
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The number of MOs in the given compound
Concept introduction:
Molecular orbital theory suggests that atomic orbitals of different atoms combines to create molecular orbitals.
Molecular orbitals can be constructed from linear combination of atomic orbitals.
Bonding orbotals are formed by the additive combination of atomic orbitals and the antibonding orbitals are formed by the substractive combination of atomic orbitals.
Antibonding orbital is a molecular orbital that results when two parallel atomic orbitals with opposite phases interact.
Antibonding orbitals have higher energy than the bonding molecular orbitals.
Ground state and and exited states are the positions with lower and higher energy respectively.
HOMO is a molecular orbital which is the abbrevation of Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital.
LUMO is also a molecular orbital which is the short form of Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital.
If the lobes at the ends of the MO are in phase, then the MO is symmetric.
If the two lobes are out phase then the MO is antisymmetric.
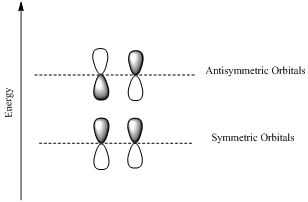
(b)
Interpretation: The designation of HOMO for the given molecule’s molecular orbital has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Molecular orbital theory suggests that atomic orbitals of different atoms combines to create molecular orbitals.
Molecular orbitals can be constructed from linear combination of atomic orbitals.
Bonding orbotals are formed by the additive combination of atomic orbitals and the antibonding orbitals are formed by the substractive combination of atomic orbitals.
Antibonding orbital is a molecular orbital that results when two parallel atomic orbitals with opposite phases interact.
Antibonding orbitals have higher energy than the bonding molecular orbitals.
Ground state and and exited states are the positions with lower and higher energy respectively.
HOMO is a molecular orbital which is the abbrevation of Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital.
LUMO is also a molecular orbital which is the short form of Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital.
If the lobes at the ends of the MO are in phase, then the MO is symmetric.
If the two lobes are out phase then the MO is antisymmetric.
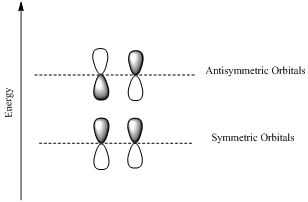
(c)
Interpretation: Number of nodes in the given molecule has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Molecular orbital theory suggests that atomic orbitals of different atoms combines to create molecular orbitals.
Molecular orbitals can be constructed from linear combination of atomic orbitals.
Bonding orbotals are formed by the additive combination of atomic orbitals and the antibonding orbitals are formed by the substractive combination of atomic orbitals.
Antibonding orbital is a molecular orbital that results when two parallel atomic orbitals with opposite phases interact.
Antibonding orbitals have higher energy than the bonding molecular orbitals.
Ground state and and exited states are the positions with lower and higher energy respectively.
HOMO is a molecular orbital which is the abbrevation of Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital.
LUMO is also a molecular orbital which is the short form of Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital.
If the lobes at the ends of the MO are in phase, then the MO is symmetric.
If the two lobes are out phase then the MO is antisymmetric.
Node is the site with zero electron density.
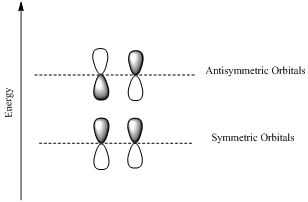
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 28 Solutions
Organic Chemistry; Organic Chemistry Study Guide A Format: Kit/package/shrinkwrap
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
