
Concept explainers
Draw the organic products formed in each reaction.
a.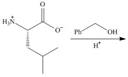 d.
d. 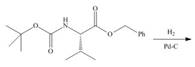
b.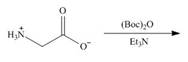 e.
e. 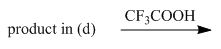
c. f.
f. 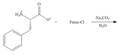
(a)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: An ester is formed by the reaction of carboxylic with alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. This reaction is known as Fischer Esterification.
Answer to Problem 29.60P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
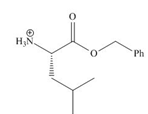
Explanation of Solution
In the given reaction, the oxygen of carboxyl group takes a proton from an acid. The carbon of carbonyl carbon acts as an electrophile where the attacking of oxygen of alcohol takes place and gives 1, 2-addition. The transfer of proton takes place leads to the elimination of water molecule. In the final step, deprotonation takes place. The corresponding reaction is shown below.
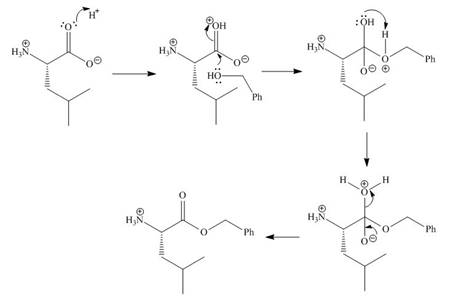
Figure 1
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Treatment of amine with t-butoxypyrocarbonate in the presence of triethyl amine yields t-butoxy carbonyl group.
Answer to Problem 29.60P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
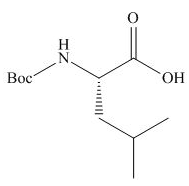
Explanation of Solution
The full form of
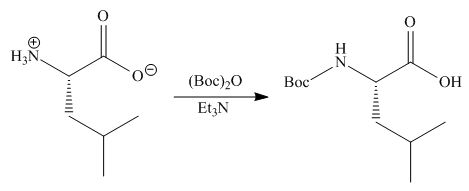
Figure 2
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The full form of DCC is dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. It is a dehydrating agent which is used to synthesized amides, nitriles and ketones.
Answer to Problem 29.60P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
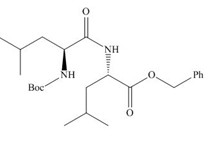
Explanation of Solution
As amine are basic in nature and they have tendency to convert carboxylic acid to carboxylate. In the given reaction, carboxylic acid adds to the DCC and forms a good leaving group which displaces by amine in nucleophilic substitution reaction. DCC forms an amide linkage. The corresponding reaction is shown below.
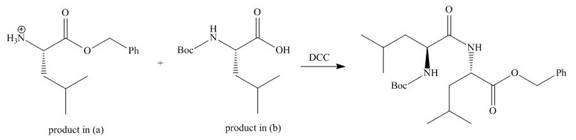
Figure 3
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 29.60P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
Explanation of Solution
In the given reaction, the reactant undergoes catalytic reduction in the presence of
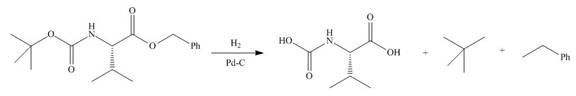
Figure 4
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 4.
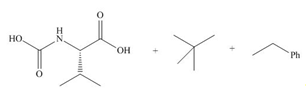
(e)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The halogenated derivative of acetic acid is TFA. The full form of TFA is trifluoroacetic acid. It is used to break the ester bond in peptide synthesis.
Answer to Problem 29.60P
The organic products formed in given reaction are,
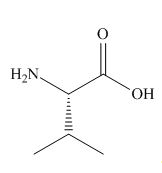
Explanation of Solution
Treatment of given compound with trifluoroacetic acid cleaves the bond
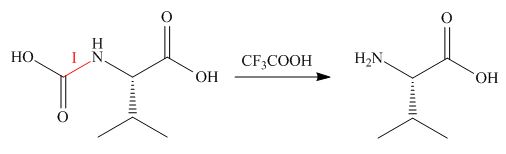
Figure 5
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The full form of Fmoc-Cl is fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl chloride. The molecular formula of Fmoc-Cl is
Answer to Problem 29.60P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
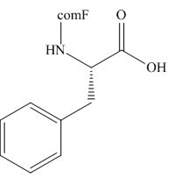
Explanation of Solution
The Fmoc-Cl introduces a group i.e. comF which protects the amine group towards action of sodium carbonate. In the given reaction, treatment of given compound with sodium carbonate in the presence of Fmoc-Cl forms a product with comF group as shown below.
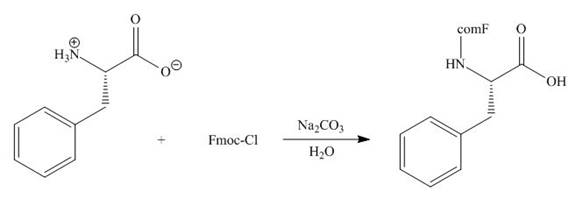
Figure 6
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 6.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 29 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Please provide steps to work for complete understanding.arrow_forwardPlease provide steps to work for complete understanding.arrow_forwardIdentify the Functional Groups (FG) in the following molecules. Classify C atoms as tertiary, 30, or quaternary 40. Identify secondary 20 and tertiary, 30 hydrogen atoms. Please provide steps to undertand each labeling.arrow_forward
- Identify the Functional Groups (FG) in the following molecules. Classify C atoms as tertiary, 30, or quaternary 40. Identify secondary 20 and tertiary, 30 hydrogen atoms. Please provide steps to undertand each labeling.arrow_forwardIdentify the Functional Groups (FG) in the following molecules. Classify C atoms as tertiary, 30, or quaternary 40. Identify secondary 20 and tertiary, 30 hydrogen atoms. Please provide steps to undertand each labeling.arrow_forwardIdentify the Functional Groups (FG) in the following molecules. Classify C atoms as tertiary, 30, or quaternary 40. Identify secondary 20 and tertiary, 30 hydrogen atoms. Please provide steps to undertand each labeling.arrow_forward
- A certain chemical reaction releases 24.7 kJ/g of heat for each gram of reactant consumed. How can you calculate what mass of reactant will produce 1460. J of heat? Set the math up. But don't do any of it. Just leave your answer as a math expression. Also, be sure your answer includes all the correct unit symbols. mass M 0.0 x μ 00 1 Garrow_forwardPlease don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Don't used hand raitingarrow_forwarda) Propose a method to synthesize the following product. More than one step reaction is required. (10 marks)arrow_forwardthe vibrational frequency of I2 is 214.5 cm-1. (i) Using the harmonic oscillator model, evaluate the vibrational partition function and the mean vibrational energy of I2 at 1000K. (ii) What is the characteristic vibrational temperature of I2? (iii) At 1000K, assuming high-temperature approximation, evaluate the vibrational partition function and the mean vibrational energy of I2. (iv) Comparing (i) and (iii), is the high-temperature approximation good for I2 at 1000K?arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

