
(a)
Interpretation:
It should be identified that will a thermal 1, 3-migrations of carbon occur with whether retention or inversion of configuration.
Concept introduction:
Pericyclic reactions are “ any concerted reaction in which bonds are formed or brocken in a cyclic transition state”. There is a single transition state from start to finish, in contrast to a stepwise reaction.
There are mainly three types of pericyclic reactions,
- 1) Electrocyclic reactions
- 2) Cycloaddition reactions
- 3) Sigmatropic reactions
In a sigmatropic reaction “ one new sigma-bond is formed as another breaks.”
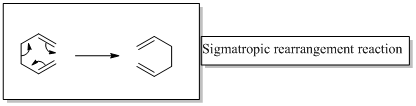
Sigmatropic rearrangement reactions are named with digits. For example a [1, 3] sigmatropic rearrangement describe a reaction in which the residue migrates from position 1 to position 3.
Migration of carbon and hydrogen will occur in a sigmatropic rearrangement reaction.
When hydrogen migrates in a sigmatropic rearrangement, the s orbital of the hydrogen is partially bonded to both the migration origin and the migration terminus in the transition state.
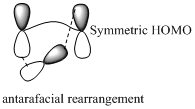
Migration of hydrogen in suprafacial and antarafacial rearrangement can be represented as follows,


Migration of carbon occurs through two ways because it has a two lobed p orbital. Carbon can simultaneously interact with the migration origin and the migration terminus using one lobe of its p orbital.
Migration of carbon in suprafacial and antarafacial rearrangement can be represented as follows,
Carbon migrating with one lobe of its p orbital interacting


Carbon migrating with both lobe of its p orbital interacting

Inversion of configuration is the inversion of a chiral center in a molecule in a
Retention of configuration is the preservation of integrity of the spatial arrangement of bonds to a chiral center during a chemical reaction.
(b)
Interpretation:
It should be identified that will a thermal 1, 5-migrations of carbon occur with whether retention or inversion of configuration.
Concept introduction:
Pericyclic reactions are “ any concerted reaction in which bonds are formed or brocken in a cyclic transition state”. There is a single transition state from start to finish, in contrast to a stepwise reaction.
There are mainly three types of pericyclic reactions,
- 1) Electrocyclic reactions
- 2) Cycloaddition reactions
- 3) Sigmatropic reactions
In a sigmatropic reaction “ one new sigma-bond is formed as another breaks.”

Sigmatropic rearrangement reactions are named with digits. For example a [1, 3] sigmatropic rearrangement describe a reaction in which the residue migrates from position 1 to position 3.
Migration of carbon and hydrogen will occur in a sigmatropic rearrangement reaction.
When hydrogen migrates in a sigmatropic rearrangement, the s orbital of the hydrogen is partially bonded to both the migration origin and the migration terminus in the transition state.
Migration of hydrogen in suprafacial and antarafacial rearrangement can be represented as follows,


Migration of carbon occurs through two ways because it has a two lobed p orbital. Carbon can simultaneously interact with the migration origin and the migration terminus using one lobe of its p orbital.
Migration of carbon in suprafacial and antarafacial rearrangement can be represented as follows,
Carbon migrating with one lobe of its p orbital interacting


Carbon migrating with both lobe of its p orbital interacting


Inversion of configuration is the inversion of a chiral center in a molecule in a chemical reaction.
Retention of configuration is the preservation of integrity of the spatial arrangement of bonds to a chiral center during a chemical reaction.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 28 Solutions
Pearson eText Organic Chemistry -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
- Provide the semi-developed formula of isooxazole obtained by reacting acetylacetone and hydroxylamine.arrow_forwardGiven a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound (R1-CO-CH2-CO-R2), indicate the formula of the compound obtaineda) if I add hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to give an isooxazole.b) if I add thiosemicarbazide (NH2-CO-NH-NH2) to give an isothiazole.arrow_forwardAn orange laser has a wavelength of 610 nm. What is the energy of this light?arrow_forward
- The molar absorptivity of a protein in water at 280 nm can be estimated within ~5-10% from its content of the amino acids tyrosine and tryptophan and from the number of disulfide linkages (R-S-S-R) between cysteine residues: Ε280 nm (M-1 cm-1) ≈ 5500 nTrp + 1490 nTyr + 125 nS-S where nTrp is the number of tryptophans, nTyr is the number of tyrosines, and nS-S is the number of disulfide linkages. The protein human serum transferrin has 678 amino acids including 8 tryptophans, 26 tyrosines, and 19 disulfide linkages. The molecular mass of the most dominant for is 79550. Predict the molar absorptivity of transferrin. Predict the absorbance of a solution that’s 1.000 g/L transferrin in a 1.000-cm-pathlength cuvet. Estimate the g/L of a transferrin solution with an absorbance of 1.50 at 280 nm.arrow_forwardIn GC, what order will the following molecules elute from the column? CH3OCH3, CH3CH2OH, C3H8, C4H10arrow_forwardBeer’s Law is A = εbc, where A is absorbance, ε is the molar absorptivity (which is specific to the compound and wavelength in the measurement), and c is concentration. The absorbance of a 2.31 × 10-5 M solution of a compound is 0.822 at a wavelength of 266 nm in a 1.00-cm cell. Calculate the molar absorptivity at 266 nm.arrow_forward
- How to calculate % of unknown solution using line of best fit y=0.1227x + 0.0292 (y=2.244)arrow_forwardGiven a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound, state the (condensed) formula of the compound obtaineda) if I add hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to give an isooxazole.b) if I add thiosemicarbazide (NH2-CO-NH-NH2) to give an isothiazole.arrow_forwardComplete the following acid-base reactions and predict the direction of equilibrium for each. Justify your prediction by citing pK values for the acid and conjugate acid in each equilibrium. (a) (b) NHs (c) O₂N NH NH OH H₁PO₁arrow_forward
- 23.34 Show how to convert each starting material into isobutylamine in good yield. ཅ ནད ཀྱི (b) Br OEt (c) (d) (e) (f) Harrow_forwardPlease help me Please use https://app.molview.com/ to draw this. I tried, but I couldn't figure out how to do it.arrow_forwardPropose a synthesis of 1-butanamine from the following: (a) a chloroalkane of three carbons (b) a chloroalkane of four carbonsarrow_forward
 EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning



