
Biological Science, Loose-leaf Edition (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780135272800
Author: Scott Freeman, Kim Quillin, Lizabeth Allison, Michael Black, Greg Podgorski, Emily Taylor, Jeff Carmichael
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 29, Problem 15PIAT
Summary Introduction
To review:
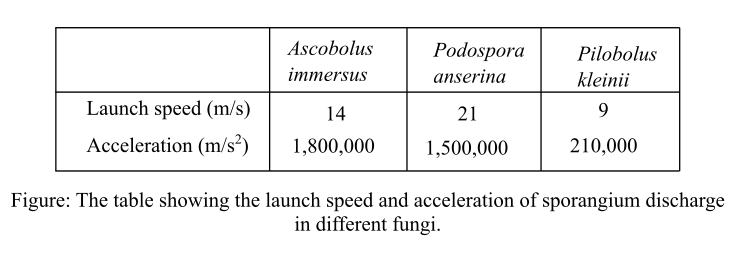
The comparison between the launch speed and acceleration of Pilobolus and other
Introduction:
The sporangium is the structure, in which the process of meiosis occurs during the life cycle of sporophytic mycelium. The sporangium discharge occurs in several spore-shooting fungi. The table below shows the data related to the launch speed and the acceleration of sporangium discharge in different fungi.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
students in a science class investiged the conditions under which corn seeds would germinate most successfully. BAsed on the results which of these factors appears most important for successful corn seed germination.
I want to write the given physician orders in the kardex form
Amino
Acid Coclow
TABle
3'
Gly
Phe
Leu
(G)
(F) (L)
3-
Val
(V)
Arg (R)
Ser (S)
Ala
(A)
Lys (K)
CAG
G
Glu
Asp (E)
(D)
Ser
(S)
CCCAGUCAGUCAGUCAG
0204
C
U
A G
C
Asn
(N)
G
4
A
AGU
C
GU
(5)
AC
C
UGA
A
G5
C
CUGACUGACUGACUGAC
Thr
(T)
Met (M)
lle
£€
(1)
U
4
G
Tyr
Σε
(Y)
U
Cys (C)
C
A
G
Trp (W) 3'
U
C
A
Leu
בוט
His
Pro
(P)
££
(H)
Gin
(Q)
Arg
흐름
(R)
(L)
Start
Stop
8. Transcription and Translation Practice: (Video 10-1 and 10-2)
A. Below is the sense strand of a DNA gene. Using the sense strand, create the antisense
DNA strand and label the 5' and 3' ends.
B. Use the antisense strand that you create in part A as a template to create the mRNA
transcript of the gene and label the 5' and 3' ends.
C. Translate the mRNA you produced in part B into the polypeptide sequence making sure
to follow all the rules of translation.
5'-AGCATGACTAATAGTTGTTGAGCTGTC-3' (sense strand)
4
Chapter 29 Solutions
Biological Science, Loose-leaf Edition (7th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the structure and function of Eukaryotic cells, including their organelles? How are Eukaryotic cells different than Prokaryotic cells, in terms of evolution which form of the cell might have came first? How do Eukaryotic cells become malignant (cancerous)?arrow_forwardWhat are the roles of DNA and proteins inside of the cell? What are the building blocks or molecular components of the DNA and proteins? How are proteins produced within the cell? What connection is there between DNA, proteins, and the cell cycle? What is the relationship between DNA, proteins, and Cancer?arrow_forwardWhy cells go through various types of cell division and how eukaryotic cells control cell growth through the cell cycle control system?arrow_forward
- In one paragraph show how atoms and they're structure are related to the structure of dna and proteins. Talk about what atoms are. what they're made of, why chemical bonding is important to DNA?arrow_forwardWhat are the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins).arrow_forwardThe Sentinel Cell: Nature’s Answer to Cancer?arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Question You are working to characterize a novel protein in mice. Analysis shows that high levels of the primary transcript that codes for this protein are found in tissue from the brain, muscle, liver, and pancreas. However, an antibody that recognizes the C-terminal portion of the protein indicates that the protein is present in brain, muscle, and liver, but not in the pancreas. What is the most likely explanation for this result?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain/discuss how “slow stop” and “quick/fast stop” mutants wereused to identify different protein involved in DNA replication in E. coli.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question A gene that codes for a protein was removed from a eukaryotic cell and inserted into a prokaryotic cell. Although the gene was successfully transcribed and translated, it produced a different protein than it produced in the eukaryotic cell. What is the most likely explanation?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
