(a)
To determine:
Whether a H bond will be formed in a reaction between H3C-CH=O and H2O with the help of a figure.
Introduction:
(b)
To determine:
With the help of diagrams if the molecules Cl2, NH3 and CH4 will be polar or not.
Introduction:
When atoms combine to form molecules, they form chemical bonds by sharing, donating or accepting electrons. In case of sharing, the combining atoms may or may not share the electrons equally. If one of the atoms is more electronegative, it pulls the shared electron cloud towards itself and acquires negative charge. The other atom thus acquires positive charge. Such a molecule is called polar.
(c)
To determine:
The pH of a solution with a H+ concentration of 0.00001 M.
Introduction:
Dissociation of water results in generation of H+ and OH- ions. However, these ions are equal in number. Acids are compounds that release H+ in solution and bases are compounds that release OH- in solution. The pH scale expresses the concentration of H+ ions in a solution. pH less than 7 is indicative of acidic solution and pH above 7 indicates a basic (alkaline) solution. pH 7 is an indicator of a neutral solution.
(d)
To determine:
The pH of a solution with a OH- concentration of 0.00001 M.
Introduction:
Dissociation of water results in generation of H+ and OH- ions. However, these ions are equal in number. Acids are compounds that release H+ in solution and bases are compounds that release OH- in solution. The pH scale expresses the concentration of H+ ions in a solution. pH less than 7 is indicative of acidic solution and pH above 7 indicates a basic (alkaline) solution. pH 7 is an indicator of a neutral solution.
(e)
To determine:
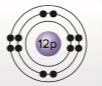
The kinds of bonds that magnesium can make based on the diagram of its atomic structure.
Introduction:
Atoms combine with other atoms by making chemical bonds with them. These bonds can be made by either sharing, donating or accepting electrons. The number of electrons in the outer-most orbital of an atom determine its tendency to form bonds. These electrons are called valence electrons. Chemical bonds are formed in a way that the outer-most orbital is completely filled with electrons.
(f)
To determine:
The kind of ion that Magnesium would make, depending on its valence.
Introduction:
Atoms combine with other atoms by making chemical bonds with them. These bonds can be made by either sharing, donating or accepting electrons. The number of electrons in the outer-most orbital of an atom determine its tendency to form bonds. These electrons are called valence electrons. Chemical bonds are formed in a way that the outer-most orbital is completely filled with electrons.
Explanation:
Looking at the atomic structure of Magnesium, it is observed that the 12 electrons are distributed is different orbital as 2, 8 and 2 electrons. The outer-most orbital has 2 electrons. Thus, Mg forms bonds by giving up its two valence electrons to atoms that may accept them. Thus, Mg loses 2 electrons to become positively charged ion Mg2+. Positively charged ions are also known as cations.
Conclusion:
Magnesium loses two electrons from its outer-most orbital to gain positive charge on its ion.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK FOUNDATIONS IN MICROBIOLOGY: BASIC
- You implant an FGF10-coated bead into the anterior flank of a chicken embryo, directly below the level of the wing bud. What is the phenotype of the resulting ectopic limb? Briefly describe the expected expression domains of 1) Shh, 2) Tbx4, and 3) Tbx5 in the resulting ectopic limb bud.arrow_forwardDesign a grafting experiment to determine if limb mesoderm determines forelimb / hindlimb identity. Include the experiment, a control, and an interpretation in your answer.arrow_forwardThe Snapdragon is a popular garden flower that comes in a variety of colours, including red, yellow, and orange. The genotypes and associated phenotypes for some of these flowers are as follows: aabb: yellow AABB, AABb, AaBb, and AaBB: red AAbb and Aabb: orange aaBB: yellow aaBb: ? Based on this information, what would the phenotype of a Snapdragon with the genotype aaBb be and why? Question 21 options: orange because A is epistatic to B yellow because A is epistatic to B red because B is epistatic to A orange because B is epistatic to A red because A is epistatic to B yellow because B is epistatic to Aarrow_forward
- A sample of blood was taken from the above individual and prepared for haemoglobin analysis. However, when water was added the cells did not lyse and looked normal in size and shape. The technician suspected that they had may have made an error in the protocol – what is the most likely explanation? The cell membranes are more resistant than normal. An isotonic solution had been added instead of water. A solution of 0.1 M NaCl had been added instead of water. Not enough water had been added to the red blood cell pellet. The man had sickle-cell anaemia.arrow_forwardA sample of blood was taken from the above individual and prepared for haemoglobin analysis. However, when water was added the cells did not lyse and looked normal in size and shape. The technician suspected that they had may have made an error in the protocol – what is the most likely explanation? The cell membranes are more resistant than normal. An isotonic solution had been added instead of water. A solution of 0.1 M NaCl had been added instead of water. Not enough water had been added to the red blood cell pellet. The man had sickle-cell anaemia.arrow_forwardWith reference to their absorption spectra of the oxy haemoglobin intact line) and deoxyhemoglobin (broken line) shown in Figure 2 below, how would you best explain the reason why there are differences in the major peaks of the spectra? Figure 2. SPECTRA OF OXYGENATED AND DEOXYGENATED HAEMOGLOBIN OBTAINED WITH THE RECORDING SPECTROPHOTOMETER 1.4 Abs < 0.8 06 0.4 400 420 440 460 480 500 520 540 560 580 600 nm 1. The difference in the spectra is due to a pH change in the deoxy-haemoglobin due to uptake of CO2- 2. There is more oxygen-carrying plasma in the oxy-haemoglobin sample. 3. The change in Mr due to oxygen binding causes the oxy haemoglobin to have a higher absorbance peak. 4. Oxy-haemoglobin is contaminated by carbaminohemoglobin, and therefore has a higher absorbance peak 5. Oxy-haemoglobin absorbs more light of blue wavelengths and less of red wavelengths than deoxy-haemoglobinarrow_forward
- With reference to their absorption spectra of the oxy haemoglobin intact line) and deoxyhemoglobin (broken line) shown in Figure 2 below, how would you best explain the reason why there are differences in the major peaks of the spectra? Figure 2. SPECTRA OF OXYGENATED AND DEOXYGENATED HAEMOGLOBIN OBTAINED WITH THE RECORDING SPECTROPHOTOMETER 1.4 Abs < 0.8 06 0.4 400 420 440 460 480 500 520 540 560 580 600 nm 1. The difference in the spectra is due to a pH change in the deoxy-haemoglobin due to uptake of CO2- 2. There is more oxygen-carrying plasma in the oxy-haemoglobin sample. 3. The change in Mr due to oxygen binding causes the oxy haemoglobin to have a higher absorbance peak. 4. Oxy-haemoglobin is contaminated by carbaminohemoglobin, and therefore has a higher absorbance peak 5. Oxy-haemoglobin absorbs more light of blue wavelengths and less of red wavelengths than deoxy-haemoglobinarrow_forwardWhich ONE of the following is FALSE regarding haemoglobin? It has two alpha subunits and two beta subunits. The subunits are joined by disulphide bonds. Each subunit covalently binds a haem group. Conformational change in one subunit can be transmitted to another. There are many variant ("mutant") forms of haemoglobin that are not harmful.arrow_forwardWhich ONE of the following is FALSE regarding haemoglobin? It has two alpha subunits and two beta subunits. The subunits are joined by disulphide bonds. Each subunit covalently binds a haem group. Conformational change in one subunit can be transmitted to another. There are many variant ("mutant") forms of haemoglobin that are not harmful.arrow_forward
- During a routine medical check up of a healthy man it was found that his haematocrit value was highly unusual – value of 60%. What one of the options below is the most likely reason? He will have a diet high in iron. He is likely to be suffering from anaemia. He lives at high altitude. He has recently recovered from an accident where he lost a lot of blood. He has a very large body size.arrow_forwardExplain what age of culture is most likely to produce an endospore?arrow_forwardExplain why hot temperatures greater than 45 degrees celsius would not initiate the sporulation process in endospores?arrow_forward
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning





