
Concept explainers
Complete the following table to help you review the structures and functions of the four classes of organic molecules.
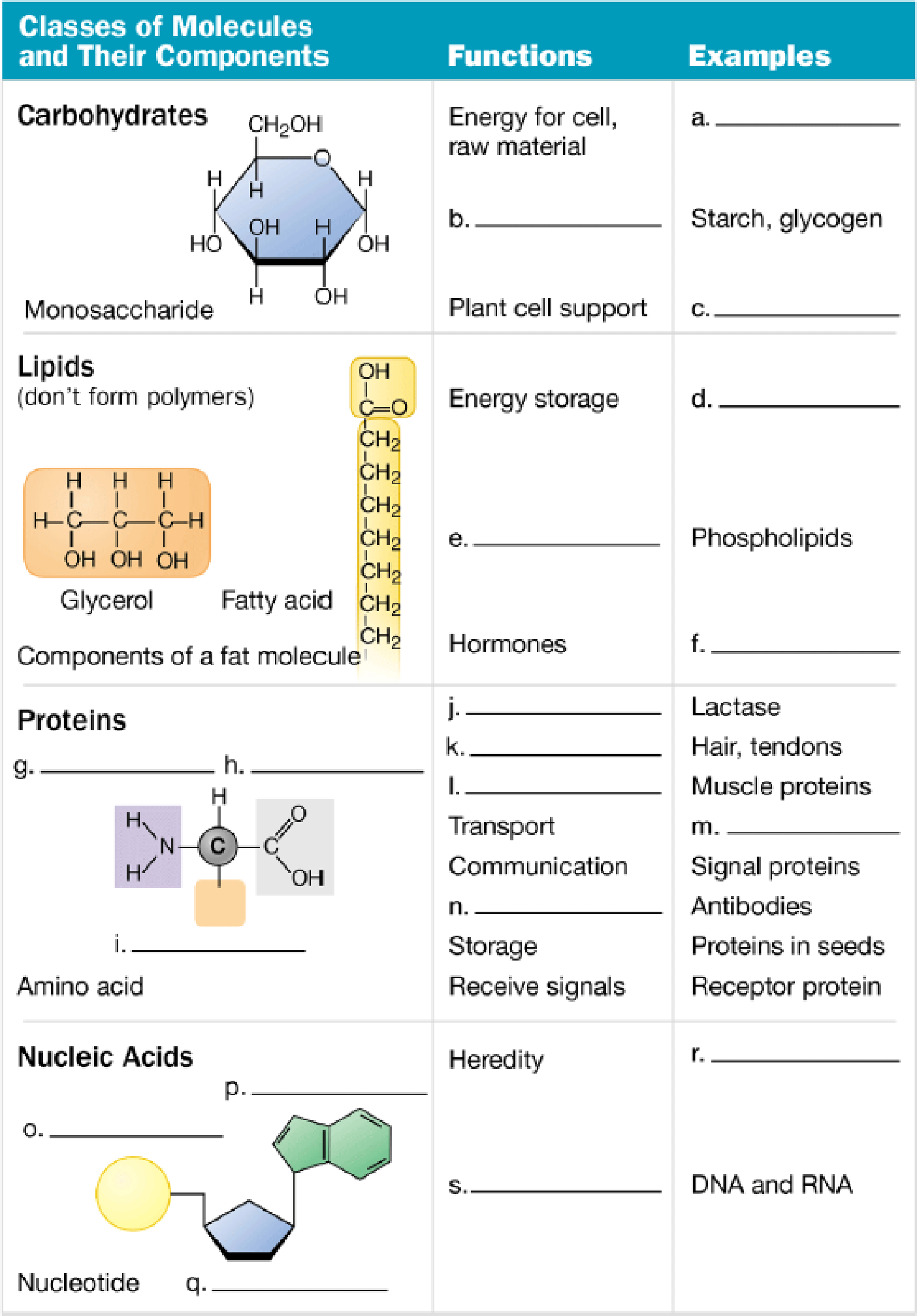
To create: The concept map to review the structures and functions of the four classes of organic molecules.
Introduction: The four classes of molecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids are important to sustain the life. Carbohydrates serve as a fuel and building material for cellsand tissues. Lipid comprises a diverse group of molecules. It does not mix with water. A protein is a polymer of amino acids. It is structurally and functionally most complex and varied. Nucleic acid is the genetic material that consists of a polynucleotide.
Answer to Problem 1CC
Pictorial representation: Fig. 1 shows the completed concept map of structures and functions of the four classes of organic molecules.
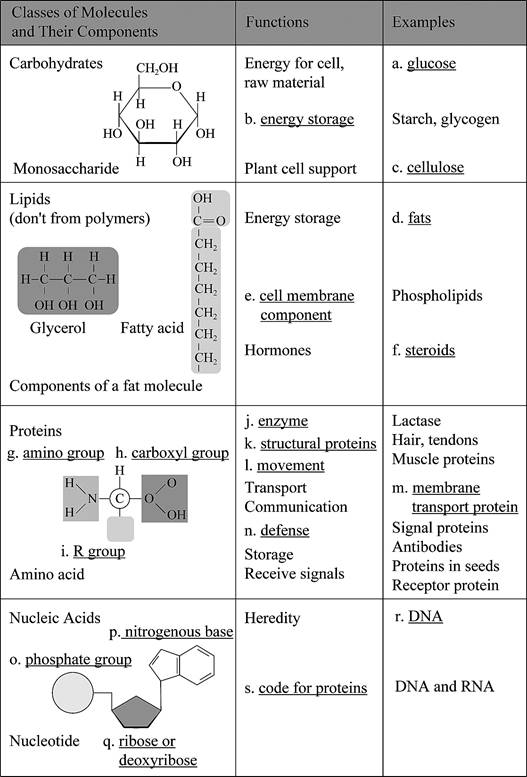
Fig.1: Concept map of the structures and functions of the four classes of organic molecules.
Explanation of Solution
a.
Correct answer: Glucose
Explanation: Glucose is the raw material from which cell will get energy. Hence, the correct answer is Glucose.
b.
Correct answer: Energy storage
Explanation: The starch and glycogen is used as storage material of energy. Hence, the correct answer is energy storage.
c.
Correct answer: Cellulose
Explanation: Cellulose is polysaccharides which is a polymer of glucose molecule. Hence, the correct answer is cellulose.
d.
Correct answer: Fats
Explanation: Fats are a type of lipid. It is composed of glycerol and fatty acids. Hence, the correct answer is fats.
e.
Correct answer: Cell membrane component
Explanation: Cell is the outermost boundary of animal cell. It is made of phospholipid bilayer. Hence, the correct answer is cell membrane component.
f.
Correct answer: Steroids
Explanation: Steroids are hormones such as estrogen. Hence, the correct answer is steroids.
g.
Correct answer: Amino group
Explanation: Protein is made of amino acids. An amino acid contains amino group which is
h.
Correct answer: Carboxylic group
Explanation: Protein is made of amino acids. An amino acid contains carboxylic group which is
i.
Correct answer: R group
Explanation: Protein is made of amino acids. An amino acid contains a side group which is called R group. Hence, the correct answer is R group.
j.
Correct answer: Enzyme
Explanation: Proteins have broad functions such as enzymes, structural proteins, transport, movement, defense, and storage. Lactase is an enzyme used for breakdown of lactose molecule. Hence, the correct answer is Enzyme.
k.
Correct answer: Structural proteins
Explanation: Proteins have broad functions such as enzymes, structural proteins, transport, movement, defense, and storage. Hair and tendons are structural proteins. Hence, the correct answer is structural proteins.
l.
Correct answer: Movement
Explanation: Muscle is a protein that helps in movement. Hence, the correct answer is movement.
m.
Correct answer: Membrane transport protein
Explanation: Membrane transport protein helps in transport of different molecules across the membrane. Hence, the correct answer is Membrane transport protein.
n.
Correct answer: Defense
Explanation: Signal protein helps in communication. Antibodies are immunoglobulin protein that helps in body defense. Hence, the correct answer is defense.
o.
Correct answer: Phosphate group
Explanation: Nucleic acid is a polymer of nucleotides. A nucleotide consists of phosphate group, sugar and nitrogenous base. Hence, the correct answer is phosphate group.
p.
Correct answer: Nitrogenous base
Explanation: Nucleic acid is a polymer of nucleotides. A nucleotide consists of phosphate group, sugar and nitrogenous base. Hence, the correct answer is nitrogenous base.
q.
Correct answer: Ribose or deoxyribose
Explanation: Nucleic acid is a polymer of nucleotides. A nucleotide consists of phosphate group, sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and nitrogenous base. Hence, the correct answer is ribose or deoxyribose.
r.
Correct answer: DNA
Explanation: Nucleic acid is a polymer of nucleotides. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the hereditary material. Hence, the correct answer is DNA.
s.
Correct answer: Code for protein
Explanation: Nucleic acid is a polymer of nucleotides. DNA and RNA have information to code for protein. Hence, the correct answer is code for protein.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Books a la Carte Plus Mastering Biology with eText -- Access Card Package (8th Edition)
- If you wanted to reduce the difference between peak and trough levels that occur with repeated administration of a drug, how would you adjust the dose and dose interval without changing the plateau concentration (plateau is the average of peak and trough levels)? Select your answers for both dose and interval. Hint: It may be helpful to think about this problem using an example such as food. How would you eat if you wanted to maintain very steady hunger/satiety levels without changing your total caloric intake? Options: A. Dose; Increase dose B. Dose; Decrease dose C. Dose; Do not change dose D. Interval; Increase the interval between doses (give the drug less frequently) E. Interval; Decrease the interval between doses (give the drug more frequently) F. Interval; Do not change the intervalarrow_forwardWhat percentage of a drug is eliminated after 4 half-lives? Please round to the nearest percent. Show the matharrow_forwardBriefly explain the 6 domain of interprofessional collaboration: Role clarification, Team functioning, Interprofessional communication, Patient/client/family/community-centered care, Interprofessional conflict resolution, Collaborative leadership. Provide a specific negative events that nursing student would observe in a clinical setting for each domain.arrow_forward
- what is an intermittent water course and what kind of fish habitat it would providearrow_forwardwhy are native freshwater mussels are an important part of great lakes ecosystemarrow_forwardwhat morphological features differentiate the lamprey species and other species in the great lakesarrow_forward
- There are a wide range of therapeutic applications available as options for patients. Medical professionals should be aware of these applications so they can make informed recommendations to patients. To gain a better understanding of some therapeutic applications and how they are related to RNA and mRNA, research long non-coding RNA. Respond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: What is lncRNA and what does it do? How does IncRNA differ from mRNA? What are some therapeutic applications associated with lncRNA? Think about possible future uses of this application. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this application and its continued use?arrow_forwardfour fish or mussel species that are native to the great lakesarrow_forwardThere are a wide range of therapeutic applications available as options for patients. Medical professionals should be aware of these applications so they can make informed recommendations to patients. To gain a better understanding of some therapeutic applications and how they are related to RNA and mRNA, research long non-coding RNA. Respond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: What is lncRNA and what does it do? How does IncRNA differ from mRNA? What are some therapeutic applications associated with lncRNA? Think about possible future uses of this application. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this application and its continued use?arrow_forward
- four physial characteristics of a fish or a mussel that would help you identify it to a speciesarrow_forwarddescribe what you would do in this situation, you are working ona. river and it will take 20 minutes by boat to get back to the field truck, you are 1 hour from finishing the field work on the last day of field trip. you hear thunder int he dsitnace, what did you do?arrow_forwardunu grow because auxin is still produced in the tip to Another of Boysen and Jensen's experiments included the use of mica, explain why one of the shoots was able to show phototropism and the other was not. Mica Wafer Ligh c. They then t but this time permeable n shoot. Why phototropis Light Mica Wafer Coleoptile tips Tips removed: agar Explain why the shoo direction after the ag the cut shoot, even tarrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College





