
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS & ENGINEERS
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134296074
Author: GIANCOLI
Publisher: VST
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 28, Problem 19P
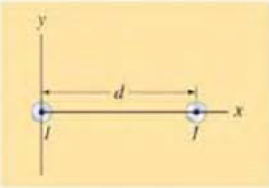
(II) Let two long parallel wires, a distance d apart, carry equal currents I in the same direction. One wire is at x = 0, the other at x = d, Fig. 28–38. Determine
FIGURE 28–38 Problem 19 and 20.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!
a) Use the node-voltage method to find v1, v2, and
v3 in the circuit in Fig. P4.14.
b) How much power does the 40 V voltage source
deliver to the circuit?
Figure P4.14
302
202
w
w
+
+
+
40 V
V1
80 Ω 02
ΣΑΩ
28 A
V3 +
w
w
102
202
Please solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!
Chapter 28 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS & ENGINEERS
Ch. 28 - The magnetic field due to current in wires in your...Ch. 28 - Compare and contrast the magnetic field due to a...Ch. 28 - Two insulated long wires carrying equal currents I...Ch. 28 - Prob. 4QCh. 28 - (a) Write Ampres law for a path that surrounds...Ch. 28 - Use the Biot-Savart law to show that the field of...Ch. 28 - Prob. 9QCh. 28 - Why does twisting the lead-in wires to electrical...Ch. 28 - Compare the Biot-Savart law with Coulombs law....Ch. 28 - Will a magnet attract any metallic object, such as...
Ch. 28 - An unmagnetized nail will not attract an...Ch. 28 - Prob. 18QCh. 28 - Prob. 5PCh. 28 - (II) A third wire is placed in the plane of the...Ch. 28 - Prob. 18PCh. 28 - (II) Let two long parallel wires, a distance d...Ch. 28 - (II) Repeat Problem 19 if the wire at x = 0...Ch. 28 - Prob. 36PCh. 28 - (II) A wire, in a plane, has the shape shown in...Ch. 28 - (II) A circular conducting ring of radius R is...Ch. 28 - Prob. 40PCh. 28 - Prob. 56GPCh. 28 - A rectangular loop of wire carries a 2.0-A current...Ch. 28 - Prob. 60GPCh. 28 - A 175-g model airplane charged to 18.0 mC and...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
In rabbits, chocolate-colored fur (w+) is dominant to white fur (w), straight fur (c+) is dominant to curly fur...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
What are the four types of tissues, and what are their characteristics?
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Using the forked-line, or branch diagram, method, determine the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of these trihyb...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Your bore cells, muscle cells, and skin cells look different because a. different kinds of genes are present in...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
The following data were obtained from a disk-diffusion test. Antibiotic Zone of Inhibition A 15 mm B 0 mm c 7 m...
Microbiology: An Introduction
1. Why is the quantum-mechanical model of the atom important for understanding chemistry?
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You're on an interplanetary mission, in an orbit around the Sun. Suppose you make a maneuver that brings your perihelion in closer to the Sun but leaves your aphelion unchanged. Then you must have Question 2 options: sped up at perihelion sped up at aphelion slowed down at perihelion slowed down at aphelionarrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE DO NOT USE LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward་ The position of a particle is described by r = (300e 0.5t) mm and 0 = (0.3t²) rad, where t is in seconds. Part A Determine the magnitude of the particle's velocity at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. v = Value Submit Request Answer Part B ? Units Determine the magnitude of the particle's acceleration at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. a = Value A ? Unitsarrow_forward
- Solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardA spiral transition curve is used on railroads to connect a straight portion of the track with a curved portion. (Figure 1) Part A v = v₁ft/s 600 ft y = (106) x³ If the spiral is defined by the equation y = (106)³, where x and y are in feet, determine the magnitude of the acceleration of a train engine moving with a constant speed of v₁ = 30 ft/s when it is at point x = 600 ft. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? a = Value Unitsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Magnets and Magnetic Fields; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IgtIdttfGVw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY