
Concept explainers
Who’s the Pollinator? Massonia depressa is a low-growing succulent plant native to the desert of South Africa. The dull-colored flowers of this

A The dull petalless, ground-level flower of Massonia depressa are accessible to rodents, who push their heads through the stamens to reach the nectar at the bottom of floral cups. Note the pollen on the gerbil’s snout.
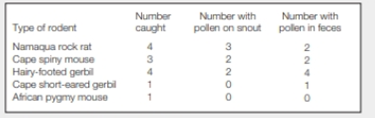
B Evidence of visits to M. depressa by rodents.
| Mammals allowed access to plants | Mammals excluded from plants | |
| Percent of plants that set fruit | 30.4 | 4.3 |
| Average number of fruits per pant | 1.39 | 0.47 |
| Average number of seeds per plant | 20.0 | 1.96 |
C Fruit and seed production of M. depressa with and without visits by mammals. Mammals were excluded from plants by wire cages with openings large enough for insects to pass through. Twenty-three plants were tested in each group.
FIGURE 29.7 Testing pollination of M. depressa by rodents.
How many rodents were captured? Of these, how many showed some evidence of ingesting M. depressa pollen?
To determine: The number of rodents captured.
Introduction: In the flowering plants, pollination is one of the necessary processes for sexual reproduction. Pollination involves the arrival of the pollen grains on a receptive stigma. Pollination takes place with the help of pollinating agents such as by wind or animal. Pollinators are the animal pollination vectors. The pollen, nectar, and other rewards are used by the plants to attract the pollinators. A plant called Massonia depressa is a low-growing moist plant that is commonly found in the semi-desert of South Africa. The leaves of these plants are sometimes maroon or green colored. The desert rodents such as gerbils are found to pollinate Massonia depressa plant.
Explanation of Solution
The environmental agents or animals are the pollination vectors, which help to transfer pollen from anther to stigma. As given in the data, Massonia depressa consists of dull-colored flowers with little petals, which usually grow at ground levels that are gathered together between the leaves. These petals have a tendency to release a yeasty aroma in order to make nectars. All adaptations in these flowers attract pollinators and rodents that help the flowers in pollination.
Refer Fig.29.7B, “Evidence of visits to M.depressa by rodents” in the textbook. The researchers believed that the gerbils, the desert rodents, pollinated this plant. In order to confirm this, they captured 13 rodents and checked for pollen on their snout and in the feces.
The number of rodents captured is 13.
To determine: The number of rodents that shows some evidence of ingesting Massonia depressa.
Introduction: A plant called Massonia depressa is a low-growing moist plant that is commonly found in the semi-desert of South Africa. The leaves of these plants are sometimes maroon or green colored. The desert rodents such as gerbils are found to pollinate Massonia depressa plant.
Explanation of Solution
The researchers observed that out of 13 rodents caught, seven of them had pollen on their snout. This sign suggested that the rodents pushed their heads through the stamens to arrive at the nectar. Also, out of the 13 rodents caught, nine of them had pollen in the feces. Some of the members of rodents also had both pollen on their snout and in their feces.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 29 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
- What is the concept "calories consumed must equal calories burned" in regrads to nutrition?arrow_forwardYou intend to insert patched dominant negative DNA into the left half of the neural tube of a chick. 1) Which side of the neural tube would you put the positive electrode to ensure that the DNA ends up on the left side? 2) What would be the internal (within the embryo) control for this experiment? 3) How can you be sure that the electroporation method itself is not impacting the embryo? 4) What would you do to ensure that the electroporation is working? How can you tell?arrow_forwardDescribe a method to document the diffusion path and gradient of Sonic Hedgehog through the chicken embryo. If modifying the protein, what is one thing you have to consider in regards to maintaining the protein’s function?arrow_forward
- The following table is from Kumar et. al. Highly Selective Dopamine D3 Receptor (DR) Antagonists and Partial Agonists Based on Eticlopride and the D3R Crystal Structure: New Leads for Opioid Dependence Treatment. J. Med Chem 2016.arrow_forwardThe following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin. You are a chef in a fancy new science-themed restaurant. You have a recipe that calls for 1 teaspoon of resinferatoxin, but you feel uncomfortable serving foods with "toxins" in them. How much capsaicin could you substitute instead?arrow_forwardWhat protein is necessary for packaging acetylcholine into synaptic vesicles?arrow_forward
- 1. Match each vocabulary term to its best descriptor A. affinity B. efficacy C. inert D. mimic E. how drugs move through body F. how drugs bind Kd Bmax Agonist Antagonist Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamicsarrow_forward50 mg dose of a drug is given orally to a patient. The bioavailability of the drug is 0.2. What is the volume of distribution of the drug if the plasma concentration is 1 mg/L? Be sure to provide units.arrow_forwardDetermine Kd and Bmax from the following Scatchard plot. Make sure to include units.arrow_forward
- Choose a catecholamine neurotransmitter and describe/draw the components of the synapse important for its signaling including synthesis, packaging into vesicles, receptors, transporters/degradative enzymes. Describe 2 drugs that can act on this system.arrow_forwardThe following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin. a) Which has a higher potency? b) Which is has a higher efficacy? c) What is the approximate Kd of capsaicin in uM? (you can round to the nearest power of 10)arrow_forwardWhat is the rate-limiting-step for serotonin synthesis?arrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





