
Concept explainers
A particle in the cyclotron shown in Figure 28.16a gains energy qΔV from the alternating power supply each time it passes from one dee to the other. The time interval for each full orbit is
so the particle’s average rate of increase in energy’ is
Notice that this power input is constant in time. On the other hand, the rate of increase in the radius r of its path is not constant. (a) Show that the rate of increase in the radius r of the panicle’s path is given by
(b) Describe how the path of the particles in Figure 28.16a is consistent with the result of part (a). (c) At what rate is the radial position of the protons in a cyclotron increasing immediately before the protons leave the cyclotron? Assume the cyclotron has an outer radius of 0.350 m, an accelerating voltage of ΔV = 600 V, and a magnetic field of magnitude 0.800 T. (d) By how much does the radius of the protons’ path increase during their last full revolution?
Figure 28.16 (a) A cyclotron consists of an ion source at P, two does D1 and D2 across which an alternating potential difference is applied, and a uniform magnetic field. (The south pole of the magnet is not shown.) (b) The first cyclotron, invented by E. O. Lawrence and M. S. Livingston in 1934.
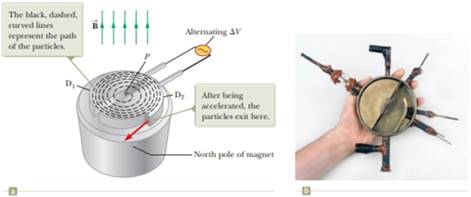
(a)
To prove: The rate of increase in the radius
Answer to Problem 29.28P
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The time interval of full orbit is
The formula for the energy is,
Here,
Differentiating equation (1) with respect to time
The above equation can be rewritten as,
Substitute
The formula for the centripetal force is,
The above equation can be rewritten as,
Differentiating equation (3) with respect to time
Deducing from equation (2) and equation (4),
Conclusion:
Therefore, the rate of increase in the radius
(b)
Answer to Problem 29.28P
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The time interval of full orbit is
The formula of change of radius with time is,
The value of the path of the particle is consistent with respect to time as according to the above formula the path is dependent on the radius of circle and the magnitude of the magnetic field which remains constant for a path.
Thus, the path of the particle is consistent.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the path of the particle is consistent.
(c)
Answer to Problem 29.28P
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The time interval of full orbit is
The formula for the change of radius with time is,
Substitute
Thus, the rate of increase of the radial direction of proton is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the rate of increase of the radial direction of proton is
(d)
Answer to Problem 29.28P
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The time interval of full orbit is
The formula for the velocity is,
Substitute
Thus, the velocity of proton is
The formula for the energy is,
Substitute
The formula for the energy at the end is,
Substitute
The formula for the radius at the end is,
Substitute
The formula for the increase in the radius is,
Substitute
Thus the increase in the radius of the path of proton is
Conclusion:
Therefore, increase in the radius of the path of proton is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 29 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
- 220 V is supplied to 800 primary turns of an autotransformer. What will the outputvoltage be across 200 secondary turns? 2. A filament transformer has a turns ratio of 1:20. What current must be supplied to theprimary windings if 5 A is required by the filament? 3. The filament transformer in the previous question is supplied with 150 V to theprimary side. What is the secondary voltage? 4. 440 V is supplied to 1000 primary turns of an autotransformer. If the desired outputvoltage is 100 V how many secondary turns must be tapped?arrow_forward220 volts is supplied across 1200 winding of the primary coil of the autotransformer.If 1650 windings are tapped, what voltage will be supplied to the primary coil of thehigh-voltage transformer?2. A kVp meter reads 86 kVp and the turns ratio of the high-voltage step-up transformeris 1200. What is the true voltage across the meter?3. The supply voltage from the autotransformer to the filament transformer is 60 volts. If theturns ratio of the filament transformer is 1/12, what is the filament voltage?4. If the current in the primary side of the filament transformer in question 3 were 0.5 A,what would be the filament current?5. The supply to a high-voltage step-up transformer with a turns ratio of 550 is 190 volts.What is the voltage across the x-ray tube?arrow_forward220 V is supplied to 800 primary turns of an autotransformer. What will the outputvoltage be across 200 secondary turns? 2. A filament transformer has a turns ratio of 1:20. What current must be supplied to theprimary windings if 5 A is required by the filament? 3. The filament transformer in the previous question is supplied with 150 V to theprimary side. What is the secondary voltage? 4. 440 V is supplied to 1000 primary turns of an autotransformer. If the desired outputvoltage is 100 V how many secondary turns must be tapped?arrow_forward
- Assume ax(u) is constant, then show thatarrow_forwardOne strain of bacteria was found to have a membrane potential of -120 mVmV at a pHpH of 7.5. A bacterium can be modeled as a 1.5-μmμm-diameter sphere. How many positive ions are needed on the exterior surface to establish this membrane potential? (There are an equal number of negative ions on the interior surface.) Assume that the membrane properties are the same as those of mammalian cells.arrow_forwardQ: Draw the fabrication layers of a transistor with metal and semiconductor MS junction (Schottkyj unction).arrow_forward

 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning





