
Concept explainers
Show the products you would expect to obtain from reaction of glyceryl Trioleate with the following reagents:
(a) Excess Br2 in CH2Cl2
(b) H2/Pd
(c) NaOH/H2O
(d) O3, then Zn/CH3CO2H
(e) LiAlH4, then H3O1
(f) CH3MgBr, then H3O1
a) Excess Br2 in CH2Cl2
Interpretation:
The product expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with excess bromine in CH2Cl2 is to be given.
Concept introduction:
When compounds containing more than one olefinic double bond are treated with bromine in excess, addition of bromine to all the olefinic double bonds in the molecule takes place.
To give:
The product expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with excess bromine in CH2Cl2.
Answer to Problem 20AP
The product expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with excess bromine in CH2Cl2 is

Explanation of Solution
Glyceryl trioleate has three olefinic diuble bonds. When glyceryl trioleate is treated with excess bromine in CH2Cl2 addition of bromine takes place to all the three double bonds in the molecule.
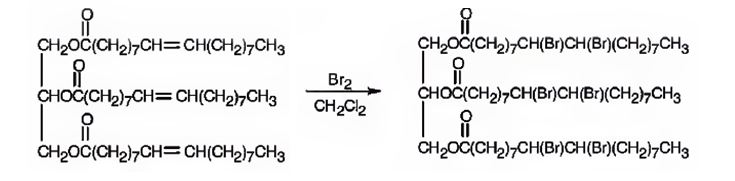
The product expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with excess bromine in CH2Cl2 is

b) H2/Pd
Interpretation:
The product expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with H2/Pd is to be given.
Concept introduction:
When compounds containing more than one olefinic double bond are treated with H2/Pd, reduction occurs and addition of hydrogen to all the double bonds in the molecule takes place.
To give:
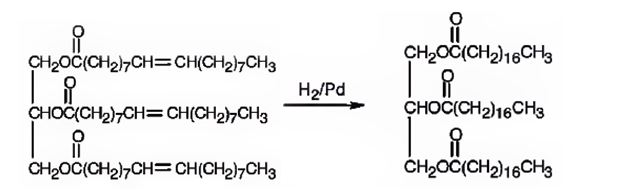
The product expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with H2/Pd.
Answer to Problem 20AP
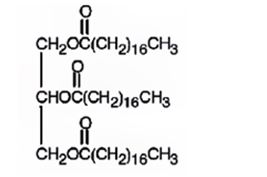
The product expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with H2/Pd is
Explanation of Solution
When glyceryl trioleate is treated with H2/Pd, addition of hydrogen takes place to the three double bonds in the molecule to yield a saturated compound.
The product expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with H2/Pd is

c) NaOH/H2O
Interpretation:
The products expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with NaOH/H2O are to be given.
Concept introduction:
When an oil or fat is treated with aqueous NaOH, the ester linkages in them get hydrolyzed to yield glycerol and sodium salt of the acid.
To give:
The products expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with NaOH/H2O.
Answer to Problem 20AP
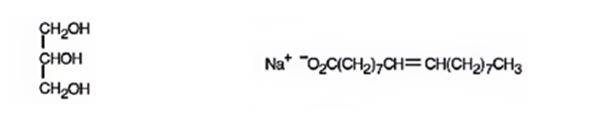
The products expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with NaOH/H2O are given below.
Explanation of Solution
When glyceryl trioleate is treated with aqueous NaOH, the ester linkages in them get hydrolyzed to yield glycerol and sodium oleate.
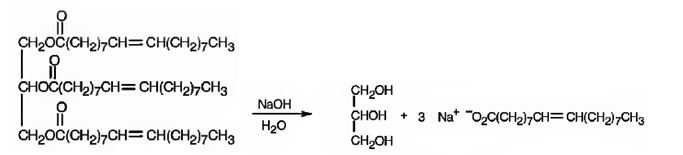
The products expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with NaOH/H2O are given below.

d) O3, then Zn/CH3CO2H
Interpretation:
The products expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with O3, then with Zn/CH3COOH are to be given.
Concept introduction:
When a compound with double bond is treated with ozone and then with Zn/ CH3COOH, the double bond gets cleaved and the products have an oxygen atom attached to each carbon originally in the double bond.
To give:
The products expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with O3, then with Zn/CH3COOH.
Answer to Problem 20AP
The products expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with O3, then with Zn/CH3COOH are given below.

Explanation of Solution
When glyceryl trioleate is treated with O3 and then with Zn/CH3COOH, ozone adds to the three double bonds to yield a triozonide which is cleaved when treated with Zn/CH3COOH to give two different aldehydes as products. The aldehyde carbons are present in a double bond in glyceryl trioleate.
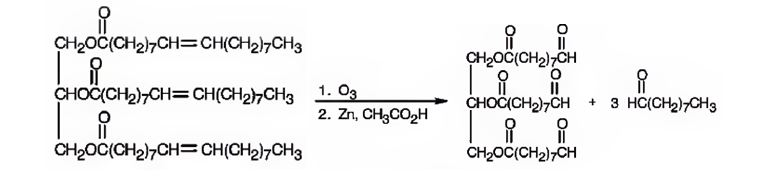
The products expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with O3, then with Zn/CH3COOH are given below.

e) LiAlH4, then H3O+
Interpretation:
The products expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with LiAlH4, then with H3O+ are to be given.
Concept introduction:
When oils and fats are reduced with LiAlH4, then with H3O+, the eater linkages are reduced to give glycerol and the free acid. Double bonds are not reduced by LiAlH4.
To give:
The products expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with LiAlH4, then with H3O+.
Answer to Problem 20AP
The products expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with LiAlH4, then with H3O+ are given below.
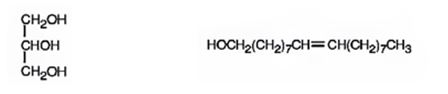
Explanation of Solution
When glyceryl trioleate is treated with LiAlH4 and then with H3O+ the ester linkages in it are reduced to alcohols. LiAlH4 does not reduce the double bonds in glyceryl trioleate.
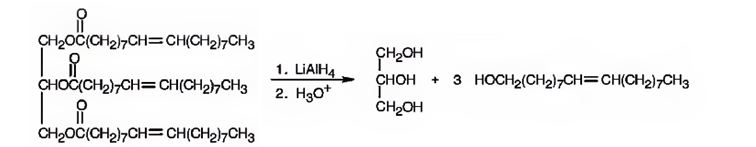
The products expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with LiAlH4, then with H3O+ are given below.

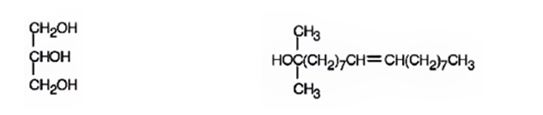
f) CH3MgBr, then H3O+
Interpretation:
The products expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with CH3MgBr, then with H3O+ are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Esters when treated with a Grignard reagent and then with H3O+, react with two equivalents of the Grignard reagent to yield a tertiary alcohol. In oils and fats addition of Grignard reagent will take place to all the three carbonyl groups in the ester.
To give:
The products expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with CH3MgBr, then with H3O+.
Answer to Problem 20AP
The products expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with CH3MgBr, then with H3O+ are given below.
Explanation of Solution
When glyceryl trioleate is treated with CH3MgBr, addition to carbonyl carbons takes place. The addition product when hydrolyzed with H3O+ yields three equivalents of a tertiary alcohol and glycerol as products.
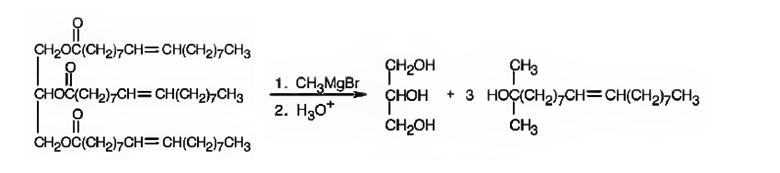
The products expected to be formed when glyceryl trioleate reacts with CH3MgBr, then with H3O+ are given below.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 27 Solutions
OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Physical Universe
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- 4) Which oxygen atom in the structure below is most basic / nucleophilic? Please explain by discussing the electron density around each oxygen atom. Show at least three resonance structures for the compound. оогоarrow_forwardCan you show me this problem. Turn them into lewis dot structures for me please and then answer the question because I cant seem to comprehend it/ The diagrams on the picture look too small I guess.arrow_forwardThe fire releases 2.80 x 107 Joules of heat energy for each liter of oil burned. The water starts out at 24.5 °C, raising the water's temperature up to 100 °C, and then raises the temperature of the resulting steam up to 325 °C. How many liters of water will be needed to absorb the heat from the fire in this way, for each 1.0 liter of crude oil burned? 4186 J/(kg°C) = heat of water 2020 J/(kg°C) = heat of steam 2,256,000 (i.e. 2.256 x 106) J/kg = latent heat of vaporization for water (at the boiling point of 100 °C).arrow_forward
- 6 Which of the following are likely to be significant resonance structures of a resonance hybrid? Draw another resonance structure for each of the compounds you select as being a resonance form. (A Br: Br: A B C D Earrow_forwardWrite the systematic (IUPAC) name for the following organic molecules. Note for advanced students: you do not need to include any E or Z prefixes in your names. Br structure Br Br Oweuarrow_forwardConservation of mass was discussed in the background. Describe how conservation of mass (actual, not theoretical) could be checked in the experiment performed.arrow_forward
- What impact would adding twice as much Na2CO3 than required for stoichiometric quantities have on the quantity of product produced? Initial results attachedarrow_forwardGiven that a theoretical yield for isolating Calcium Carbonate in this experiment would be 100%. From that information and based on the results you obtained in this experiment, describe your success in the recovery of calcium carbonate and suggest two possible sources of error that would have caused you to not obtain 100% yield. Results are attached form experimentarrow_forward5) Calculate the flux of oxygen between the ocean and the atmosphere(2 pts), given that: (from Box 5.1, pg. 88 of your text): Temp = 18°C Salinity = 35 ppt Density = 1025 kg/m3 Oxygen concentration measured in bulk water = 263.84 mmol/m3 Wind speed = 7.4 m/s Oxygen is observed to be about 10% initially supersaturated What is flux if the temperature is 10°C ? (2 pts) (Hint: use the same density in your calculations). Why do your calculated values make sense (or not) based on what you know about the relationship between gas solubility and temperature (1 pt)?arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

