
The circuit in Figure P27.85 shows four capacitors connected to a battery. The switch S is initially open, and all capacitors have reached their final charge. The capacitances are C1 = 6.00 μF, C2 = 12.00 μF, C3 = 8.00 μF, and C4 = 4.00 μF. a. Find the potential difference across each capacitor and the charge stored in each. b. The switch is now closed. What is the new final potential difference across each capacitor and the new charge stored in each?
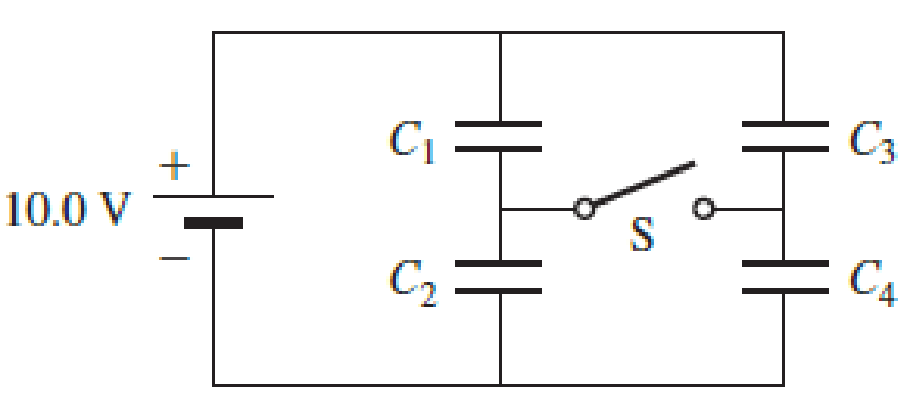
Figure P27.85
(a)
The potential difference across the capacitors and the charge stores in each capacitor.
Answer to Problem 85PQ
The charge stored in
The potential difference across the capacitors
Explanation of Solution
The circuit diagram,
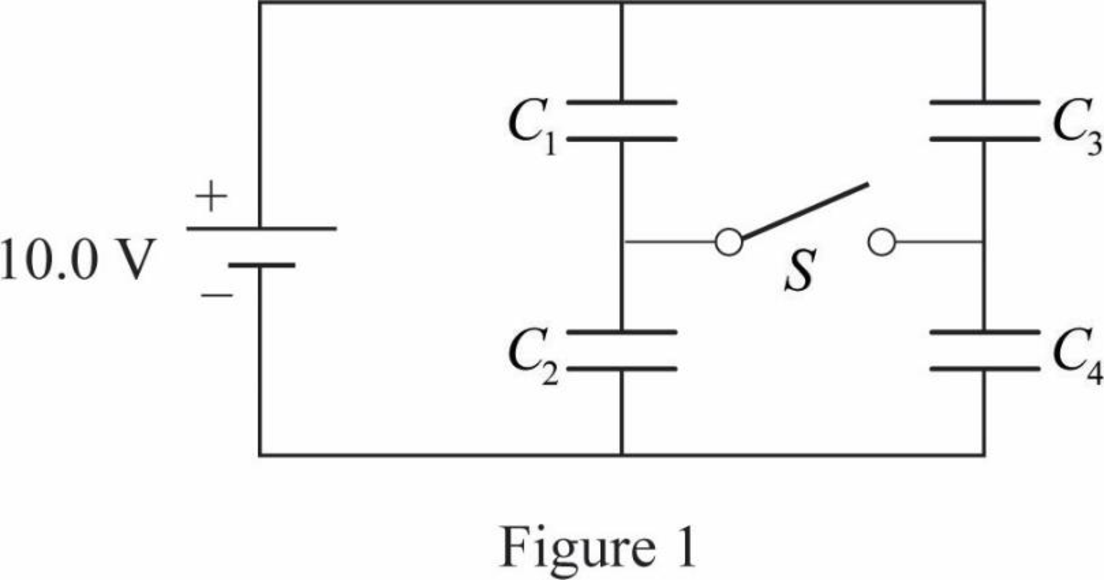
Since, the capacitors
Write the expression to find the equivalent capacitance on
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression to find the charges on
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression to find the equivalent capacitance on
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression to find the charges on
Here,
Substitute
Write the equation to find the voltage across the capacitor.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the charge stored in
The potential difference across the capacitors
(b)
The potential difference across the capacitors and the charge stores in each capacitor when the switch is closed.
Answer to Problem 85PQ
The charge stored in
The potential difference across the capacitors
Explanation of Solution
The circuit diagram,
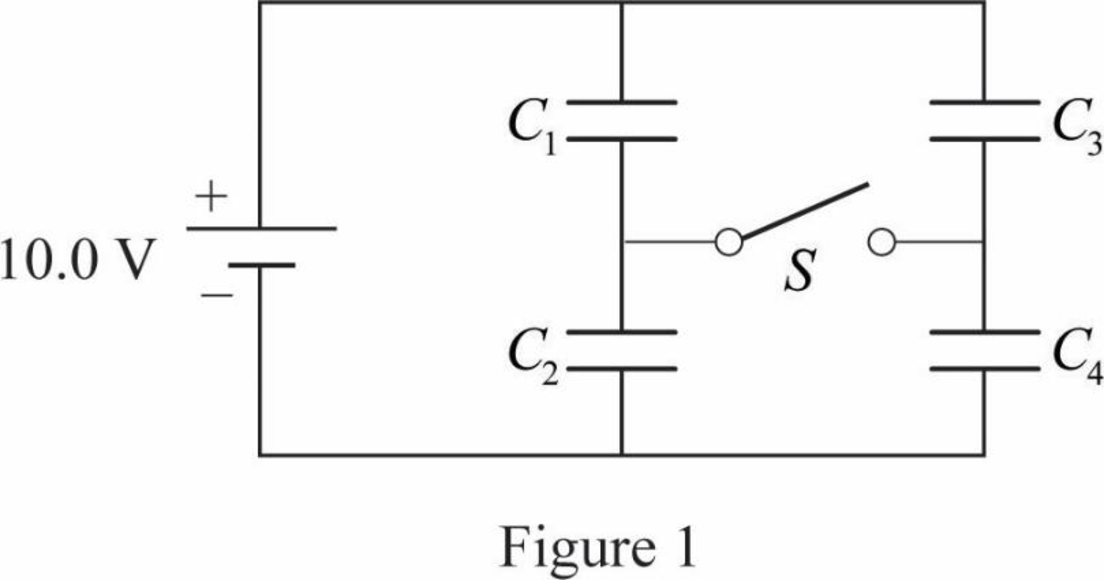
When the switch is closed, the capacitors
Write the expression to find the equivalent capacitance on
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression to find the equivalent capacitance on
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression to find the equivalent capacitance of the circuit.
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression to find the charges on the capacitors.
Here,
Substitute
Write the equation to find the voltage across the capacitor.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the charge stored in
The potential difference across the capacitors
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 27 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
- 4 Problem 4) A particle is being pushed up a smooth slot by a rod. At the instant when 0 = rad, the angular speed of the arm is ė = 1 rad/sec, and the angular acceleration is = 2 rad/sec². What is the net force acting on the 1 kg particle at this instant? Express your answer as a vector in cylindrical coordinates. Hint: You can express the radial coordinate as a function of the angle by observing a right triangle. (20 pts) Ꮎ 2 m Figure 3: Particle pushed by rod along vertical path.arrow_forward4 Problem 4) A particle is being pushed up a smooth slot by a rod. At the instant when 0 = rad, the angular speed of the arm is ė = 1 rad/sec, and the angular acceleration is = 2 rad/sec². What is the net force acting on the 1 kg particle at this instant? Express your answer as a vector in cylindrical coordinates. Hint: You can express the radial coordinate as a function of the angle by observing a right triangle. (20 pts) Ꮎ 2 m Figure 3: Particle pushed by rod along vertical path.arrow_forwardplease solve and answer the question correctly. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardA shot putter releases a shot at 13 m/s at an angle of 42 degrees to the horizontal and from a height of 1.83 m above the ground. Calculate. Note: For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the steps and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise. Answer all parts and show all work please.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





