
College Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781938168000
Author: Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher: OpenStax College
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 27, Problem 34CQ
When particles scattering light are smaller than its wavelength, the amount of scattering is proportional to
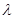 How does this relate to the fact that the sky is blue?
How does this relate to the fact that the sky is blue?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
For each of the actions depicted, determine the direction (right, left, or zero) of the current induced to flow through the resistor in the circuit containing the secondary coil. The coils are wrapped around a plastic core. Immediately after the switch is closed, as shown in the figure, (Figure 1) in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? If the switch is then opened, as shown in the figure, in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? I have the answers to the question, but would like to understand the logic behind the answers. Please show steps.
When violet light of wavelength 415 nm falls on a single slit, it creates a central diffraction peak that is 8.60
cm wide on a screen that is 2.80 m away.
Part A
How wide is the slit?
ΟΙ ΑΣΦ
?
D= 2.7.10-8
Submit Previous Answers Request Answer
× Incorrect; Try Again; 8 attempts remaining
m
Two complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values.
Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all steps
Chapter 27 Solutions
College Physics
Ch. 27 - What type of experimental evidence indicates that...Ch. 27 - Give an example of a wave characteristic of light...Ch. 27 - How do wave effects depend on the size of the...Ch. 27 - Under what conditions can light be modeled like a...Ch. 27 - Go outside in the sunlight and observe your...Ch. 27 - Why does the wavelength of light decrease when it...Ch. 27 - Does Huygens's principle apply to all types of...Ch. 27 - Young's double slit experiment breaks a single...Ch. 27 - Suppose you use the same double slit to perform...Ch. 27 - Is it possible to create a situation in which...
Ch. 27 - Figure 27.55 shows the central part of the...Ch. 27 - What is the advantage of a diffraction grating...Ch. 27 - What are the advantages of a diffraction grating...Ch. 27 - Can the lines in a diffraction grating be too...Ch. 27 - If a beam of white light passes through a...Ch. 27 - Suppose pure-wavelength light falls on a...Ch. 27 - Suppose a feather appears green but has no green...Ch. 27 - It is possible that there is no minimum in the...Ch. 27 - As the width of the slit producing a single-slit...Ch. 27 - A beam of light always spreads out. Why can a beam...Ch. 27 - What effect does increasing the wedge angle have...Ch. 27 - How is the difference in paths taken by two...Ch. 27 - Is there a phase change in the light reflected...Ch. 27 - In placing a sample on a microscope slide, a glass...Ch. 27 - Answer the above question if the fluid between the...Ch. 27 - While contemplating the food value of a slice of...Ch. 27 - An inventor notices that a soap bubble is dark at...Ch. 27 - A non-reflective coating like the one described in...Ch. 27 - Why is it much more difficult to see interference...Ch. 27 - Under what circumstances is the phase of light...Ch. 27 - Can a sound wave in air be polarized? Explain.Ch. 27 - No light passes through two perfect polarizing...Ch. 27 - Explain what happens to the energy carried by...Ch. 27 - When particles scattering light are smaller than...Ch. 27 - Using the information given in the preceding...Ch. 27 - When light is reflected at Brewster's angle from a...Ch. 27 - Explain how microscopes can use wave optics to...Ch. 27 - A bright white light under water is collimated and...Ch. 27 - Show that when light passes from air to water, its...Ch. 27 - Find the range of visible wavelengths of light in...Ch. 27 - What is the index of refraction of a material for...Ch. 27 - Analysis of an interference effect in a clear...Ch. 27 - What is the ratio of thicknesses of crown glass...Ch. 27 - At what angle is the first-order maximum for...Ch. 27 - Calculate the angle for the third-order maximum of...Ch. 27 - What is the separation between two slits for which...Ch. 27 - Find the distance between two slits that produces...Ch. 27 - Calculate the wavelength of light that has its...Ch. 27 - What is the wavelength of light falling on double...Ch. 27 - At what angle is the fourth-order maximum for the...Ch. 27 - What is the highest-order maximum for 400-nm light...Ch. 27 - Find the largest wavelength of light falling on...Ch. 27 - What is the smallest separation between two slits...Ch. 27 - (a) What is the smallest separation between two...Ch. 27 - (a) If the first-order maximum for pure-wavelength...Ch. 27 - Figure 27.56 shows a double slit located a...Ch. 27 - Using the result of the problem above, calculate...Ch. 27 - Using the result of the problem two problems...Ch. 27 - A diffraction grating has 2000 lines per...Ch. 27 - Find the angle for the third-order maximum for...Ch. 27 - How many lines per centimeter are there on a...Ch. 27 - What is the distance between lines on a...Ch. 27 - Calculate the wavelength of light that has its...Ch. 27 - An electric current through hydrogen gas produces...Ch. 27 - (a) What do the four angles in the above problem...Ch. 27 - What is the maximum number of lines per centimeter...Ch. 27 - The yellow light from a sodium vapor lamp seems to...Ch. 27 - What is the spacing between structures in a...Ch. 27 - Structures on a bird feather act like a reflection...Ch. 27 - An opal such as that shown in Figure 27.17 acts...Ch. 27 - At what angle does a diffraction grating produces...Ch. 27 - Show that a diffraction grating cannot produce a...Ch. 27 - If a diffraction grating produces a first-order...Ch. 27 - (a) Find the maximum number of lines per...Ch. 27 - €37. (a) Show that a 30,000-line-per-centimeter...Ch. 27 - A He—Ne laser beam is reflected from the surface...Ch. 27 - The analysis shown in the figure below also...Ch. 27 - Unreasonable Results Red light of wavelength of...Ch. 27 - Unreasonable Results (a) What visible wavelength...Ch. 27 - Construct Your Own Problem Consider a spectrometer...Ch. 27 - (a) At what angle is the first minimum for 550-nm...Ch. 27 - (a) Calculate the angle at which a 2.00- m -wide...Ch. 27 - (a) How wide is a single slit that produces its...Ch. 27 - (a) What is the width of a single slit that...Ch. 27 - Find the wavelength of light that has its third...Ch. 27 - Calculate the wavelength of light that produces...Ch. 27 - (a) Sodium vapor light averaging 589 nm in...Ch. 27 - (a) Find the angle of the third diffraction...Ch. 27 - (a) Find the angle between the first minima for...Ch. 27 - (a) What is the minimum width of a single slit (in...Ch. 27 - (a) If a single slit produces a first minimum at...Ch. 27 - A double slit produces a diffraction pattern that...Ch. 27 - Integrated Concepts A water break at the entrance...Ch. 27 - Integrated Concepts An aircraft maintenance...Ch. 27 - The 300-m-diameter Arecibo radio telescope...Ch. 27 - Assuming the angular resolution found for the...Ch. 27 - Diffraction spreading for a flashlight is...Ch. 27 - (a) What is the minimum angular spread of a 633-nm...Ch. 27 - A telescope can be used to enlarge the diameter of...Ch. 27 - The limit to the eye's acuity is actually related...Ch. 27 - What is the minimum diameter mirror on a telescope...Ch. 27 - You are told not to shoot until you see the whites...Ch. 27 - (a) The planet Pluto and its Moon Charon are...Ch. 27 - The headlights of a car are 1.3 m apart. What is...Ch. 27 - When dots are placed on a page from a laser...Ch. 27 - Unreasonable Results An amateur astronomer wants...Ch. 27 - Construct Your Own Problem Consider diffraction...Ch. 27 - A soap bubble is 100 nm thick and illuminated by...Ch. 27 - An oil slick on water is 120 nm thick and...Ch. 27 - Calculate the minimum thickness of an oil slick on...Ch. 27 - Find the minimum thickness of a soap bubble that...Ch. 27 - A film of soapy water (n=1.33) on top of a plastic...Ch. 27 - What are the three smallest non-zero thicknesses...Ch. 27 - Suppose you have a lens system that is to be used...Ch. 27 - (a) As a soap bubble thins it becomes dark,...Ch. 27 - A film of oil on water will appear dark when it is...Ch. 27 - Figure 27.34 shows two glass slides illuminated by...Ch. 27 - Figure 27.34 shows two 7.50-cm-long glass slides...Ch. 27 - Repeat Exercise 27.70, but take the light to be...Ch. 27 - Repeat Exercise 27.71, but take the light to be...Ch. 27 - Unreasonable Results To save money on making...Ch. 27 - What angle is needed between the direction of...Ch. 27 - The angle between the axes of two polarizing...Ch. 27 - If you have completely polarized light of...Ch. 27 - What angle would the axis of a polarizing filter...Ch. 27 - At the end of Example 27.8, it was stated that the...Ch. 27 - Show that if you have three polarizing filters,...Ch. 27 - Prove that, if I is the intensity of light...Ch. 27 - At what angle will light reflected from diamond be...Ch. 27 - What is Brewster's angle for light traveling in...Ch. 27 - A scuba diver sees light reflected from the...Ch. 27 - At what angle is light inside crown glass...Ch. 27 - Light reflected at 55.6° from a window is...Ch. 27 - (a) Light reflected at 62.5° from a gemstone in a...Ch. 27 - If b is Brewster's angle for light reflected from...Ch. 27 - Integrated Concepts If a polarizing filter reduces...Ch. 27 - Integrated Concepts Suppose you put on two pairs...Ch. 27 - Integrated Concepts (a) On a day when the...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
7. Both Tim and Jan (problem 6) have a widow’s peak (see Module 9.8), but Mike has a straight hairline. What ar...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
22. The seeds in bush bean pods are each the product of an independent fertilization event. Green seed color is...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Determine [OH], [H+], and the pH of each of the following solutions. a. 1.0 M KCl b. 1.0 M KC2H3O2
Chemistry
With two pairs of genes involved (P/p and Z/z), a testcross (ppzz) with an organism of unknown genotype indicat...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Draw the following orbitals: a. 3s orbital b. 4s orbital c. 3p orbital
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
In mechanism, photophosphorylation is most similar to A. substrate-level phosphorylation in glycolysis. B. oxid...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculate the center of mass of the hollow cone shown below. Clearly specify the origin and the coordinate system you are using. Z r Y h Xarrow_forward12. If all three collisions in the figure below are totally inelastic, which will cause more damage? (think about which collision has a larger amount of kinetic energy dissipated/lost to the environment? I m II III A. I B. II C. III m m v brick wall ע ע 0.5v 2v 0.5m D. I and II E. II and III F. I and III G. I, II and III (all of them) 2marrow_forwardCan you solve this 2 question teach me step by step and draw for mearrow_forward
- From this question and answer can you explain how get (0,0,5) and (5,0,,0) and can you teach me how to solve thisarrow_forwardCan you solve this 2 question and teach me using ( engineer method formula)arrow_forward11. If all three collisions in the figure below are totally inelastic, which brings the car of mass (m) on the left to a halt? I m II III m m ע ע ע brick wall 0.5v 2m 2v 0.5m A. I B. II C. III D. I and II E. II and III F. I and III G. I, II and III (all of them)arrow_forward
- How can you tell which vowel is being produced here ( “ee,” “ah,” or “oo”)? Also, how would you be able to tell for the other vowels?arrow_forwardYou want to fabricate a soft microfluidic chip like the one below. How would you go about fabricating this chip knowing that you are targeting a channel with a square cross-sectional profile of 200 μm by 200 μm. What materials and steps would you use and why? Disregard the process to form the inlet and outlet. Square Cross Sectionarrow_forward1. What are the key steps involved in the fabrication of a semiconductor device. 2. You are hired by a chip manufacturing company, and you are asked to prepare a silicon wafer with the pattern below. Describe the process you would use. High Aspect Ratio Trenches Undoped Si Wafer P-doped Si 3. You would like to deposit material within a high aspect ratio trench. What approach would you use and why? 4. A person is setting up a small clean room space to carry out an outreach activity to educate high school students about patterning using photolithography. They obtained a positive photoresist, a used spin coater, a high energy light lamp for exposure and ordered a plastic transparency mask with a pattern on it to reduce cost. Upon trying this set up multiple times they find that the full resist gets developed, and they are unable to transfer the pattern onto the resist. Help them troubleshoot and find out why pattern of transfer has not been successful. 5. You are given a composite…arrow_forward
- Two complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find r and θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all stepsarrow_forwardAn electromagnetic wave is traveling through vacuum in the positive x direction. Its electric field vector is given by E=E0sin(kx−ωt)j^,where j^ is the unit vector in the y direction. If B0 is the amplitude of the magnetic field vector, find the complete expression for the magnetic field vector B→ of the wave. What is the Poynting vector S(x,t), that is, the power per unit area associated with the electromagnetic wave described in the problem introduction? Give your answer in terms of some or all of the variables E0, B0, k, x, ω, t, and μ0. Specify the direction of the Poynting vector using the unit vectors i^, j^, and k^ as appropriate. Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardAnother worker is performing a task with an RWL of only 9 kg and is lifting 18 kg, giving him an LI of 2.0 (high risk). Questions:What is the primary issue according to NIOSH?Name two factors of the RWL that could be improved to reduce risk.If the horizontal distance is reduced from 50 cm to 30 cm, how does the HM change and what effect would it have?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Modern Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781111794378
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Spectra Interference: Crash Course Physics #40; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-ob7foUzXaY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY