
The question requires us to determine the reason which causes the selling of coffee to rise at the higher
Explanation of Solution
Generally, consumers are willing to purchase a product at a higher price when the product is either a necessity good or a Giffen good.
To help the farmers' people think that buying fair trade coffee is necessary, then people are willing to buy the coffee even at the higher price. So, the necessity factor will support the sellers to sell some coffee at a higher price.
The following graph will show the impact of a law that is preventing the price of coffee to fall below the fair-trade price:
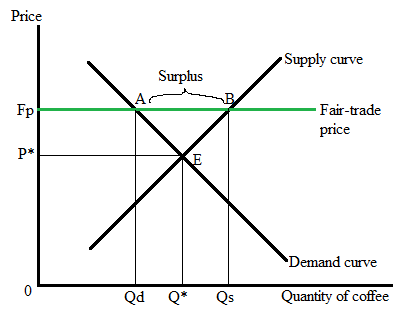
Here, E represents the initial equilibrium point in the market where Q* is the
At the equilibrium price, P*
Quantity demanded = Quantity supplied = Q*
Later, a law sets the fair-trade price Fp higher than the equilibrium price (P*). At this higher fair-trade price, the quantity supplied (Qs) is higher than the quantity demanded (Qd).
When Qs is more than Qd, the market represents the situation of surplus in the economy.
So, at a fare-trade price market will face a surplus of coffee.
Chapter 2R Solutions
EBK KRUGMAN'S ECONOMICS F/AP COURSE
- (d) Calculate the total change in qı. Total change: 007 (sp) S to vlijnsi (e) B₁ is our original budget constraint and B2 is our new budget constraint after the price of good 1 (p1) increased. Decompose the change in qı (that occurred from the increase in p₁) into the income and substitution effects. It is okay to estimate as needed via visual inspection. Add any necessary information to the graph to support your 03 answer. Substitution Effect: Income Effect:arrow_forwardeverything is in image (8 and 10) there are two images each separate questionsarrow_forwardeverything is in the picture (13) the first blank has the options (an equilibrium or a surplus) the second blank has the options (a surplus or a shortage)arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





