusting entries is to adjust the revenue, and the expenses during the period in which they actually occurs.
Adjusting entry for prepaid rent is as follows:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January 31, 2021 | Rent expense | 500 | |
| Prepaid rent | 500 | ||
| (To record the rent expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) |
Table (2)
Following is the rules of debit and credit of above transaction:
- Rent expense is an expense, and it decreased the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, it is debited.
- Prepaid rent is an asset account. There is a decrease in assets, therefore it is credited.
b.
Record the adjusting entry for supplies expense.
b.
Explanation of Solution
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January 31, 2021 | Supplies expense (1) | 3,800 | ||
| Supplies | 3,800 | |||
| (To record the supplies expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) |
Table (3)
Following is the rules of debit and credit of above transaction:
- Supplies expense is an expense, and it decreased the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, it is debited.
- Supplies are an asset account. There is a decrease in assets, therefore it is credited.
Working note:
Calculate the value of supplies expense at end of the October month
c.
Record the adjusting entry for service revenue recognized at the end of the accounting year.
c.
Explanation of Solution
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January 31, 2021 | Deferred revenue | 3,200 | ||
| Service revenue | 3,200 | |||
| (To record the service revenue recognized at the end of the accounting year) |
Table (4)
- Deferred revenue is a liability account. There is a decrease in liability, therefore it is debited.
- Service revenue is revenue, and it increased the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, it is credited.
d.
Record the adjusting entry for salaries expense.
d.
Explanation of Solution
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January 31, 2021 | Salaries expense | 5,800 | ||
| Salaries payable | 5,800 | |||
| (To record the salaries expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) |
Table (5)
- Salaries expense is an expense, and it decreased the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, it is debited.
- Salaries payable is a liability account. There is a decrease in liability, therefore it is credited.
3.
Prepare the adjusted
3.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusted trial balance:
Adjusted trial balance is that statement which contains complete list of accounts with their adjusted balances, after all relevant adjustments have been made. This statement is prepared at the end of every financial period.
The adjusted trial balance of Company D is as follows:
| Company D | ||
| Adjusted Trial Balance | ||
| January 31, 2021 | ||
| Accounts (Refer working note (2) ) | Debit in $ | Credit in $ |
| Cash | 30,100 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 6,600 | |
| Supplies | 2,800 | |
| Prepaid Rent | 5,500 | |
| Land | 50,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | 2,700 | |
| Deferred Revenue | 500 | |
| Salaries Payable | 5,800 | |
| Common Stock | 65,000 | |
| 13,900 | ||
| Service Revenue | 28,700 | |
| Salaries Expense | 17,300 | |
| Rent Expense | 500 | |
| Supplies Expense | 3,800 | |
| Totals | 116,600 | 116,600 |
Table (6)
Working note:
Calculate the ending balance of all accounts:
| Accounts | Beginning balance +Adjustment | Ending balance | ||
| Cash | = | = | 30,100 | |
| Accounts Receivable | = | = | 6,600 | |
| Supplies | = | = | 2,800 | |
| Prepaid Rent | = | = | 5,500 | |
| Land | = | = | 50,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | = | = | 2,700 | |
| Deferred Revenue | = | = | 500 | |
| Salaries Payable | = | = | 5,800 | |
| Common Stock | = | = | 65,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | = | = | 13,900 | |
| Service Revenue | = | = | 28,700 | |
| Salaries Expense | = | = | 17,300 | |
| Rent Expense | = | = | 500 | |
| Supplies Expense | = | = | 3,800 |
Table (7)
(2)
Thus, the total of debit, and credit columns of an adjusted trial balance is $116,600.
4.
Prepare the income statement of Company D for the year ended January 31, 2021.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
The income statement of Company D for the year ended January 31, 2021 is as follows:
| Company D | ||
| Income statement | ||
| For the year ended January 31, 2021 | ||
| Particulars | Amount in $ | Amount in $ |
| Service revenue (A) | 28,700 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Salaries expense | 17,300 | |
| Rent expense | 500 | |
| Supplies expense | 3,800 | |
| Total expense (B) | 21,600 | |
| Net income | 7,100 | |
Table (8)
Therefore, the net income of Company D is $7,100.
5.
Prepare the classified
5.
Explanation of Solution
The classified balance sheet of Company D at January 31, 2021 is as follows:
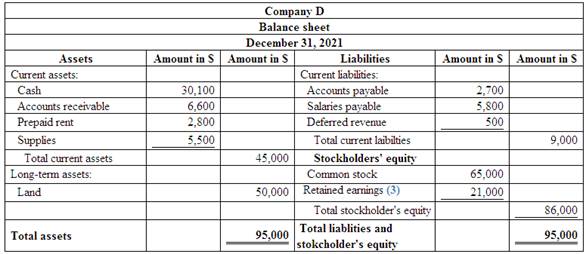
Figure (2)
Working Note:
Calculate the retained earnings:
Therefore, the total assets of Company D are $95,000, and the total liabilities and
6.
Record the closing entries of Company D.
6.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries:
The journal entries prepared to close the temporary accounts to Retained Earnings account are referred to as closing entries. The revenue, expense, and dividends accounts are referred to as temporary accounts because the information and figures in these accounts is held temporarily and consequently transferred to permanent account at the end of accounting year.
The closing entries of Company D are as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| 2021 | Service revenue | 28,700 | |
| January 31 | Retained earnings | 28,700 | |
| (To close revenue account) | |||
| 2021 | Retained earnings | 21,600 | |
| January 31 | Salaries expense | 17,300 | |
| Rent expense | 500 | ||
| Supplies expense | 3,800 | ||
| (To close all expense account) | |||
Table (7)
Closing entry for revenue account:
In this closing entry, the service revenue account is closed by transferring the amount of service revenue to the retained earnings in order to bring the revenue accounts balance to zero.
Closing entry for expenses account:
In this closing entry, salaries expense, rent expense, and supplies expense are closed by transferring the amount of all expenses to the retained earnings in order to bring all the expense accounts balance to zero.
7.a.
Calculate the amount of profit reported for the month of January.
7.a.
Explanation of Solution
The amount of reported profit is $7,100 .
b.
Calculate the ratio of current assets to current liabilities at the end of January.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Here,
Current assets is $45,000
Current liabilities is $9,000
Therefore, the current ratio of Company D is 5.00.
c.
Indicate whether Company D appears good or bad in financial condition.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Financial condition of Company D is good, because profit is greater than zero and current assets is greater than its current liability. So, the company can earn revenue from its customer and able to pay obligation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Financial Accounting
- I need assistance with this financial accounting question using appropriate principles.arrow_forwardWhich accounting element creates contra-revenue when customers pay early? (A) Cash discounts given (B) Sales returns (C) Trade discounts (D) Allowance for bad debts. MCQarrow_forwardI want the correct answer with accounting questionarrow_forward
- Idris Industries began the year with retained earnings of $375,000. During the year, the company recorded revenues of $642,000 and expenses of $489,000. It also paid dividends of $52,400. What was Idris Industries' net income for the year?arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this accounting question using proper accounting principles.arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the correct explanation.arrow_forward
- Could you explain the steps for solving this financial accounting question accurately?arrow_forwardI need assistance with this general accounting question using appropriate principles.arrow_forwardDuring a specific period, Norton Enterprises reported a decrease in total assets of $18,700 and a decrease in stockholders' equity of $7,200. By what amount and direction must total liabilities have changed during that same period?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





