
(a)
Interpretation: The kind of sigmatropic rearrangement that occurs in each of the given reactions has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Pericyclic reactions are “ any concerted reaction in which bonds are formed or brocken in a cyclic transition state”. There is a single transition state from start to finish, in contrast to a stepwise reaction.
There are mainly three types of pericyclic reactions,
- 1) Electrocyclic reactions
- 2) Cycloaddition reactions
- 3) Sigmatropic reactions
In a sigmatropic reaction “ one new sigma-bond is formed as another breaks.”
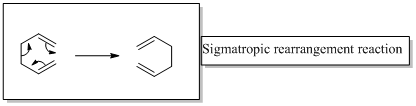
Sigmatropic rearrangement reactions are named with digits. For example a [1, 3] sigmatropic rearrangement describe a reaction in which the residue migrates from position 1 to position 3.
(b)
Interpretation: Using arrows the electron rearrangement takes place in the given reactions has to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Pericyclic reactions are “ any concerted reaction in which bonds are formed or brocken in a cyclic transition state”. There is a single transition state from start to finish, in contrast to a stepwise reaction.
There are mainly three types of pericyclic reactions,
- 1) Electrocyclic reactions
- 2) Cycloaddition reactions
- 3) Sigmatropic reactions
In a sigmatropic reaction “ one new sigma-bond is formed as another breaks.”

Sigmatropic rearrangement reactions are named with digits. For example a [1, 3] sigmatropic rearrangement describe a reaction in which the residue migrates from position 1 to position 3.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 28 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- Another standard reference electrode is the standard calomel electrode: Hg2Cl2(s) (calomel) + 2e2 Hg() +2 Cl(aq) This electrode is usually constructed with saturated KCI to keep the Cl- concentration constant (similar to what we discussed with the Ag-AgCl electrode). Under these conditions the potential of this half-cell is 0.241 V. A measurement was taken by dipping a Cu wire and a saturated calomel electrode into a CuSO4 solution: saturated calomel electrode potentiometer copper wire CuSO4 a) Write the half reaction for the Cu electrode. b) Write the Nernst equation for the Cu electrode, which will include [Cu2+] c) If the voltage on the potentiometer reads 0.068 V, solve for [Cu²+].arrow_forward2. (Part B). Identify a sequence of FGI that prepares the Synthesis Target 2,4-dimethoxy- pentane. All carbons in the Synthesis Target must start as carbons in either ethyne, propyne or methanol. Hint: use your analysis of Product carbons' origins (Part A) to identify possible structure(s) of a precursor that can be converted to the Synthesis Target using one FGI. All carbons in the Synthesis Target must start as carbons in one of the three compounds below. H = -H H = -Me ethyne propyne Synthesis Target 2,4-dimethoxypentane MeOH methanol OMe OMe MeO. OMe C₂H₁₂O₂ Product carbons' origins Draw a box around product C's that came from A1. Draw a dashed box around product C's that came from B1.arrow_forwardDraw the skeletal ("line") structure of the smallest organic molecule that produces potassium 3-hydroxypropanoate when reacted with KOH. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Sarrow_forward
- draw skeletal structures for the minor products of the reaction.arrow_forward1. Provide missing starting materials, reagents, products. If a product cannot be made, write NP (not possible) in the starting material box. C7H12O Ph HO H 1) 03-78 C 2) Me₂S + Ph .H OH + 2nd stereoisomer OH Ph D + enantiomer cat OsO 4 NMO H2O acetonearrow_forwardPlease note that it is correct and explains it rightly:Indicate the correct option. The proportion of O, C and H in the graphite oxide is:a) Constant, for the quantities of functional groups of acids, phenols, epoxy, etc. its constants.b) Depending on the preparation method, as much oxidant as the graphite is destroyed and it has less oxygen.c) Depends on the structure of the graphic being processed, whether it can be more tridimensional or with larger crystals, or with smaller crystals and with more edges.arrow_forward
- Check the box under each a amino acid. If there are no a amino acids at all, check the "none of them" box under the table. Note for advanced students: don't assume every amino acid shown must be found in nature. ནང་་་ OH HO HO NH2 + NH3 O OIL H-C-CO CH3-CH O C=O COOH COOH + H2N C-H O H2N C H CH3-CH CH2 HO H3N O none of them 口 CH3 CH2 OH Хarrow_forwardWhat is the systematic name of the product P of this chemical reaction? 010 HO-CH2-CH2-C-OH ☐ + NaOH P+ H2Oarrow_forward1. Provide missing starting materials, reagents, products. If a product cannot be made, write NP (not possible) in the starting material box. a) C10H12 Ph OMe AcOHg+ + enantiomer Br C6H10O2 + enantiomerarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
